Ultrasound Cases 506 Of 2000 Debris In Urinary Bladder

Ultrasound Cases 506 Of 2000 Debris In Urinary Bladder Ascites Gall Debris within the bladder is commonly seen on ultrasound. the etiology of bladder debris is varied and the likelihood that urinary debris represents positive urine culture is under investigation. we hypothesize that bladder debris will increase the likelihood that a urine culture is positive compared to those without bladder debris. The management of patients in whom bladder debris is seen on rbus is also uncertain and may be based on many clinical factors (e.g. ongoing fever, urinary symptoms, etc.). one recent study in adults concluded that bladder debris is not significantly associated with an abnormal urinalysis . in that study, the imaging and urine sample were.

Apa Itu Ultrasound Dominic Sharp Renal and bladder ultrasound (rbus) is recom . was used to evaluate the association between debris. c.p. nelson, boston children’s. mended in evaluation of children after an initial, on rbus and positive urine culture results. hospital, 300 longwood avenue, boston, ma 02115, usa. caleb.nelson@childrens. harvard.edu (c.p. nelson) keywords. The sensitivity and specificity for bladder debris in detecting positive urine cultures was 52% and 86%, respectively. forty seven percent of those with bladder debris had positive cultures, compared with 12% of those without debris (p < 0.01). the relative risk of positive urine culture if debris is present is 3.90 (95% ci 2.73 5.55). Objectives. the purpose of this study was to determine the significance of urinary bladder debris detected by sonography. methods. we conducted a retrospective analysis of urinalysis results in age matched patients with and without bladder debris detected by transabdominal sonography. Purpose to evaluate the correlation between the presence of bladder debris on ultrasound and urinalysis results in the emergency department setting. methods adult patients presenting to the emergency department with an ultrasound of the bladder and a urinalysis performed within 24 h of the ultrasound were included in this retrospective study. two radiologists in consensus evaluated for the.

Bladder Debris On Renal And Bladder Ultrasound A Significant Predictor Objectives. the purpose of this study was to determine the significance of urinary bladder debris detected by sonography. methods. we conducted a retrospective analysis of urinalysis results in age matched patients with and without bladder debris detected by transabdominal sonography. Purpose to evaluate the correlation between the presence of bladder debris on ultrasound and urinalysis results in the emergency department setting. methods adult patients presenting to the emergency department with an ultrasound of the bladder and a urinalysis performed within 24 h of the ultrasound were included in this retrospective study. two radiologists in consensus evaluated for the. Renal and bladder ultrasound (rbus) is recommended in evaluation of children after an initial, febrile urinary tract infection. although it is not uncommon to observe debris within the bladder lumen on sonography, the significance of this finding is uncertain. debris may be interpreted as an indication of ongoing infection, but there have been no studies to date investigating the association. However, the rate at which urinary debris is associated with a positive urine culture is not currently well described. mcquaid et al. [10] recently published their findings on 34 pediatric patients with bladder debris seen on ultrasound. they reported a significant association between bladder debris and positive urine culture, with an odds.
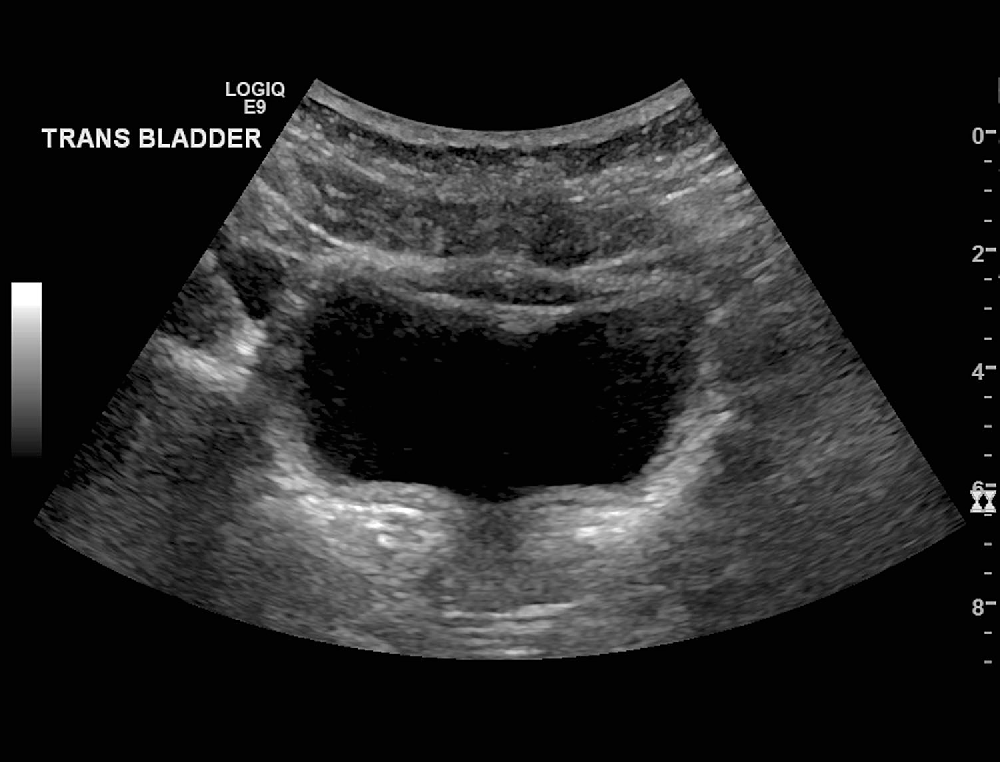
Bladder Debris On Ultrasound In The Emergency Department Correlation Renal and bladder ultrasound (rbus) is recommended in evaluation of children after an initial, febrile urinary tract infection. although it is not uncommon to observe debris within the bladder lumen on sonography, the significance of this finding is uncertain. debris may be interpreted as an indication of ongoing infection, but there have been no studies to date investigating the association. However, the rate at which urinary debris is associated with a positive urine culture is not currently well described. mcquaid et al. [10] recently published their findings on 34 pediatric patients with bladder debris seen on ultrasound. they reported a significant association between bladder debris and positive urine culture, with an odds.
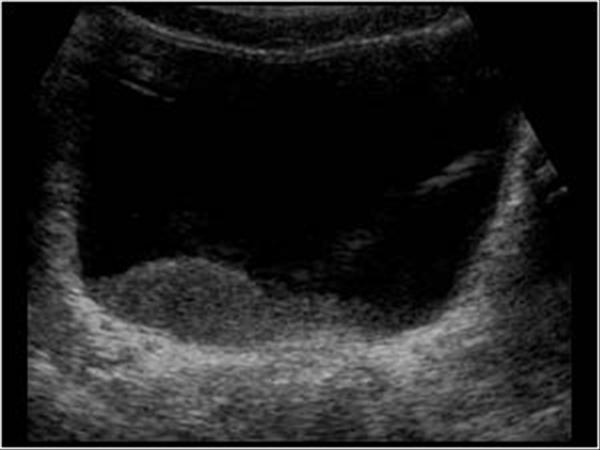
Pediatrics 9 2 Pediatric Urinary Tract Case 9 2 8 Miscellaneous

Comments are closed.