Understanding Distance Time Graphs Part 1 Graphical Analysis
Understanding Distance Time Graphs Part 1 Graphical Analysis Distance–time graph for uniform motion. distance time graph can tell us about the uniform motion of a body in three ways: if the object is stationary, the distance covered in a particular interval of time is zero. hence, the graph is a horizontal line along the x axis. if the object moves slowly, it covers less distance in a given interval of. The graph of position versus time in figure 2.48(a) is a curve rather than a straight line. the slope of the curve becomes steeper as time progresses, showing that the velocity is increasing over time. the slope at any point on a position versus time graph is the instantaneous velocity at that point.

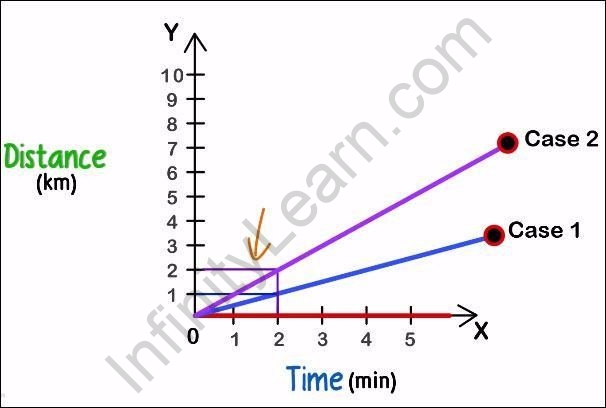
Understanding Distance Time Graphs Part 1 Graphical Analysis If we call the horizontal axis the x axis and the vertical axis the y axis, as in figure 2.8.1 2.8. 1, a straight line graph has the general form. y = mx b. (2.8.1) (2.8.1) y = m x b. here m m is the slope, defined to be the rise divided by the run of the straight line (figure 2.8.1 2.8. 1). A distance time graph shows how far an object has travelled in a given time. it is a simple line graph that denotes distance versus time findings on the graph. distance is plotted on the y axis. time is plotted on the x axis. note: curved lines on a distance time graph indicate that the speed is changing. you may also want to check out these. We already know that for a uniform motion, the distance time graph is a straight line. this is because a body in uniform motion covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. now if a body is undergoing non uniform motion, the body covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. this makes the distance time graph non linear. Show step. the person traveled 30 km 30 km in 30 minutes, 30 minutes, this would mean they would travel 60 km 60 km in 1 hour, 1 hour, therefore, their speed was 60 km h. 60 km h. you could also find this using the speed, distance, time formula. speed= distance time = 30 0.5 =60 km h speed = timedistance = 0.530 = 60 km h.

Comments are closed.