Where Do Primary Consumers Get Their Carbon From
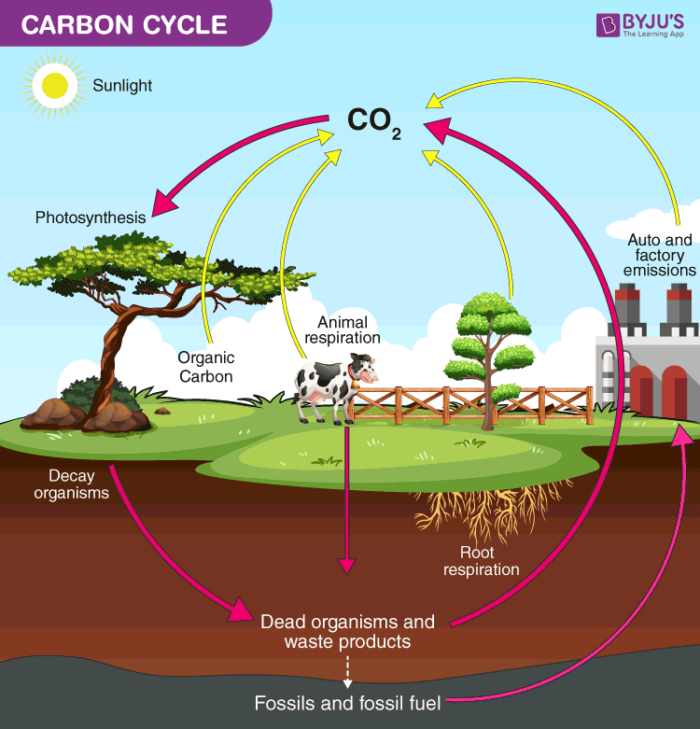
Carbon Cycle Definition Process Diagram Of Carbon Cycle Glucose, carbohydrates, lipids, protein, dna. name an organic molecule that carbon is found in. co2. what molecule to trees get their carbon from? eating plants. where do primary consumers get their energy from? cellular respiration and decomposition. what processes adds carbon to the atmosphere? photosynthesis. What happens when fossil fuels are burned. lots of breaking c's and h's an exothermic reaction. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what inorganic molecule is carbon normally found in?, name an organic molecule that carbon is found in, what molecule do trees get their carbon from? and more.
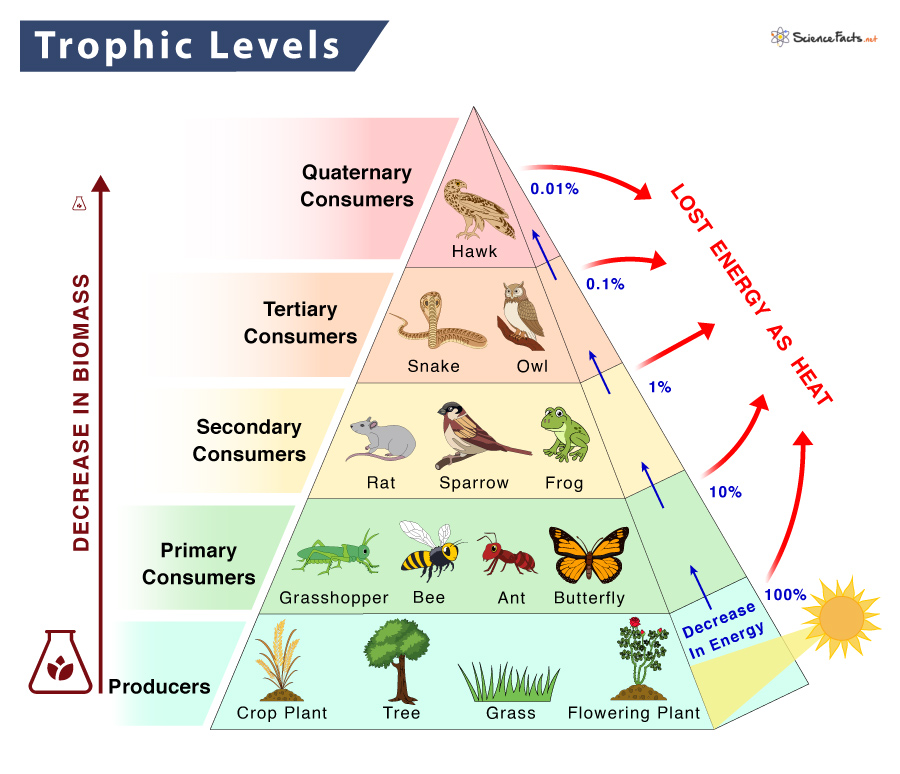
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram However carbon dioxide is acquired, a by product of the process is oxygen. the photosynthetic organisms are responsible for depositing approximately 21 percent oxygen content of the atmosphere that we observe today. heterotrophs and autotrophs are partners in biological carbon exchange (especially the primary consumers, largely herbivores). List three ways that we could reduce the extra carbon that is getting into the atmosphere. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like name an organic molecule that carbon is found in, what molecule do trees get their carbon from?, where do primary consumers get their carbon from? and more. What role do producers play in the carbon cycle. the earths producer organisms are primarily its green terrestrial plants and the algae in the oceans. these plants use the carbon from carbon dioxide to create sugar molecules through the process of photosynthesis. terrestrial plants get their carbon dioxide from the atmosphere while marine. Some of the carbon atoms in your body today may long ago have resided in a dinosaur's body, or perhaps were once buried deep in the earth's crust as carbonate rock minerals. figure 20.3.1 20.3. 1: carbon dioxide gas exists in the atmosphere and is dissolved in water. photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide gas to organic carbon, while.
