Urology Bladder Stones
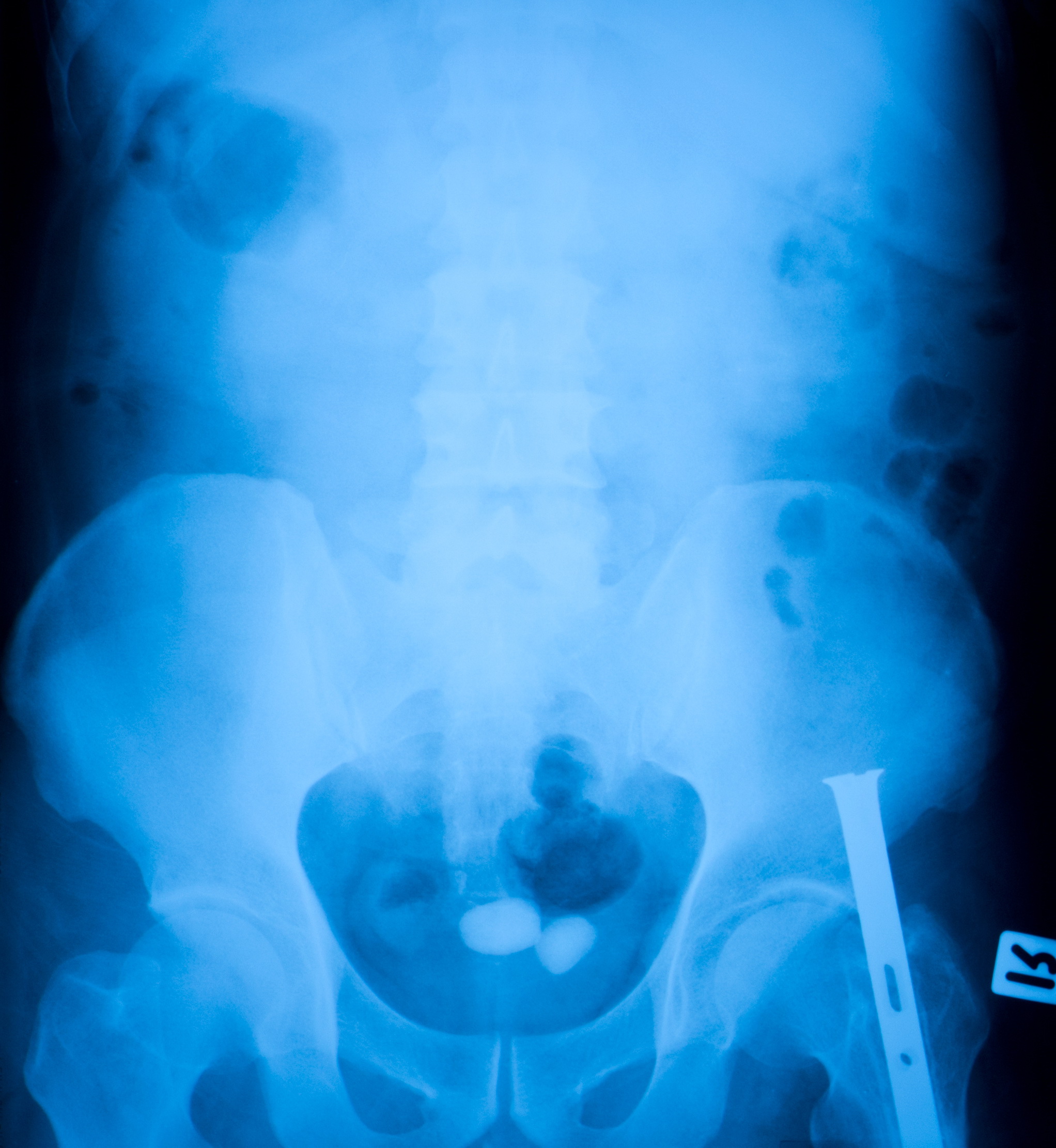
Bladder Stones Bladder Stone Causes Urology Austin Bladder stones are hardened mineral clumps that form in your bladder. they develop when pee remains in your bladder for a long time. the most common symptom is abdominal pain, but it can also cause problems peeing. if you can’t pee out a bladder stone, a urologist can break it up or remove it. Bladder stones treatments. tweet. most bladder stones treatment involve removing the stone. but addressing the underlying problem—such as an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) —is equally important and acts as a preventative measure to keep stones from occurring again. while some patients may be asked to increase their water.

What Are Bladder Stones Its Symptoms Causes And Treatment Symptoms. sometimes bladder stones — even large ones — cause no problems. but if a stone irritates the bladder wall or blocks the flow of urine, signs and symptoms may include: lower abdominal pain. pain during urination. frequent urination. difficulty urinating or interrupted urine flow. blood in the urine. Bladder stones, or " calculi," are hard, calcified masses that form in the bladder, often as the result of urine remaining stationary for too long. stones can also develop in the upper urinary tract and pass into the bladder, where they become stuck. although bladder stones occur in both genders, and affect people of various ages and health. Stones may form in the bladder when the bladder is not emptied completely. this can be due to nerve damage that impairs a patient’s ability to urinate, recurrent urinary tract infections, or an enlarged prostate. the resulting stones may or may not be associated with symptoms, including blood in urine, pain with urination, weakened urinary. Diagnosis. diagnosing bladder stones may involve: a physical exam. your doctor will likely feel your lower abdomen to see if your bladder is enlarged (distended) or may perform a rectal exam to determine whether your prostate is enlarged. you'll also discuss any urinary signs or symptoms that you're having.

How Can You Differentiate Between Kidney And Bladder Stones St Pete Stones may form in the bladder when the bladder is not emptied completely. this can be due to nerve damage that impairs a patient’s ability to urinate, recurrent urinary tract infections, or an enlarged prostate. the resulting stones may or may not be associated with symptoms, including blood in urine, pain with urination, weakened urinary. Diagnosis. diagnosing bladder stones may involve: a physical exam. your doctor will likely feel your lower abdomen to see if your bladder is enlarged (distended) or may perform a rectal exam to determine whether your prostate is enlarged. you'll also discuss any urinary signs or symptoms that you're having. [6,7] there are separate eau guidelines for upper tract stones and bladder stones, both of which received a minor update in 2020. [8,9] both the guidelines evaluate the strength of evidence using different methods (appendix 1). the aua assesses the level of evidence alphabetically and uses specific nomenclature to demonstrate the strength of. The stones may also block the flow of urine from the bladder. symptoms can include: abdominal pain, pressure. abnormally colored or dark colored urine. blood in the urine. difficulty urinating. frequent urge to urinate. inability to urinate except in certain positions. interruption of the urine stream.
.jpg?q=O55uB6HxE3mZScTt)
Bladder Stones Symptoms Prevention And More [6,7] there are separate eau guidelines for upper tract stones and bladder stones, both of which received a minor update in 2020. [8,9] both the guidelines evaluate the strength of evidence using different methods (appendix 1). the aua assesses the level of evidence alphabetically and uses specific nomenclature to demonstrate the strength of. The stones may also block the flow of urine from the bladder. symptoms can include: abdominal pain, pressure. abnormally colored or dark colored urine. blood in the urine. difficulty urinating. frequent urge to urinate. inability to urinate except in certain positions. interruption of the urine stream.

Comments are closed.