Ultrasonography Of The Urinary Bladder
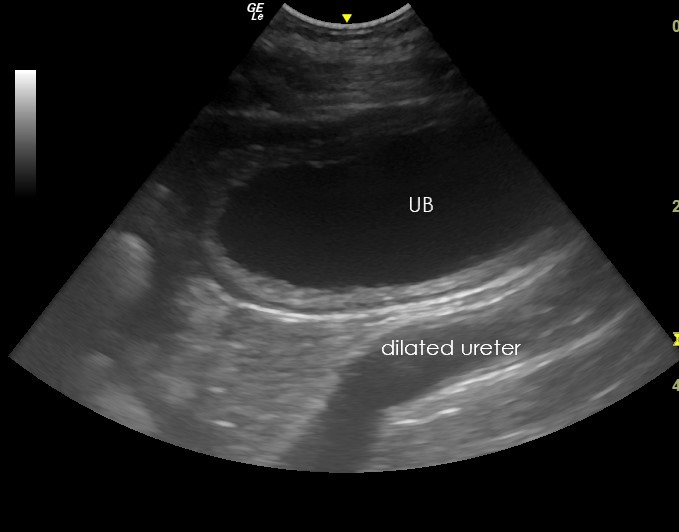
Ultrasonography Of The Urinary Bladder Make sure your bladder is full. while this can make the gentle pressure applied during the ultrasound a bit uncomfortable, a full bladder can help shift other organs, like the bowels or uterus, to. Bladder ultrasound plays an important role in diagnosing and managing urinary tract infections (utis), bladder cancer, bladder stones, and urinary incontinence. it helps in identifying changes in bladder wall thickness, abnormalities within the bladder, and issues related to bladder emptying. for patients experiencing symptoms like frequent.
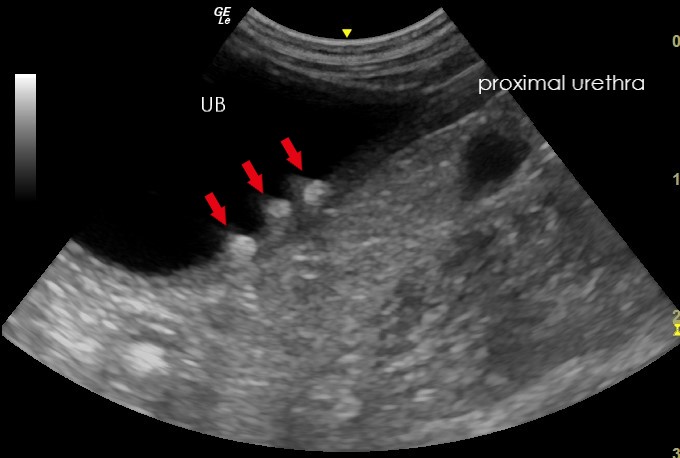
Ultrasonography Of The Urinary Bladder The most common indication for point of care ultrasound (poc us) of the urinary tract in the emergency department (ed) is flank pain, responsible for approximately 2 million ed visits in the united states annually. about 20% of patients presenting with flank pain have nephrolithiasis.[1] while computed tomography (ct) imaging is the gold standard for diagnosing urinary tract stones, poc us is. A doctor may recommend an ultrasound for a person with oab. in addition to ruling out other underlying causes of a person’s symptoms, this imaging test can check the health of the urinary tract. Step 1: bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. place the transducer with the indicator pointing towards the patient’s head in the patient’s midline, right above the pubic symphysis. rock the probe so that it points down towards the pelvic cavity. bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. An ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys can be used to detect various conditions such as: kidney or bladder stones. infections in the kidneys and urinary tract. hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidneys due to buildup of urine) pyelonephritis (infection in the kidneys that has ascended from the urinary tract) cysts or tumors in the kidneys.
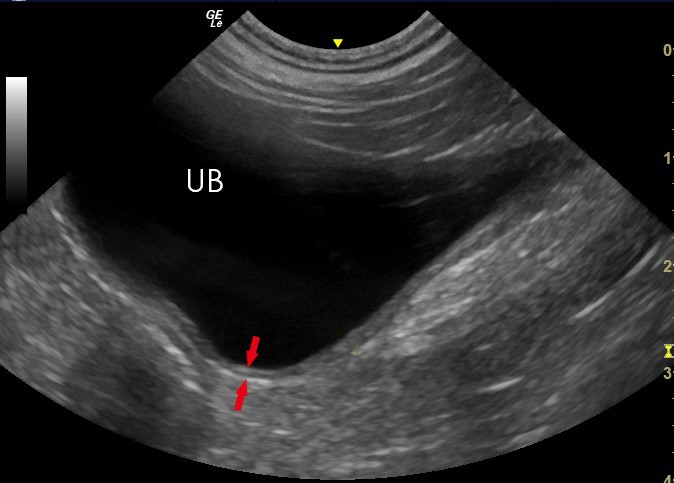
Ultrasonography Of The Urinary Bladder Step 1: bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. place the transducer with the indicator pointing towards the patient’s head in the patient’s midline, right above the pubic symphysis. rock the probe so that it points down towards the pelvic cavity. bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. An ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys can be used to detect various conditions such as: kidney or bladder stones. infections in the kidneys and urinary tract. hydronephrosis (swelling of the kidneys due to buildup of urine) pyelonephritis (infection in the kidneys that has ascended from the urinary tract) cysts or tumors in the kidneys. Ultrasonography of the urinary bladder. ultrasonography of the urinary bladder should be performed as part of every routine abdominal ultrasound examination. specific indications for bladder ultrasonography include: urinary tract infections and abnormalities identified on urinalysis. dysuria or haematuria. The urinary tract is your body’s drainage system for removing wastes and extra fluids. the urinary tract includes two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. the kidneys filter wastes and fluids to produce urine. the urine travels from the kidneys down two narrow tubes called the ureters.

Comments are closed.