Ultrasonography Of The Bladder Wall Of Patient 1 A Ultrasound

Ultrasonography Of The Bladder Wall Of Patient 1 A Ultrasound Make sure your bladder is full. while this can make the gentle pressure applied during the ultrasound a bit uncomfortable, a full bladder can help shift other organs, like the bowels or uterus, to. Step 1: bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view. place the transducer with the indicator pointing towards the patient’s head in the patient’s midline, right above the pubic symphysis. rock the probe so that it points down towards the pelvic cavity. bladder ultrasound – longitudinal view.

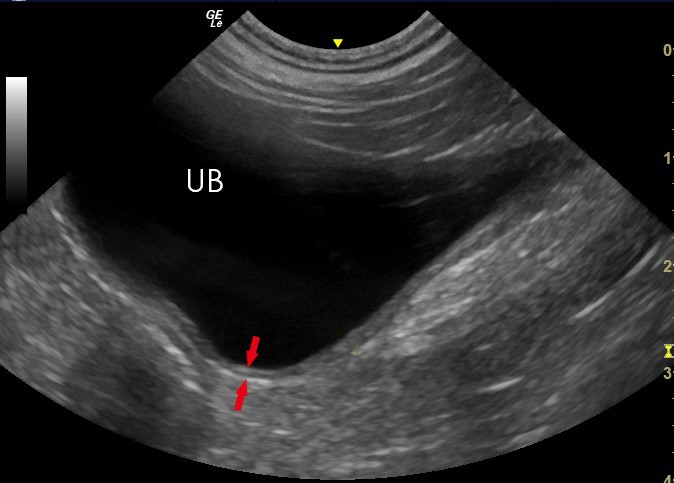
Ultrasonography Of The Bladder Wall Of Patient 1 A Ultrasound Bladder ultrasound plays an important role in diagnosing and managing urinary tract infections (utis), bladder cancer, bladder stones, and urinary incontinence. it helps in identifying changes in bladder wall thickness, abnormalities within the bladder, and issues related to bladder emptying. for patients experiencing symptoms like frequent. Download scientific diagram | ultrasonography of the bladder wall of patient 1. (a) ultrasound revealed irregular thickening of the bladder wall. (b) color doppler ultrasound revealed abundant. Bladder ultrasound interpretation and imaging techniques. interpreting bladder ultrasound images requires expertise to accurately identify normal and abnormal findings. a skilled sonographer or a medical professional can analyze the images to assess bladder volume, wall thickness, presence of calculi, and any signs of inflammation or tumors. A bladder ultrasound can also provide information on the bladder wall and the pouches of the bladder, called the diverticula. in addition, it can reveal any stones or sizeable tumors in the bladder.
Ultrasonography Of The Urinary Bladder Bladder ultrasound interpretation and imaging techniques. interpreting bladder ultrasound images requires expertise to accurately identify normal and abnormal findings. a skilled sonographer or a medical professional can analyze the images to assess bladder volume, wall thickness, presence of calculi, and any signs of inflammation or tumors. A bladder ultrasound can also provide information on the bladder wall and the pouches of the bladder, called the diverticula. in addition, it can reveal any stones or sizeable tumors in the bladder. Maximum renal lengths are recorded. renal volumes may be calculated by measuring transverse and anteroposterior (ap) diameters from a mid kidney transverse image. the standard formula (volume = length × width × ap diameter × 0.52) is utilized. the bladder lumen, wall thickness, and mucosal surface are documented. In feline patients, bladder wall thickness can range from 1.3 1.7mm, whereas a greater degree of variation exists in canine patients; 2.3mm in a minimally distended bladder and 1.4mm in a moderately distended bladder. 1,2. ultrasound examination allows clear assessment of the bladder wall layers: outer hyperechoic serosa.

Comments are closed.