Urinary Tract Sonography Phantom Bladder Lesion Clinical Report My

Urinary Tract Sonography Phantom Bladder Lesion Clinical Report My Urinary tract obstruction (uto) occurs due to blockage of urine flow along the urinary tract and generally manifests as hydronephrosis on imaging. uto may be acute or chronic, partial or complete, and unilateral or bilateral. kidney function impairment from uto, if present, is readily reversible if the obstruction is promptly corrected. The most common indication for point of care ultrasound (poc us) of the urinary tract in the emergency department (ed) is flank pain, responsible for approximately 2 million ed visits in the united states annually. about 20% of patients presenting with flank pain have nephrolithiasis.[1] while computed tomography (ct) imaging is the gold standard for diagnosing urinary tract stones, poc us is.

Urinary Bladder Ultrasound 2. tumor like lesions in the lumen of the urinary bladder. 2.1. blood clots in the urinary bladder usually form echogenic masses without acoustic shadow and without visible blood flow in doppler examination (fig. 10). they usually move when the patient changes position. large blood clots are oval and may occupy the entire lumen of the bladder. Urinary bladder masses are commonly encountered in clinical practice, with 95% arising from the epithelial layer and rarer tumors arising from the lamina propria, muscularis propria, serosa, and adventitia. the extent of neoplastic invasion into these bladder layers is assessed with multimodality imaging, and the mri based vesical imaging reporting and data system is increasingly used to aid. The bladder is a muscular sac that receives urine from your kidneys, stretching to hold the fluid until you release it during urination. bladder control, or your ability to control these muscles. Purpose to explore the application of contrast enhanced ultrasound (ceus) for the diagnosis and grading of bladder urothelial carcinoma (buc). methods the results of a two dimensional ultrasound, color doppler ultrasound and ceus, were analyzed in 173 bladder lesion cases. the ultrasound and surgical pathology results were compared, and their diagnostic efficacy was analyzed. results there.
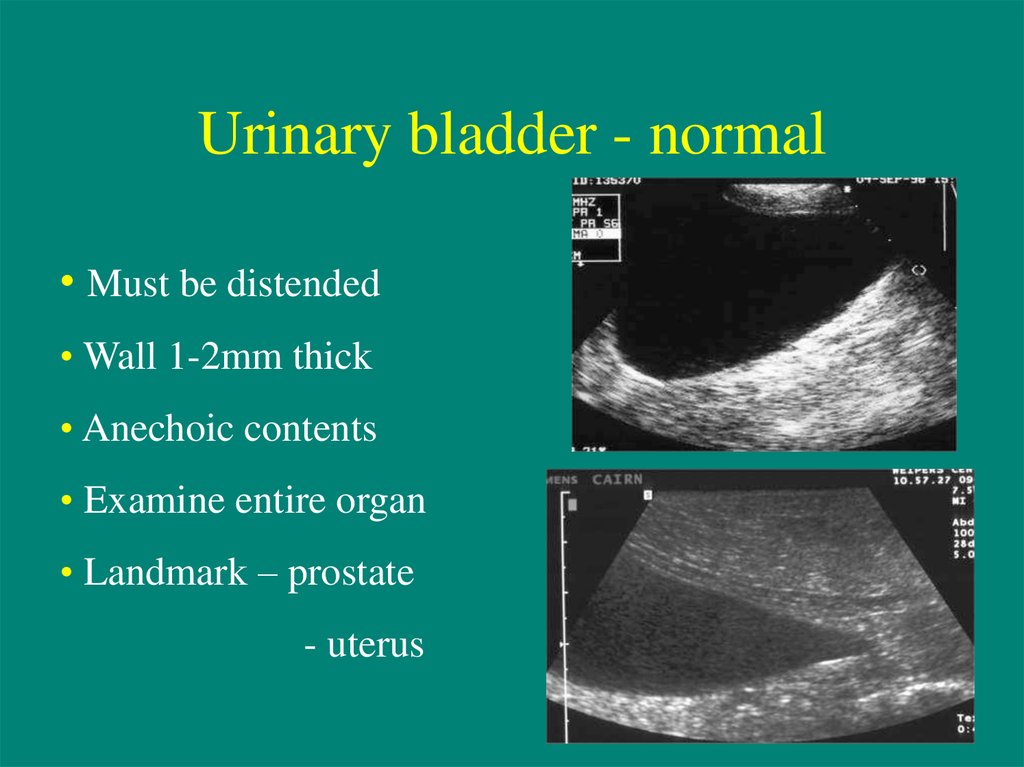
Urinary Bladder Ultrasound The bladder is a muscular sac that receives urine from your kidneys, stretching to hold the fluid until you release it during urination. bladder control, or your ability to control these muscles. Purpose to explore the application of contrast enhanced ultrasound (ceus) for the diagnosis and grading of bladder urothelial carcinoma (buc). methods the results of a two dimensional ultrasound, color doppler ultrasound and ceus, were analyzed in 173 bladder lesion cases. the ultrasound and surgical pathology results were compared, and their diagnostic efficacy was analyzed. results there. Primary bladder neoplasms can be divided into two broad categories: flat and papillary lesions. in this chapter, we provide a review of non invasive papillary urothelial neoplasms of the bladder: urothelial papilloma, inverted urothelial papilloma, papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (punlmp), non invasive low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma, and non invasive high. Background large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) of the urinary bladder is an uncommon malignant bladder tumor, and the overall prognosis is poor. contrast enhanced ultrasound (ceus) provides a new effective modality for tumor detection and diagnosis. case presentation a 30 year old man complained of repeated painless gross haematuria for half a month. conventional ultrasound.

