Urinary Bladder Carcinoma вђ Radiology Cases
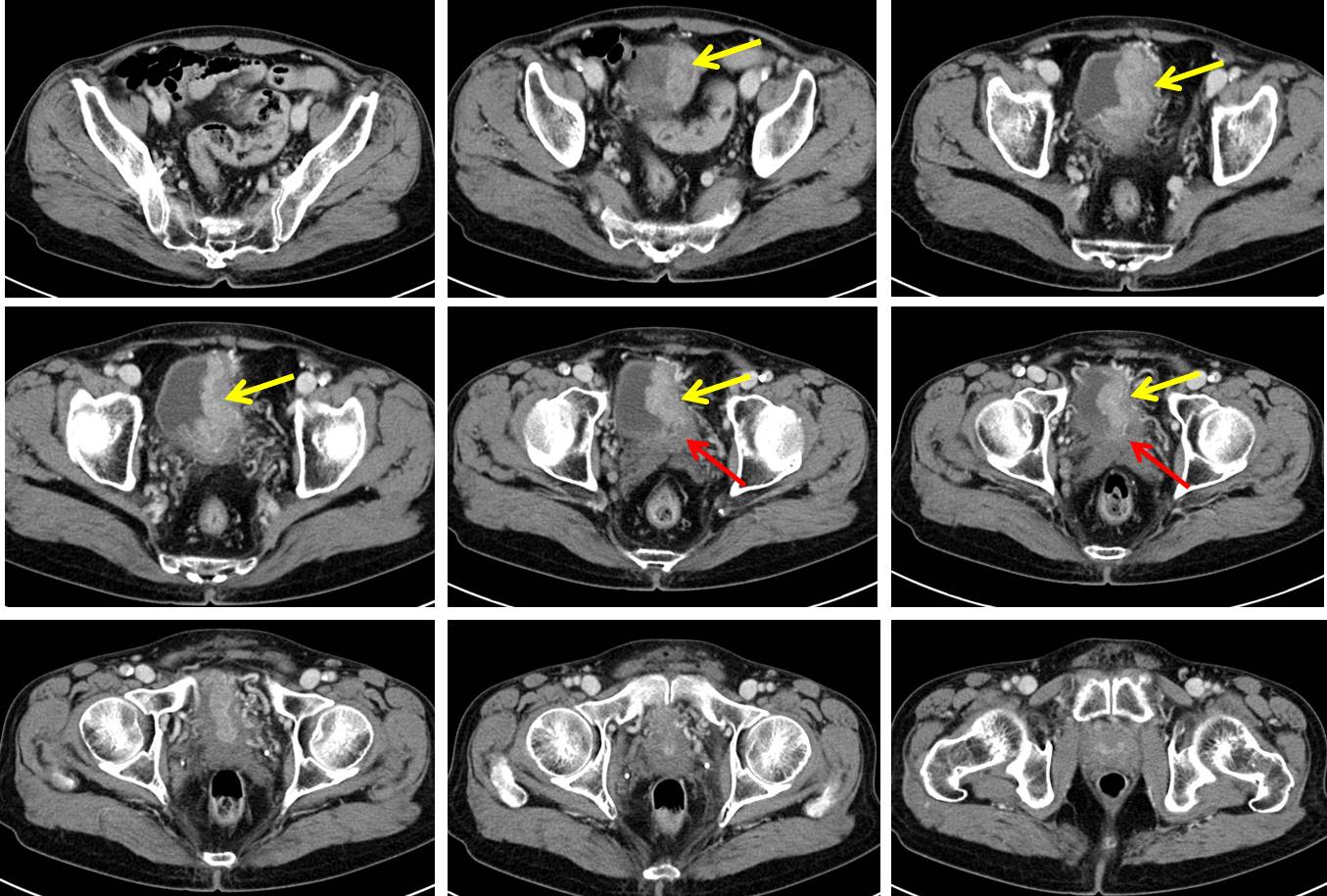
Urinary Bladder Carcinoma вђ Radiology Cases Bladder cancer is a broad term used to describe all types of cancers affecting the urinary bladder: transitional cell carcinoma (urinary bladder): most common primary neoplasm of the bladder. squamous cell carcinoma (urinary bladder): accounts for around 3 8% of all bladder cancers. adenocarcinoma (urinary bladder): accounts for around 1% of. Case discussion. pathology proven urinary bladder urothelial cell carcinoma, that is the most common primary neoplasm of the urinary bladder and the most common tumor of the entire urinary system. for tnm staging, although ct is unable to distinguish between t1, t2 and t3a (microscopic extravesical spread), it can distinguish t3b tumors.
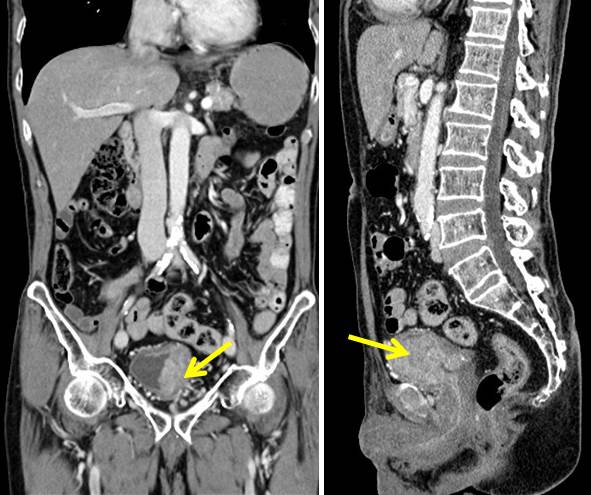
Urinary Bladder Carcinoma вђ Radiology Cases Urothelial carcinoma constitutes 90% of bladder cancer. in rare cases, bladder cancer may be an adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. since this is a urothelial disease, the tumor can also be localized to the pelvis and ureter. bladder cancer usually appears as a vegetation within the bladder, less often a red and flat lesion, visible with. Transitional cell carcinoma (tcc), also called urothelial cell carcinoma (ucc) of the bladder, is the most common primary neoplasm of the urinary bladder, and bladder tcc is the most common tumor of the entire urinary system. this article concerns itself with transitional cell carcinomas of the bladder specifically. related articles include:. Cancer of the urinary bladder is predominantly a disease of older men. this disease represents 6% of all malignancies in men, making it the fourth most common tumor. in women, bladder carcinoma represents 2% of malignancies, making it the seventh most common tumor [1]. the incidence increases with age (median age, 69–70 years). Urinary bladder cancer is a heterogeneous disease with a variety of pathologic features, cytogenetic characteristics, and natural histories. it is the fourth most common cancer in males and the tenth most common cancer in females. urinary bladder cancer has a high recurrence rate, necessitating long term surveillance after initial therapy. early detection is important, since up to 47% of.

