What Is Bacteria Types Structure Shapes Morphology
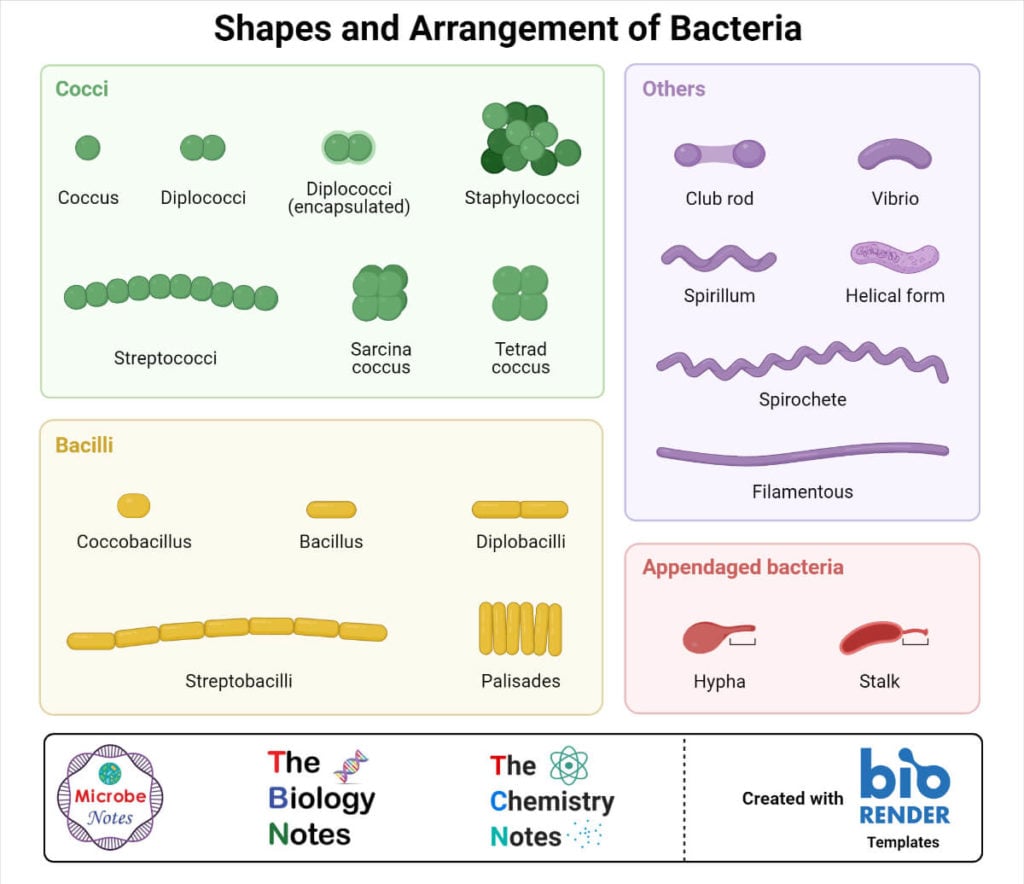
What Are Bacteria A Complete Study Note And Guide Bacteria are a type of biological cell that is prokaryotic and unicellular. due to the lack of a membrane bound nucleus, these are simpler than other types of living organisms. although only some of them can be seen by naked eyes while the rest are microscopic, they display a wide range of shapes, sizes, and structures. Bacteria shapes. bacteria come in a myriad of shapes. the three main shapes of bacteria are coccus, spiral, and bacillus. cocci are bacteria that are spherical or ovoid in shape. some cocci remain attached after binary fission, even though separate cells have been formed. for example, diplococci are cocci in pairs, streptococci are chains, and.
