Use An Ad As Framework To Show The Effect Of Monetary Restriction On

Use An Ad As Framework To Show The Effect Of Monetary Restriction On Use an ad as framework to show the effect of monetary restriction on the output level, prices and interest rate in the short run and the long run. this problem has been solved! you'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. The ad as model can convey a number of interlocking relationships between the three macroeconomic goals of growth, unemployment, and low inflation.moreover, the ad as framework is flexible enough to accommodate both the keynes’ law approach that focuses on aggregate demand and the short run, while also including the say’s law approach that focuses on aggregate supply and the long run.

Use An Ad As Framework To Show The Effect Of Monetary Restriction On (dad das) framework to analyze business cycle fluc tuations and the effects of monetary policy (c.f. jones [4]; mankiw [1]; mishkin [5]). the change in the treatment of business cycles found in textbooks has paralleled a burgeoning pedagogical literature that presents alterna tives to the traditional keynesian is lm ad as frame. Fig. 5 monetary policy in the ad as model. figure 5 shows the scenario that happens in the event of an expansionary policy by the fed. expansionary monetary policy comes in the form of lowering interest rates, which spurs consumer spending and investment spending to increase in an economy. this shifts the ad curve to the right. The ad as model and monetary policy. monetary policy is one of the two main traditional macroeconomic tools to control the aggregate economy. while fiscal policy is controlled by the. government directly, monetary policy is. controlled by the central bank in canada. chapter 14. The ad as model can convey a number of interlocking relationships between the three macroeconomic goals of growth, unemployment, and low inflation.moreover, the ad as framework is flexible enough to accommodate both the keynes’ law approach that focuses on aggregate demand and the short run, while also including the say’s law approach that focuses on aggregate supply and the long run.

Use An Ad As Framework To Show The Effect Of Monetary Restriction On The ad as model and monetary policy. monetary policy is one of the two main traditional macroeconomic tools to control the aggregate economy. while fiscal policy is controlled by the. government directly, monetary policy is. controlled by the central bank in canada. chapter 14. The ad as model can convey a number of interlocking relationships between the three macroeconomic goals of growth, unemployment, and low inflation.moreover, the ad as framework is flexible enough to accommodate both the keynes’ law approach that focuses on aggregate demand and the short run, while also including the say’s law approach that focuses on aggregate supply and the long run. The ad as model can convey a number of interlocking relationships between the three macroeconomic goals of growth, unemployment, and low inflation. moreover, the ad as framework is flexible enough to accommodate both the keynes’ law approach that focuses on aggregate demand and the short run, while also including the say’s law approach that. The keynesian zone occurs at the left of the sras curve where it is fairly flat, so movements in ad will affect output, but have little effect on the price level. say’s law says supply creates its own demand. changes in aggregate demand have no effect on real gdp and employment, only on the price level. we can show say’s law on the vertical.
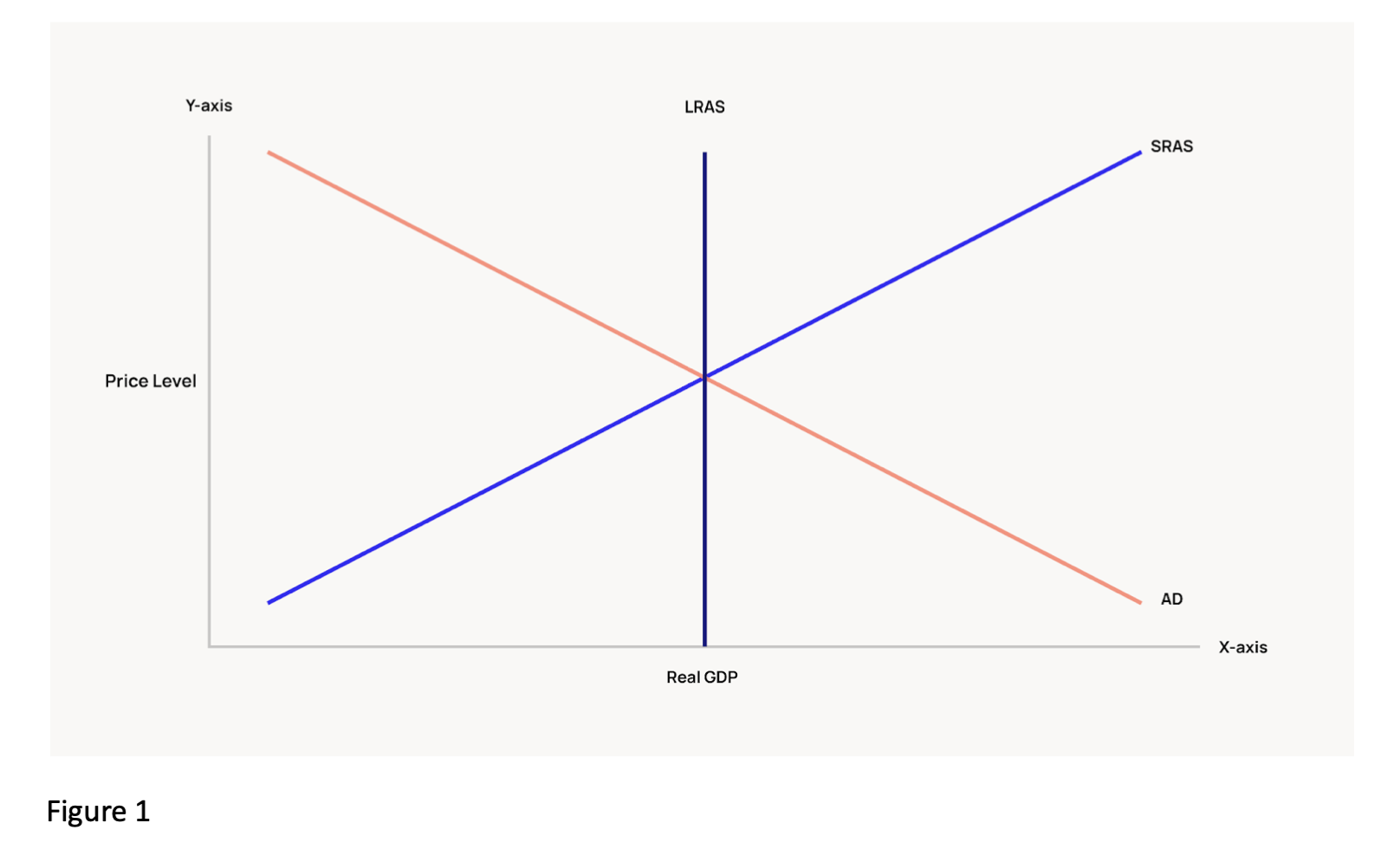
Ad As Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Model Definition Graphs The ad as model can convey a number of interlocking relationships between the three macroeconomic goals of growth, unemployment, and low inflation. moreover, the ad as framework is flexible enough to accommodate both the keynes’ law approach that focuses on aggregate demand and the short run, while also including the say’s law approach that. The keynesian zone occurs at the left of the sras curve where it is fairly flat, so movements in ad will affect output, but have little effect on the price level. say’s law says supply creates its own demand. changes in aggregate demand have no effect on real gdp and employment, only on the price level. we can show say’s law on the vertical.

Ad As Diagram Equilibrium

Comments are closed.