Types Of Radioactivity Alpha Beta And Gamma Decay 52 Off
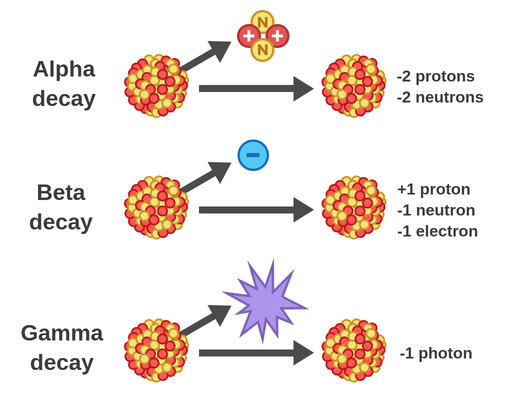
Alpha Beta Gamma Decay Learning objectives. compare qualitatively the ionizing and penetration power of alpha particles (α) (α), beta particles (β) (β), and gamma rays (γ) (γ). express the changes in the atomic number and mass number of a radioactive nuclei when an alpha, beta, or gamma particle is emitted. write nuclear equations for alpha and beta decay. Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of ionizing radiation from nuclear decay and reactions. the three main types of radioactive decay are alpha, beta, and gamma decay, but there are other nuclear reactions responsible for radioactivity. here is a look at the definition of radioactivity, its units, the types of radioactive decay, and how.

Radioactivity And The Types Of Radioactive Decay About the author. there are three major types of radioactive decay: alpha decay, beta decay and gamma decay. alpha decay involves the loss of a helium nucleus, beta decay concerns protons turning into neutrons (or vice versa) and gamma decay involves the emission of energy without changing the original atom. The most common are alpha and beta decay and gamma emission, but the others are essential to an understanding of nuclear decay reactions. figure 1.2.1: common modes of nuclear decay. the different types of decay are alpha, beta, positron emission, electron capture, gamma emission, and spontaneous fission. Often, gamma decay occurs as the result of alpha or beta decay. when a nucleus gives off an alpha or beta particle, a gamma ray is also emitted. alpha or beta decay also excites the resulting nucleus, which then emits another gamma ray to return to the ground state. for instance, when uranium 238 performs alpha decay, it