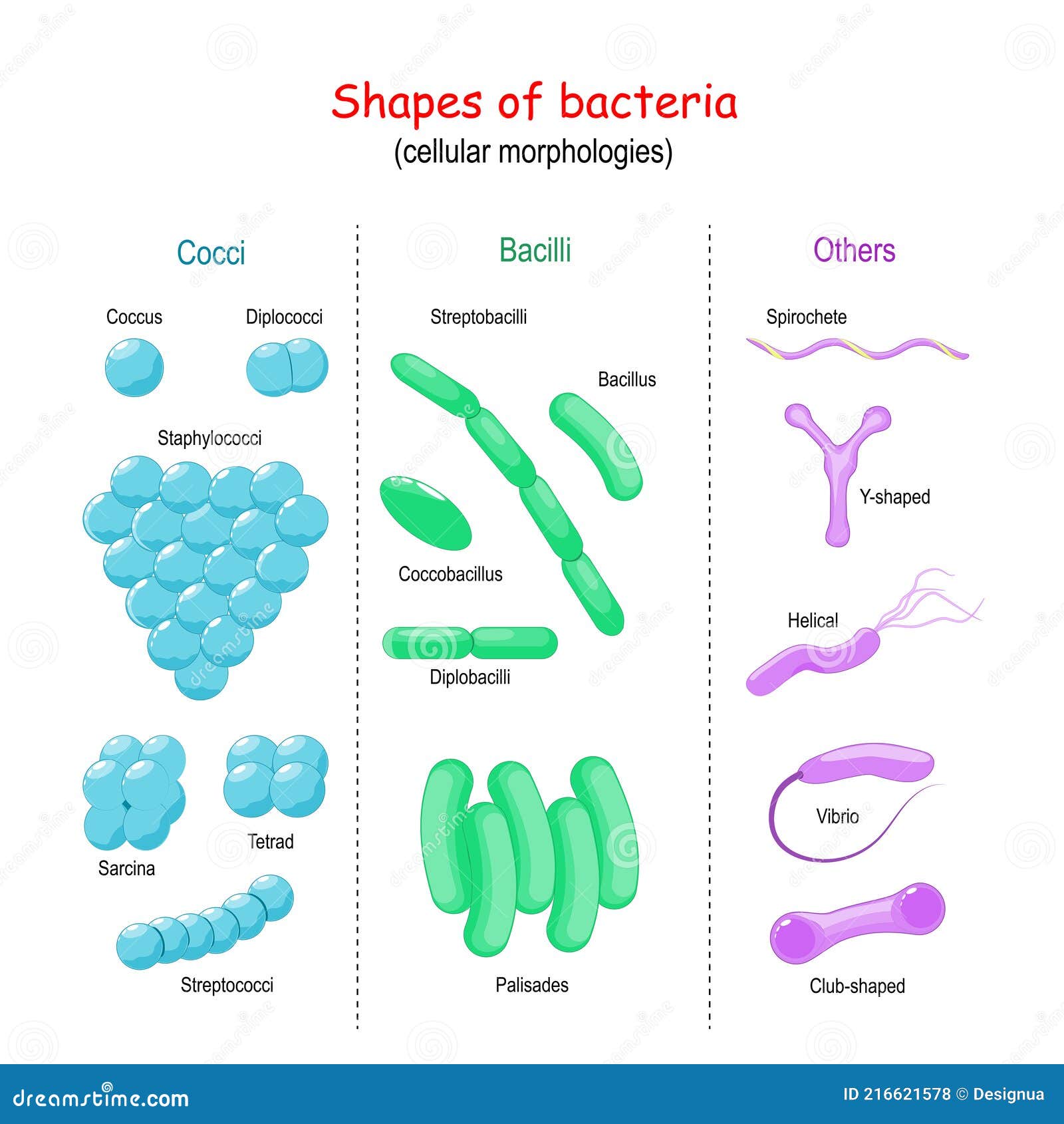
Bacteria Shape Cell Morphology Stock Vector Illustration Of Summary. there are three basic shapes of bacteria: coccus, bacillus, and spiral. based on planes of division, the coccus shape can appear in several distinct arrangements: diplococcus, streptococcus, tetrad, sarcina, and staphylococcus. the bacillus shape can appear as a single bacillus, a streptobacillus, or a coccobacillus. Bacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms and are unicellular in nature. since they lack a membrane bound nucleus, they are less complex than other living creatures. although only some bacteria can be seen by our naked eyes while the rest are microscopic in nature, they display a wide range of shapes, sizes, and structures. The average diameter of spherical bacteria is 0.5 2.0 µm. for rod shaped or filamentous bacteria, length is 1 10 µm and diameter is 0.25 1 .0 µm. e. coli , a bacillus of about average size is 1.1 to 1.5 µm wide by 2.0 to 6.0 µm long. spirochaetes occasionally reach 500 µm in length and the cyanobacterium. oscillatoria is about 7 µm in. Shape, size, and culture appearance all go into the morphological distinction of bacterial types. most bacteria exist as actively growing cells called vegetative cells. only a few subsets of bacteria are able to produce spores, viable but dormant structures which encapsulate the genome of bacteria.
