What Is Alpha Decay Definition Equation Example Rankred

What Is Alpha Decay Definition Equation Example Rankred The most popular example of this sort of nuclear transmutation is uranium decay. uranium 238 (the most common isotope of uranium found in nature) decays to form thorium 234. 23892 ur → 23490 th 42 he. where, 23892 ur is the unstable uranium 238 parent nucleus. 23490 th is the thorium 234 daughter nucleus. 42 he is the ejected alpha particle. Alpha decay examples. 1. an example of alpha decay is the transformation of uranium 238 to thorium 234. the nuclear equation for this reaction is: 238 92 u → 234 90 t h 4 2α 92 238 u → 90 234 t h 2 4 α. in this equation, the uranium 238 nucleus loses two protons and two neutrons, becoming thorium 234, while the alpha particle carries.
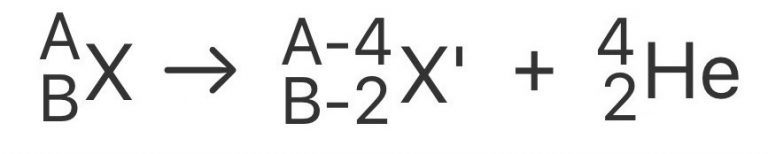
What Is Alpha Decay Definition Equation Example Rankred Geiger nuttall law. alpha decay, type of radioactive disintegration in which some unstable atomic nuclei dissipate excess energy by spontaneously ejecting an alpha particle. because alpha particles have two positive charges and a mass of four units, their emission from nuclei produces daughter nuclei having a positive nuclear charge or atomic. Alpha decay or α decay is a type of radioactive decay in which the atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle thereby transforming or decaying into a new atomic nucleus. here the atomic mass number of the newly formed atom will be reduced by four and the atomic number will be reduced by two. the emitted alpha particle is also known as a helium. V. t. e. alpha decay or α decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle (helium nucleus) and thereby transforms or "decays" into a different atomic nucleus, with a mass number that is reduced by four and an atomic number that is reduced by two. an alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium. Alpha decay is a radioactive decay that occurs when an unstable parent nucleus disintegrates into a more stable daughter nucleus, emitting an alpha particle with a helium nucleus structure \ ( ^4 2he^ {2 } \), i.e., two neutrons, two protons, an atomic mass of 4u and a 2e charge like helium nucleus. the symbol of the alpha decay is the.

Comments are closed.