Where Do Stem Cells Come From An In Depth Exploration
.webp)
Where Do Stem Cells Come From An In Depth Exploration Adult sources: bone marrow and peripheral blood. adult stem cells are typically harvested from two primary sources: bone marrow and peripheral blood. bone marrow is a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells (hscs), which can produce all the cell types found in the blood. May 24, 2024 dive deep into the origins of stem cells and understand where they come from. learn about the harvesting process, their incredible ability to divide, and their potential to treat various diseases. click to discover the role of stem cells in regenerative medicine!.

Where Do Stem Cells Come From An In Depth Exploration Stem cells: the body's master cells. stem cells are a special type of cells that have two important properties. they are able to make more cells like themselves. that is, they self renew. and they can become other cells that do different things in a process known as differentiation. stem cells are found in almost all tissues of the body. Somatic stem cells. adult stem cells, called somatic stem cells, are derived from a human donor. hematopoietic stem cells are the most widely known example. scientists have found somatic stem cells in more tissues than was once imagined, including the brain, skeletal muscle, skin, teeth, heart, gut, liver, ovarian cells, and testis. Stem cells mostly live in the bone marrow (the spongy center of certain bones). this is where they divide to make new blood cells. once blood cells mature, they leave the bone marrow and enter the bloodstream. a small number of the immature stem cells also get into the bloodstream. these are called peripheral blood stem cells. Placental and cord blood stem cells. harvested from the umbilical cords and placentas of healthy newborns, these stem cells appear to be most effective in combating blood and circulatory disorders. patients receiving stem cell transplants from placental or cord blood will need to be a “match” for the donor, as if they were receiving a.
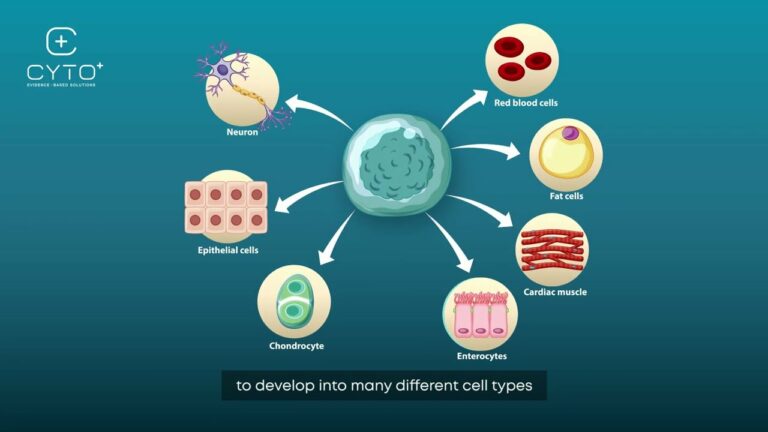
Where Do Stem Cells Come From Archives National Stem Cell Therap Stem cells mostly live in the bone marrow (the spongy center of certain bones). this is where they divide to make new blood cells. once blood cells mature, they leave the bone marrow and enter the bloodstream. a small number of the immature stem cells also get into the bloodstream. these are called peripheral blood stem cells. Placental and cord blood stem cells. harvested from the umbilical cords and placentas of healthy newborns, these stem cells appear to be most effective in combating blood and circulatory disorders. patients receiving stem cell transplants from placental or cord blood will need to be a “match” for the donor, as if they were receiving a. Stem cells have the ability to self renew. unlike muscle cells, blood cells, or nerve cells—which do not normally replicate— stem cells may replicate many times. when a stem cell divides, the resulting two daughter cells may be: 1) both stem cells, 2) a stem cell and a more differentiated cell, or 3) both more differentiated cells. Over the past 20 years, and particularly in the last decade, significant developmental milestones have driven basic, translational, and clinical advances in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine. in this article, we provide a systemic overview of the major recent discoveries in this exciting and rapidly developing field. we begin by discussing experimental advances in the generation.

Stem Cells Where Do They Come From Stem cells have the ability to self renew. unlike muscle cells, blood cells, or nerve cells—which do not normally replicate— stem cells may replicate many times. when a stem cell divides, the resulting two daughter cells may be: 1) both stem cells, 2) a stem cell and a more differentiated cell, or 3) both more differentiated cells. Over the past 20 years, and particularly in the last decade, significant developmental milestones have driven basic, translational, and clinical advances in the field of stem cell and regenerative medicine. in this article, we provide a systemic overview of the major recent discoveries in this exciting and rapidly developing field. we begin by discussing experimental advances in the generation.

Comments are closed.