Vetor De Crawford Classification Of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms
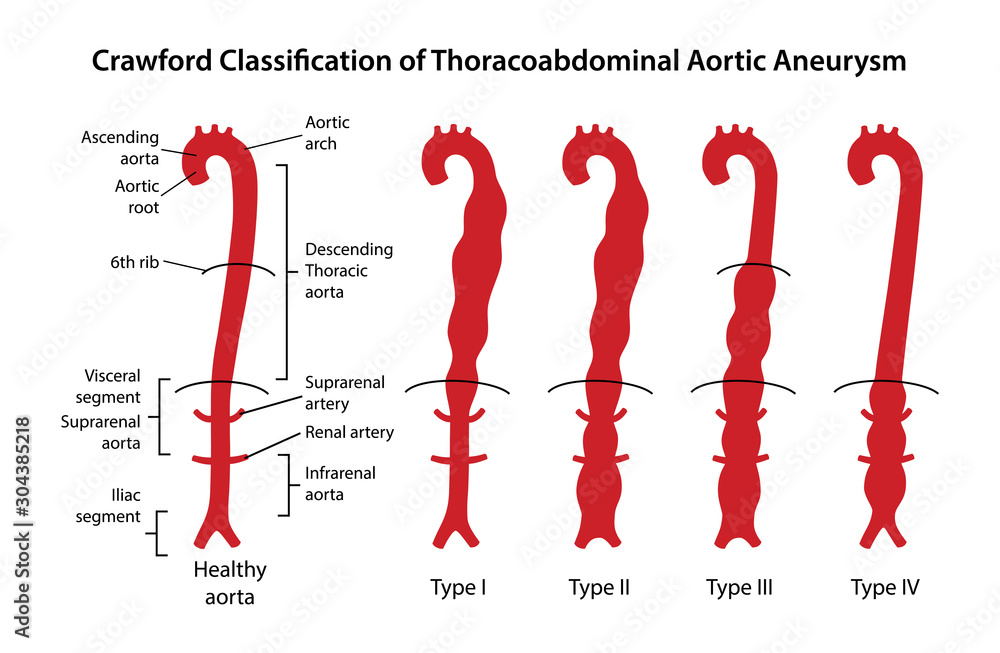
Vetor De Crawford Classification Of Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms From the subclavian to the aortoiliac bifurcation. type 3. distal thoracic aorta to the aortoiliac bifurcation. type 4. limited to the abdominal aorta below the diaphragm. reference: crawford, e. s. and j. s. coselli (1991). “thoracoabdominal aneurysm surgery.”. semin thorac cardiovasc surg 3 (4): 300 322. Classification. thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms can occur anywhere from the left subclavian artery to the bifurcation of iliac arteries. in 1986, crawford described the first taaa classification scheme based on the anatomic extent of the aneurysm . type i involves most dta from the origin of the left subclavian to the suprarenal abdominal aorta.
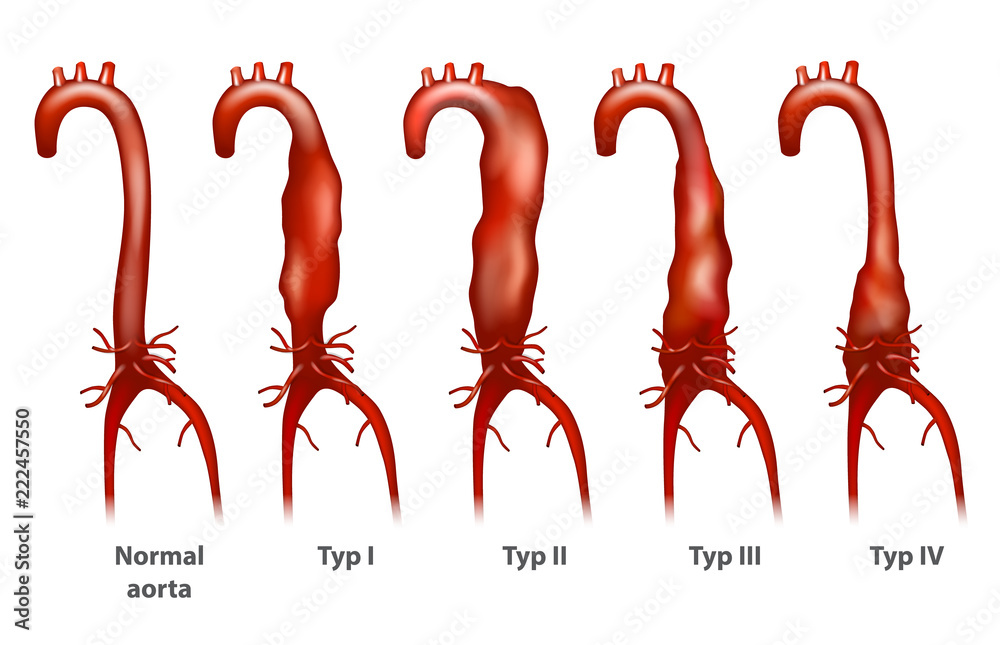
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Thoracoabdominal Crawford Classification Aortic aneurysm, thoracic diagnostic imaging*. humans. magnetic resonance imaging methods*. tomography, x ray computed methods*. untreated thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms are associated with an exceedingly high mortality rate, and surgery carries a high complication rate. crawford's classification system of thoracoabdominal aortic. Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms result from continuous dilation of the descending thoracic aorta extending into the abdominal aorta. the classification of taaa was developed by crawford in 1986 [], and then subsequently modified, and is subdivided as follows (fig. 9.1):. The first thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (taaa) repairs date from the 1950s by etheredge and rob 1, 2; in the 1960 70s the surgical technique was refined by crawford 2 4 and since then, advances in understanding and improving spinal cord and visceral protection contributed by coselli and safi, 5 9 have made it possible to reduce mortality and. One of the first successful repairs of a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (taaa) in the united states was reported in 1955 by etheredge (1). utilizing a 5 mm aortic shunt, an in situ aortic homograft repair of an extent iv aneurysm was performed via a thoracoabdominal incision (video 1). this included anastomoses of the celiac and superior.
