Urinary Bladder Diverticulum Ultrasound Case 273

Urinary Bladder Diverticulum Ultrasound Case 273 Youtube A urinary bladder diverticulum (plural: diverticula) is an outpouching from the bladder wall, whereby mucosa herniates through the bladder wall. it may be solitary or multiple in nature and can vary considerably in size. epidemiology. there are two peaks; one at 10 years and the other at 60 70 years 2. Urinary bladder diverticulum || ultrasound || case 273blog link: drmahin 2022 04 case 57 urinary bladder diverticulum clinical featu.

Bladder Diverticulum Ultrasound Case discussion. a urinary bladder diverticulum is a pouch or outpouching that forms in the bladder wall. it can be congenital or acquired and is often associated with conditions such as bladder outlet obstruction, neurogenic bladder dysfunction, or chronic bladder inflammation. urinary bladder diverticulum, although relatively uncommon, can be. Bladder diverticula are protrusions of the bladder urothelium and mucosa via muscle fibers of the bladder wall, the muscularis propria, which results in a thin walled structure connected to the bladder lumen and poorly empties during micturition. bladder diverticula occur either to congenital or acquired causes. they affect both adults and children. unlike the acquired adult form, in which. A communicating urinary bladder diverticulum is noted, containing about 390 ml of urine. case discussion to differentiate between the urinary bladder and the diverticulum, you can use color doppler to locate the urine jet which visible in the urinary bladder. Case presentation. a 65 year old male presented to the emergency department with symptoms including fever, abnormal urinalysis, and elevated post void residual. point of care ultrasound was used to rapidly diagnose a bladder diverticulum. the patient was subsequently seen by urology for outpatient bladder repair.
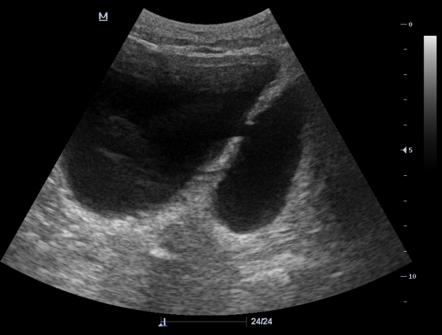
Urinary Bladder Diverticulum Radiology Reference Article A communicating urinary bladder diverticulum is noted, containing about 390 ml of urine. case discussion to differentiate between the urinary bladder and the diverticulum, you can use color doppler to locate the urine jet which visible in the urinary bladder. Case presentation. a 65 year old male presented to the emergency department with symptoms including fever, abnormal urinalysis, and elevated post void residual. point of care ultrasound was used to rapidly diagnose a bladder diverticulum. the patient was subsequently seen by urology for outpatient bladder repair. The bladder diverticulum is an outpouching of the bladder wall (powell et al., 2009). in pseudodiverticula, only the mucous membrane of the bladder herniates; the diverticulum wall is without a muscle layer. in true diverticula, the outpouching consists of all bladder wall layers. ultrasound imaging of a small bladder diverticulum. Purpose of review bladder diverticula are common in clinical practice and in adults most commonly occur in the setting of bladder outlet obstruction. they most commonly present with lower urinary tract symptoms and patients should be thoroughly investigated with a history, examination, radiological and endoscopic examination and video urodynamic studies if contemplating surgery. we aim to.
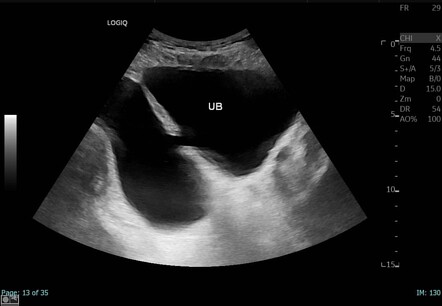
Urinary Bladder Diverticulum Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org The bladder diverticulum is an outpouching of the bladder wall (powell et al., 2009). in pseudodiverticula, only the mucous membrane of the bladder herniates; the diverticulum wall is without a muscle layer. in true diverticula, the outpouching consists of all bladder wall layers. ultrasound imaging of a small bladder diverticulum. Purpose of review bladder diverticula are common in clinical practice and in adults most commonly occur in the setting of bladder outlet obstruction. they most commonly present with lower urinary tract symptoms and patients should be thoroughly investigated with a history, examination, radiological and endoscopic examination and video urodynamic studies if contemplating surgery. we aim to.

Comments are closed.