Ultrasound Video Showing Two Large Stones In Urinary Bladder

Ultrasound Video Showing Two Large Stones In Urinary Bladder Youtube Transabdominal ultrasound scan video clip shows 2 calculi or stones in the urinary bladder that move with change in posture of the patient. initially, in the. This video shows two large stones in urinary bladder.

Ultrasound Video Showing A Large Stone In Urinary Bladder Diagnosis. diagnosing bladder stones may involve: a physical exam. your doctor will likely feel your lower abdomen to see if your bladder is enlarged (distended) or may perform a rectal exam to determine whether your prostate is enlarged. you'll also discuss any urinary signs or symptoms that you're having. Bladder stones. bladder stones are often seen after renal stones travel from the ureters into the bladder. bladder stones can also form in the bladder itself due to bladder stasis in patients with chronic urinary retention (tublin, 2001). on ultrasound, these stones appear hyperechoic and mobile with acoustic shadowing. Citation, doi, disclosures and article data. urolithiasis refers to the presence of calculi anywhere along the course of the urinary tracts. for the purpose of the article, the terms urolithiasis, nephrolithiasis, and renal kidney stones are used interchangeably, although some authors have slightly varying definitions of each. Monitoring bladder stones. the doctor may require a follow up visit three to four weeks later to perform a ct scan, x ray, or ultrasound to make sure all of the bladder stone fragments were removed. a patient's blood levels may also be monitored, as an overactive thyroid or elevated uric acid levels can contribute to bladder stone formation.
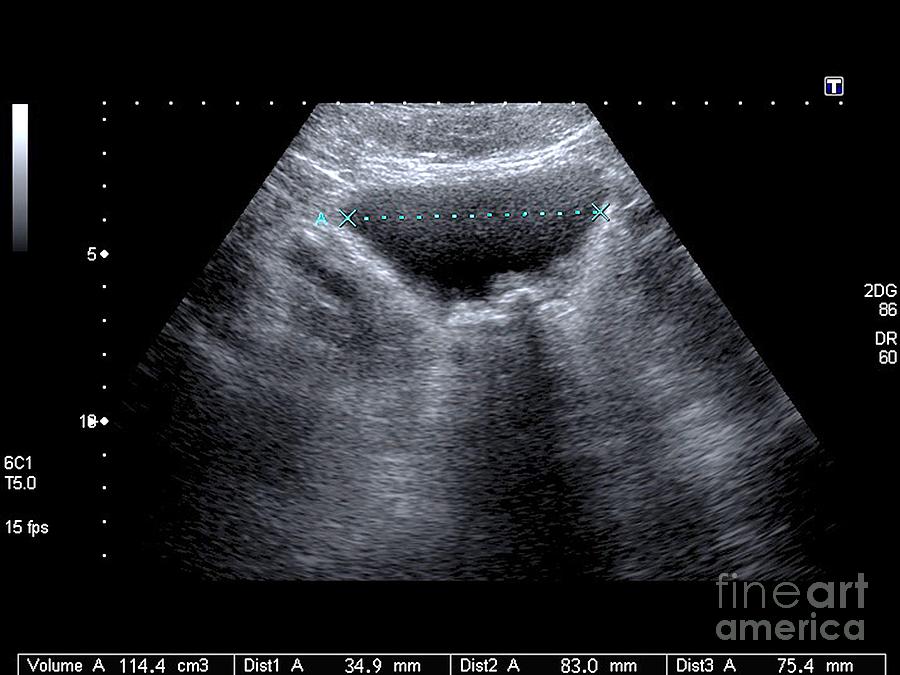
Bladder Stones Ultrasound Scan By Science Photo Library Citation, doi, disclosures and article data. urolithiasis refers to the presence of calculi anywhere along the course of the urinary tracts. for the purpose of the article, the terms urolithiasis, nephrolithiasis, and renal kidney stones are used interchangeably, although some authors have slightly varying definitions of each. Monitoring bladder stones. the doctor may require a follow up visit three to four weeks later to perform a ct scan, x ray, or ultrasound to make sure all of the bladder stone fragments were removed. a patient's blood levels may also be monitored, as an overactive thyroid or elevated uric acid levels can contribute to bladder stone formation. Large bladder stones can irritate your bladder and cause intense pain, bleeding and problems peeing. signs and symptoms of a larger bladder stone may include: changes in the color of your pee. your pee may look cloudy or dark. you may also see blood in your pee (hematuria). frequent urges to pee. Bladder ultrasound is an imaging technique widely recognized for its efficacy in examining the bladder and surrounding areas. this non invasive, safe, and relatively quick procedure has become an important tool in diagnosing and managing many urological conditions. it uses high frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the bladder.

Comments are closed.