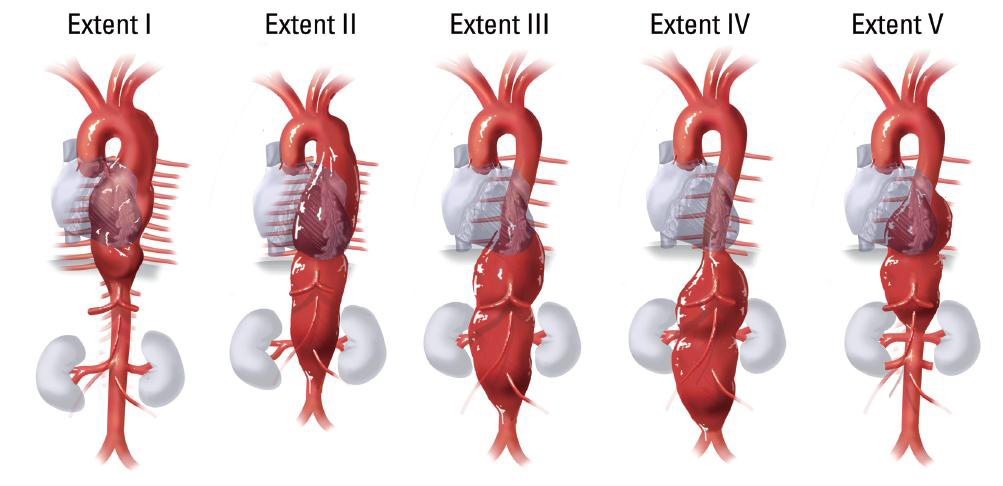
Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm Frederick Annals Of Cardiothoracic The first thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (taaa) repairs date from the 1950s by etheredge and rob 1, 2; in the 1960 70s the surgical technique was refined by crawford 2 4 and since then, advances in understanding and improving spinal cord and visceral protection contributed by coselli and safi, 5 9 have made it possible to reduce mortality and. One of the first successful repairs of a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm (taaa) in the united states was reported in 1955 by etheredge (1). utilizing a 5 mm aortic shunt, an in situ aortic homograft repair of an extent iv aneurysm was performed via a thoracoabdominal incision (video 1). this included anastomoses of the celiac and superior. Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (taaa) crawford classification. i. ii. Abstract. conventional treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (taaas) consists of graft replacement with reattachment of the main aortic branches. over the past 20 years a multimodal approach has gradually evolved to reduce the trauma of surgery by maximizing organ protection, allowing experienced surgical centers to have better.
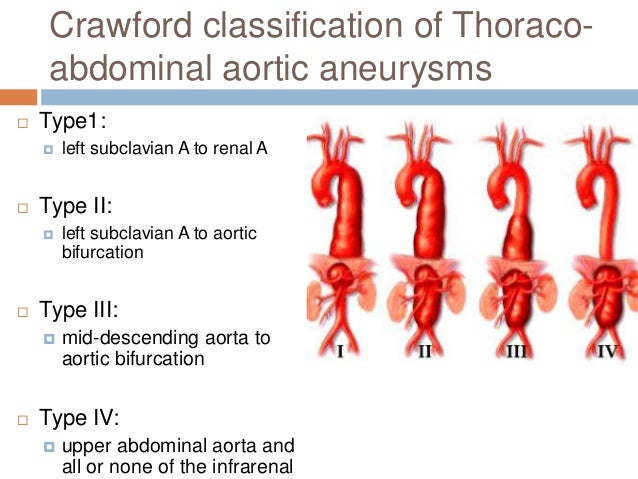
Aortic Aneurysm Imaging Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (taaa) crawford classification. i. ii. Abstract. conventional treatment of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (taaas) consists of graft replacement with reattachment of the main aortic branches. over the past 20 years a multimodal approach has gradually evolved to reduce the trauma of surgery by maximizing organ protection, allowing experienced surgical centers to have better.

Comments are closed.