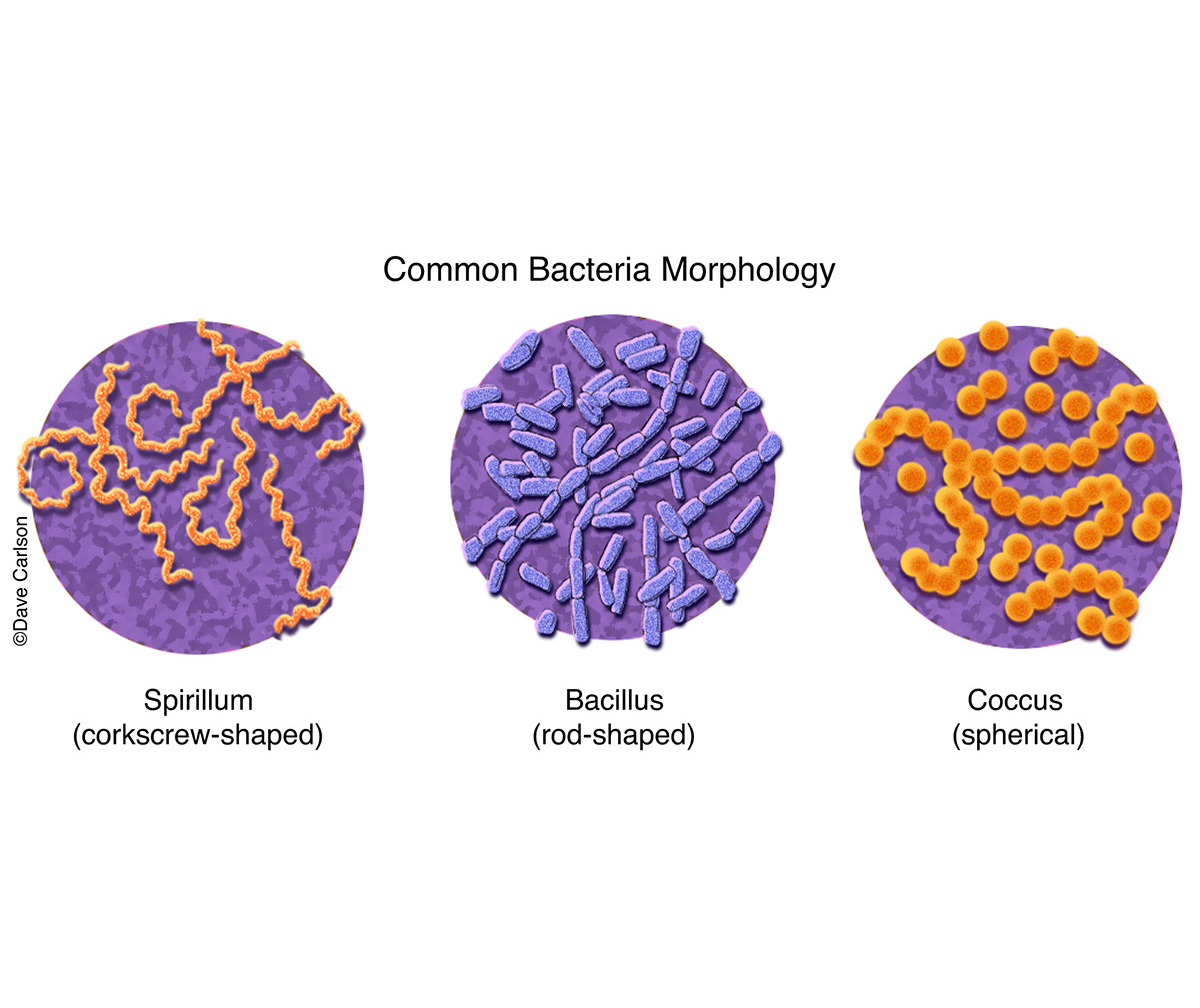
Common Bacteria Morphology Carlson Stock Art The average diameter of spherical bacteria is 0.5 2.0 µm. for rod shaped or filamentous bacteria, length is 1 10 µm and diameter is 0.25 1 .0 µm. e. coli , a bacillus of about average size is 1.1 to 1.5 µm wide by 2.0 to 6.0 µm long. spirochaetes occasionally reach 500 µm in length and the cyanobacterium. oscillatoria is about 7 µm in. Shape, size, and culture appearance all go into the morphological distinction of bacterial types. most bacteria exist as actively growing cells called vegetative cells. only a few subsets of bacteria are able to produce spores, viable but dormant structures which encapsulate the genome of bacteria. Bacteria are, in public one tenth the size of the eukaryotic cell. on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 nanometers to 0.5 µmeters. however, they can be as tiny as 0.3 µmeters and as large as 0.7 µm. it has been examined that the size of bacteria has an important role in the survival of organisms. Bacterial cellular morphologies are the shapes that are characteristic of various types of bacteria and often key to their identification. their direct examination under a light microscope enables the classification of these bacteria (and archaea). generally, the basic morphologies are spheres (coccus) and round ended cylinders or rod shaped.

Bacteria Microbiology Series Techni K Smart Knowledge Bacteria are, in public one tenth the size of the eukaryotic cell. on average, the size of bacteria ranges from 0.5 nanometers to 0.5 µmeters. however, they can be as tiny as 0.3 µmeters and as large as 0.7 µm. it has been examined that the size of bacteria has an important role in the survival of organisms. Bacterial cellular morphologies are the shapes that are characteristic of various types of bacteria and often key to their identification. their direct examination under a light microscope enables the classification of these bacteria (and archaea). generally, the basic morphologies are spheres (coccus) and round ended cylinders or rod shaped.

Comments are closed.