releases a gamma ray. The rate for radioactive decay is: decay rate = λn. with λ = the decay constant for the particular radioisotope. the decay constant, λ, which is the same as a rate constant discussed in the kinetics chapter. it is possible to express the decay constant in terms of the half life, t1 2: λ = ln2 t1 2 = 0.693 t1 2.
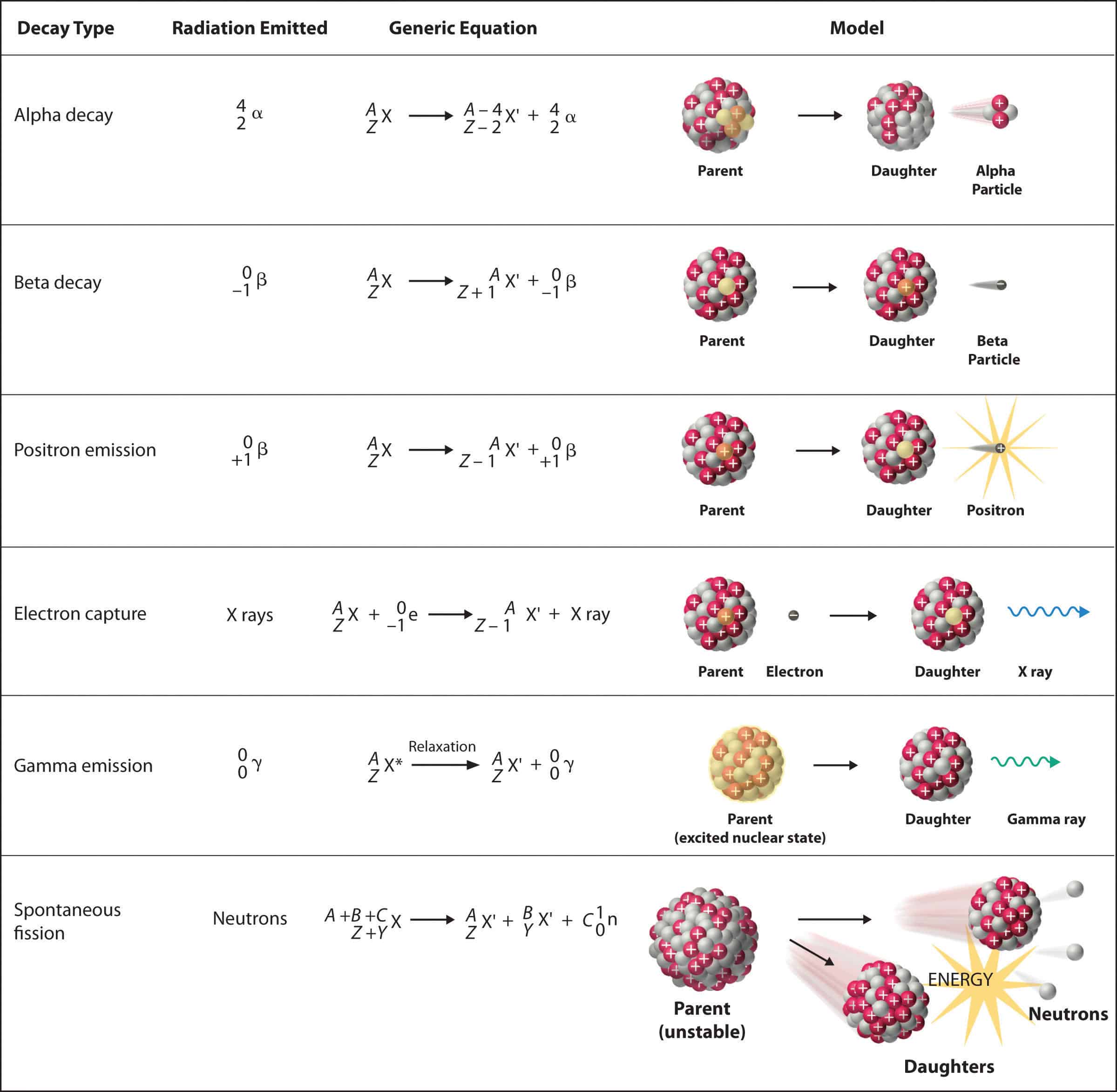
Radioactive Decay Modes Nuclear Power Often, gamma decay occurs as the result of alpha or beta decay. when a nucleus gives off an alpha or beta particle, a gamma ray is also emitted. alpha or beta decay also excites the resulting nucleus, which then emits another gamma ray to return to the ground state. for instance, when uranium 238 performs alpha decay, it releases a gamma ray. The rate for radioactive decay is: decay rate = λn. with λ = the decay constant for the particular radioisotope. the decay constant, λ, which is the same as a rate constant discussed in the kinetics chapter. it is possible to express the decay constant in terms of the half life, t1 2: λ = ln2 t1 2 = 0.693 t1 2. Types of radioactive decay. ernest rutherford’s experiments involving the interaction of radiation with a magnetic or electric field (figure 21.6) helped him determine that one type of radiation consisted of positively charged and relatively massive α particles; a second type was made up of negatively charged and much less massive β particles; and a third was uncharged electromagnetic. Gamma decay often accompanies other types of decay, such as alpha and beta, to release excess energy from the nucleus. formula and calculation of radioactive decay. the calculation of radioactive decay is based on a mathematical equation that describes how the activity (or amount of radioactive material) of a sample changes over time.