Urinary Bladder Carcinoma Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Cancer of the urinary bladder is predominantly a disease of older men. this disease represents 6% of all malignancies in men, making it the fourth most common tumor. in women, bladder carcinoma represents 2% of malignancies, making it the seventh most common tumor [1]. the incidence increases with age (median age, 69–70 years). Urinary bladder cancer is a heterogeneous disease with a variety of pathologic features, cytogenetic characteristics, and natural histories. it is the fourth most common cancer in males and the tenth most common cancer in females. urinary bladder cancer has a high recurrence rate, necessitating long term surveillance after initial therapy. early detection is important, since up to 47% of. Urothelial (transitional cell) carcinoma is the predominant histologic type in the united states and europe, where it accounts for 90 percent of all bladder cancers. in other areas of the world, non urothelial carcinomas are more frequent. much less commonly, urothelial cancers can arise in the renal pelvis, ureter, or urethra. Introduction. bladder cancer is the sixth most common malignancy in the us, with an estimated incidence of 79,030 new cases in 2017 [].approximately 90% of bladder cancers are composed of urothelial carcinoma (uc), and other histologic types, such as squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, are far less common [].

Urinary Bladder Carcinoma вђ Radiology Cases Urothelial (transitional cell) carcinoma is the predominant histologic type in the united states and europe, where it accounts for 90 percent of all bladder cancers. in other areas of the world, non urothelial carcinomas are more frequent. much less commonly, urothelial cancers can arise in the renal pelvis, ureter, or urethra. Introduction. bladder cancer is the sixth most common malignancy in the us, with an estimated incidence of 79,030 new cases in 2017 [].approximately 90% of bladder cancers are composed of urothelial carcinoma (uc), and other histologic types, such as squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma, are far less common [].

Comments are closed.