Write The Location Structure And Function Of Following Epithelial

Write The Location Structure And Function Of Following Epithelial Epithelial cells form membranes. the epithelial membrane consists of a layer of epithelial tissue and has underlying connective tissue. there are two types of epithelial membranes, mucous membrane and serous membrane. mucous membrane: it is also known as mucosa. there are goblet cells present, which secrete mucus. Epithelial tissue is one of the four tissue types. it is found lining the inner and outer body surfaces and comprising the parenchyma of the glands. it is divided into surface (covering) and glandular (secreting) epithelium. surface epithelium consists of one or more cell layers, stacked over a thin basement membrane.

41 Epithelial Tissue Worksheet Anatomy Worksheet Master Epithelial tissue function: epithelial tissues provide the body’s first line of protection from physical, chemical, and biological damage. the cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the body, controlling permeability by allowing selective transfer of materials across its surface. all substances that enter the body must cross an epithelium. Epithelial tissue rests on a structure called the basement membrane. it consists of two parts – the basal lamina and the reticular connective tissue underneath. the basal lamina is secreted by the cells of the epithelial tissue itself and contains proteins, glycoproteins, and collagen iv, a type of structural protein that forms sheets. Location: bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus ciliary columnar; digestive tract, bladder nonciliated columnar epithelium. function: allows absorbtion, secretes mucous and enzymes. pseudostratified columnar. location: trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract (ciliated cells) function: secretes mucus which is moved with cilia. For example in the stratified epithelium of the skin. tight junctions form a solid barrier to prevent movement of molecules between adjacent epithelial cells. tight junctions are found in the simple columnar epithelium of the gut tube to regulate absorption of nutrients. finally, gap junctions perform the opposite function.
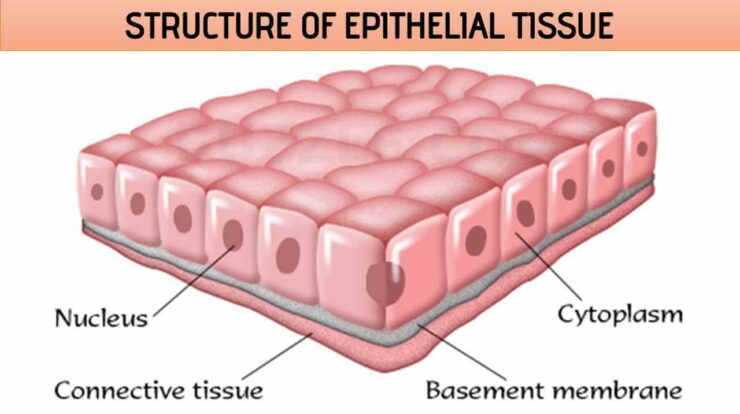
Structure Of Epithelial Tissue Free Biology Notes Rajus Biology Location: bronchi, uterine tubes, uterus ciliary columnar; digestive tract, bladder nonciliated columnar epithelium. function: allows absorbtion, secretes mucous and enzymes. pseudostratified columnar. location: trachea and most of the upper respiratory tract (ciliated cells) function: secretes mucus which is moved with cilia. For example in the stratified epithelium of the skin. tight junctions form a solid barrier to prevent movement of molecules between adjacent epithelial cells. tight junctions are found in the simple columnar epithelium of the gut tube to regulate absorption of nutrients. finally, gap junctions perform the opposite function. Types classification with examples and location. epithelial tissue is divided into two types: covering and lining epithelium, also called the surface epithelium, that forms the outer covering of the skin and some internal organs and also forms the inner lining of blood vessels, ducts, body cavities, and the inner lining of the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. Epithelial tissue: structure with diagram, function, types and location simple squamous epithelium introduction: the cells of the simple squamous epithelium are flat. they have length, and breadth but no thickness. 1. epithelial tissue features: cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following features—“abc”. they are avascular rest on a basement membrane. are compactly arranged.

Write The Location Structure And Function Of Following Epithelial Types classification with examples and location. epithelial tissue is divided into two types: covering and lining epithelium, also called the surface epithelium, that forms the outer covering of the skin and some internal organs and also forms the inner lining of blood vessels, ducts, body cavities, and the inner lining of the respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems. Epithelial tissue: structure with diagram, function, types and location simple squamous epithelium introduction: the cells of the simple squamous epithelium are flat. they have length, and breadth but no thickness. 1. epithelial tissue features: cells of simple squamous epithelium have the following features—“abc”. they are avascular rest on a basement membrane. are compactly arranged.

Write The Location Structure And Function Of Following Epithelial

Comments are closed.