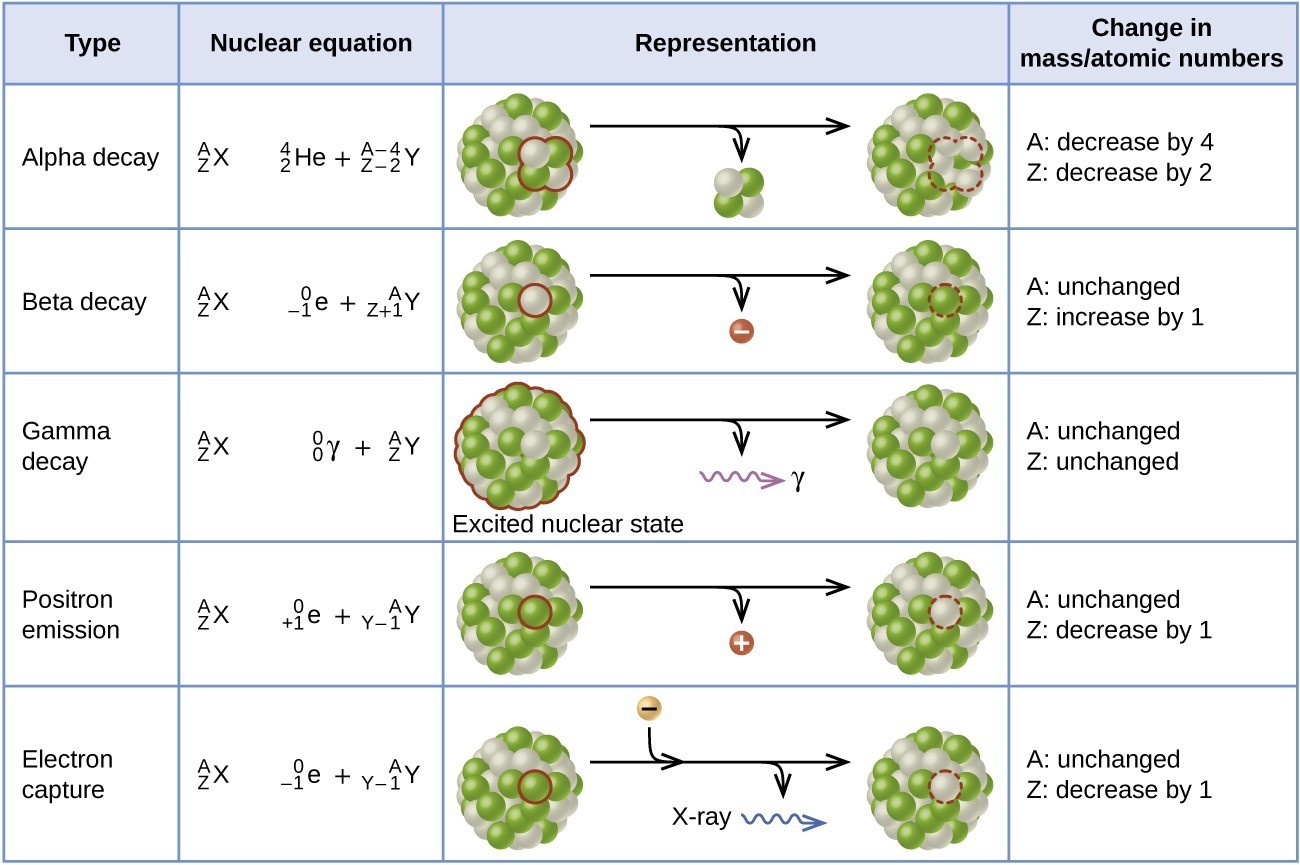
Radioactive Decay Chemistry For Majors Types of radioactive decay. ernest rutherford’s experiments involving the interaction of radiation with a magnetic or electric field (figure 21.6) helped him determine that one type of radiation consisted of positively charged and relatively massive α particles; a second type was made up of negatively charged and much less massive β particles; and a third was uncharged electromagnetic. Gamma decay often accompanies other types of decay, such as alpha and beta, to release excess energy from the nucleus. formula and calculation of radioactive decay. the calculation of radioactive decay is based on a mathematical equation that describes how the activity (or amount of radioactive material) of a sample changes over time.

Radioactive Decay And Nuclear Radiation Shalom Education

Comments are closed.