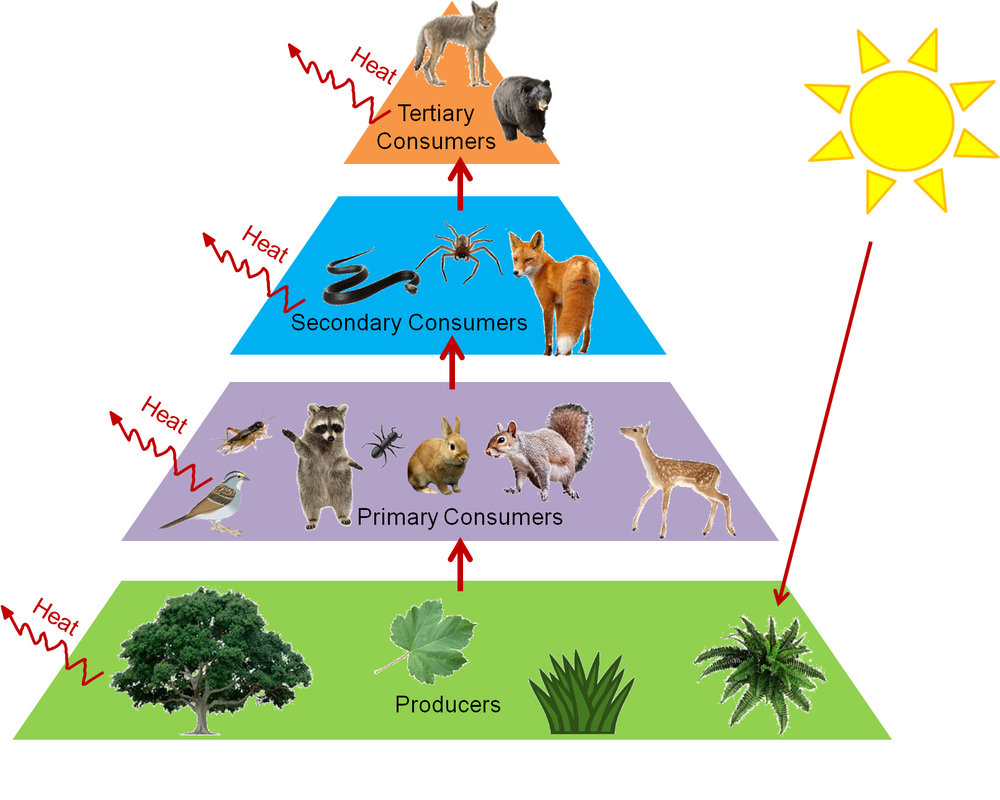
Trophic Levels And Ecological Pyramids Online Science Notes What role do producers play in the carbon cycle. the earths producer organisms are primarily its green terrestrial plants and the algae in the oceans. these plants use the carbon from carbon dioxide to create sugar molecules through the process of photosynthesis. terrestrial plants get their carbon dioxide from the atmosphere while marine. Some of the carbon atoms in your body today may long ago have resided in a dinosaur's body, or perhaps were once buried deep in the earth's crust as carbonate rock minerals. figure 20.3.1 20.3. 1: carbon dioxide gas exists in the atmosphere and is dissolved in water. photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide gas to organic carbon, while. Participants in the carbon cycle are roughly divided among producers, consumers, and decomposers of organic carbon compounds. the primary producers of organic carbon compounds from co 2 are land plants and photosynthetic bacteria. a large amount of available carbon is found in living land plants. The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle. carbon can be stored in a variety of reservoirs, including plants and animals, which is why they are considered carbon life forms. carbon is used by plants to build leaves and stems, which are then digested by animals and used for cellular growth.

How To Determine The Trophic Level Participants in the carbon cycle are roughly divided among producers, consumers, and decomposers of organic carbon compounds. the primary producers of organic carbon compounds from co 2 are land plants and photosynthetic bacteria. a large amount of available carbon is found in living land plants. The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle. carbon can be stored in a variety of reservoirs, including plants and animals, which is why they are considered carbon life forms. carbon is used by plants to build leaves and stems, which are then digested by animals and used for cellular growth.

Community Ecology Britannica

Comments are closed.