What Is A Urinary Tract Ultrasound Two Views Primary bladder neoplasms can be divided into two broad categories: flat and papillary lesions. in this chapter, we provide a review of non invasive papillary urothelial neoplasms of the bladder: urothelial papilloma, inverted urothelial papilloma, papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (punlmp), non invasive low grade papillary urothelial carcinoma, and non invasive high. Background large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (lcnec) of the urinary bladder is an uncommon malignant bladder tumor, and the overall prognosis is poor. contrast enhanced ultrasound (ceus) provides a new effective modality for tumor detection and diagnosis. case presentation a 30 year old man complained of repeated painless gross haematuria for half a month. conventional ultrasound.
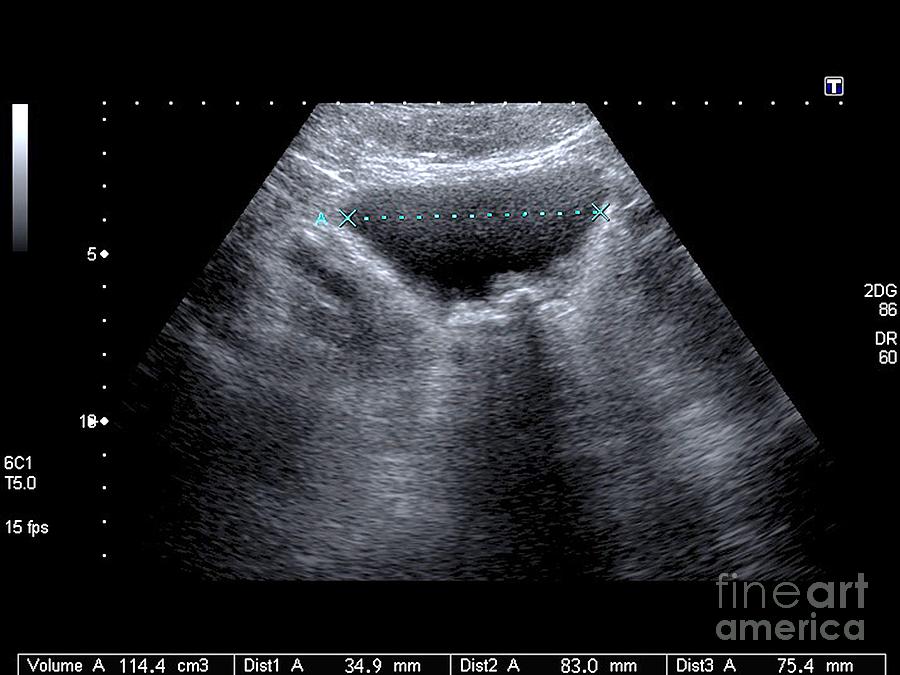
Urinary Bladder Ultrasound

Comments are closed.