Ultrasonography Shows Thickening Of The Wall Of The Uri Open I
Ultrasonography Shows Thickening Of The Wall Of The Uri Open I Reported ranges for normal bowel wall thickness in children vary in the literature and increase slightly with age; however, an approximate wall thickness of 2.5 mm in the small bowel and 2.0 mm in the colon is usually appropriate [3, 10, 11]. fig. 1. Any wall thickening, focal or diffuse, that exceeds 25 mm in thickness is more likely to be malignant. masses demonstrate focal, asymmetric wall thickening, and may extend intraluminally or be exophytic . differential diagnosis of thickening of the wall of the small bowel and colon is listed in boxes 4.1 and 4.2 .

A Ultrasonography Shows Distention And Wall Thickening Of The An ischemic bowel wall shows circumferential thickening and may show a target sign. in other cases, thickened wall without enhancement may be seen. 53. on ct images, infectious ileocolitis usually shows circumferential mural thickening of the distal ileum and cecum and may be accompanied by mesenteric lymph nodal enlargement. Urinary bladder wall thickening is a common finding and its significance depends on whether the bladder is adequately distended. radiographic features. ultrasound. in both adults and children, the wall may be considered thickened on ultrasound if it measures 6: >3 mm when distended (>25% expected volume*). Us fingerprint of the normal gi tract. the classic five layer us structure of the bowel wall is easiest apprehended by studying the wall of the fluid filled stomach. the layers, starting from inside to outside, are hyper hypo hyper hypo hyper echoic or white black white black white. Commonly, adjacent enlarged lymph nodes may be easier to sample than the affected bowel wall and if possible it is recommended that both areas be aspirated to increase the likelihood of an accurate diagnosis. diffuse, mild wall thickening (especially if the thickened layer is the muscularis) is best diagnosed with full thickness surgical biopsies.

Endoscopic Ultrasonography Shows A Transmural Thickening Of The Us fingerprint of the normal gi tract. the classic five layer us structure of the bowel wall is easiest apprehended by studying the wall of the fluid filled stomach. the layers, starting from inside to outside, are hyper hypo hyper hypo hyper echoic or white black white black white. Commonly, adjacent enlarged lymph nodes may be easier to sample than the affected bowel wall and if possible it is recommended that both areas be aspirated to increase the likelihood of an accurate diagnosis. diffuse, mild wall thickening (especially if the thickened layer is the muscularis) is best diagnosed with full thickness surgical biopsies. Ultrasound showed the wes triad. at admission, ct scan of the abdomen revealed a small bowel obstruction due to a 2.2 cm calcification in the terminal ileum, consistent with a gallstone ileus. the overall ct pattern was suspicious for a gallbladder that formed a fistula into the adjacent bowel, likely the proximal duodenum, thus leading to a. Thickening of the bile duct wall can stem from a variety of etiologies. radiographic features. ultrasound. bile duct wall thickening. bile duct walls are typically not visible when normal. possible narrowing of the ducts with obstruction. possible secondary signs of cholangitis, including debris in the biliary system. differential diagnosis.

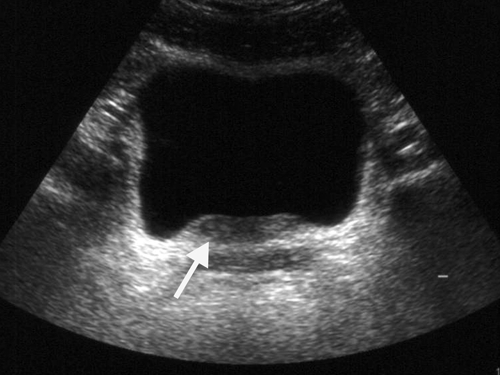
Ultrasonography Shows Thickening Of The Wall Of The Urinary Bladder Ultrasound showed the wes triad. at admission, ct scan of the abdomen revealed a small bowel obstruction due to a 2.2 cm calcification in the terminal ileum, consistent with a gallstone ileus. the overall ct pattern was suspicious for a gallbladder that formed a fistula into the adjacent bowel, likely the proximal duodenum, thus leading to a. Thickening of the bile duct wall can stem from a variety of etiologies. radiographic features. ultrasound. bile duct wall thickening. bile duct walls are typically not visible when normal. possible narrowing of the ducts with obstruction. possible secondary signs of cholangitis, including debris in the biliary system. differential diagnosis.

Urinary Bladder Wall Thickening Radiology Reference Article

Comments are closed.