Ultrasonography Shows Thickening Of The Wall Of The Urinary Bladder
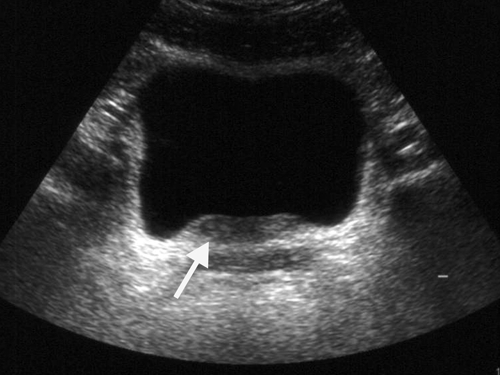
Ultrasonography Shows Thickening Of The Wall Of The Uri Open I Urinary bladder wall thickening is a common finding and its significance depends on whether the bladder is adequately distended. radiographic features. ultrasound. in both adults and children, the wall may be considered thickened on ultrasound if it measures 6: >3 mm when distended (>25% expected volume*). Boo is more common among men, because it’s often linked to prostate problems. an enlarged prostate forces the bladder to work harder to empty itself of urine. this in turn causes the bladder.

Ultrasonography Shows Thickening Of The Wall Of The Urinary Bladder Bladder wall thickening can happen as part of a number of conditions, such as uti cystitis, noncancerous tissue growths, bladder cancer, neurogenic bladder, hemorrhagic cystitis, interstitial cystits, eosinophilic cystitis, amyloidosis, bladder outlet obstruction, and benign prostatic hyperplasia. symptoms that may occur with bwt include urgent. Bladder ultrasound is an imaging technique widely recognized for its efficacy in examining the bladder and surrounding areas. this non invasive, safe, and relatively quick procedure has become an important tool in diagnosing and managing many urological conditions. it uses high frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the bladder. That thickening of the bladder walls is called trabeculation. when your bladder walls get too thick, they lose the ability to expand and contract, making it hard for your body to expel urine. Bladder trabeculation is a thickening of the bladder walls. the condition often occurs due to repeated or chronic obstructions in the urethra, which is the tube that drains urine from the bladder.

Ultrasound Imaging Urinary Bladder Trabeculation 3d Ultrasound That thickening of the bladder walls is called trabeculation. when your bladder walls get too thick, they lose the ability to expand and contract, making it hard for your body to expel urine. Bladder trabeculation is a thickening of the bladder walls. the condition often occurs due to repeated or chronic obstructions in the urethra, which is the tube that drains urine from the bladder. The sediment has settled on the gravity dependent wall of the bladder, leading to the appearance of a relative thickening of the ventral wall of the bladder compared to the dorsal wall. 5 note the anechoic shadow (arrow heads) in the far field, deep to the sediment, which is caused by a lack of ultrasound waves propagating to the deeper. The incidence of bladder carcinoma is significantly increased in patients who undergo treatment with cyclophosphamide. cyclophosphamide induced cystitis is characterized by marked bladder edema and hemorrhage. ivu or cystography shows bladder wall thickening and irregularity, with intraluminal filling defects caused by blood clots.
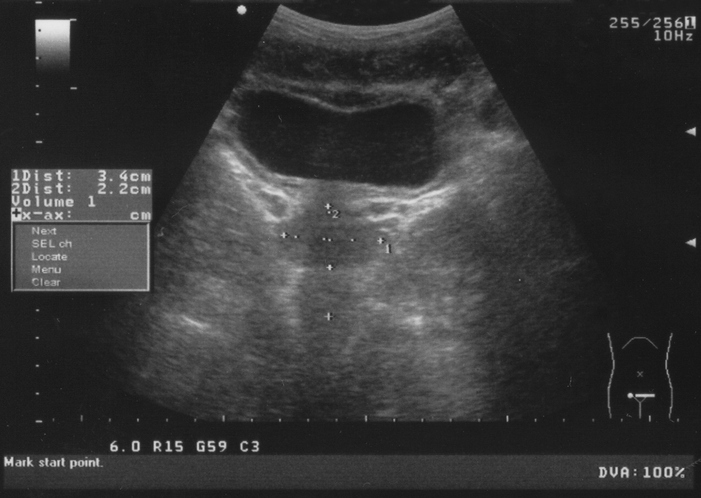
Why You May Need A Full Bladder For That Ultrasound Go Imaging The sediment has settled on the gravity dependent wall of the bladder, leading to the appearance of a relative thickening of the ventral wall of the bladder compared to the dorsal wall. 5 note the anechoic shadow (arrow heads) in the far field, deep to the sediment, which is caused by a lack of ultrasound waves propagating to the deeper. The incidence of bladder carcinoma is significantly increased in patients who undergo treatment with cyclophosphamide. cyclophosphamide induced cystitis is characterized by marked bladder edema and hemorrhage. ivu or cystography shows bladder wall thickening and irregularity, with intraluminal filling defects caused by blood clots.

Comments are closed.