Types Of Muscle Tissue Skeletal Smooth Cardiac Muscle

Structure Of Three Basic Muscle Types Muscle System Mcat Content Cardiac muscle is found only in the walls of the heart. when cardiac muscle contracts, the heart beats and pumps blood. cardiac muscle contains a great many mitochondria, which produce atp for energy. this helps the heart resist fatigue. contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary, like those of smooth muscle. The three types of muscle cells are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. their morphologies match their specific functions in the body. skeletal muscle is voluntary and responds to conscious stimuli. the cells are striated and multinucleated appearing as long, unbranched cylinders. cardiac muscle is involuntary and found only in the heart.
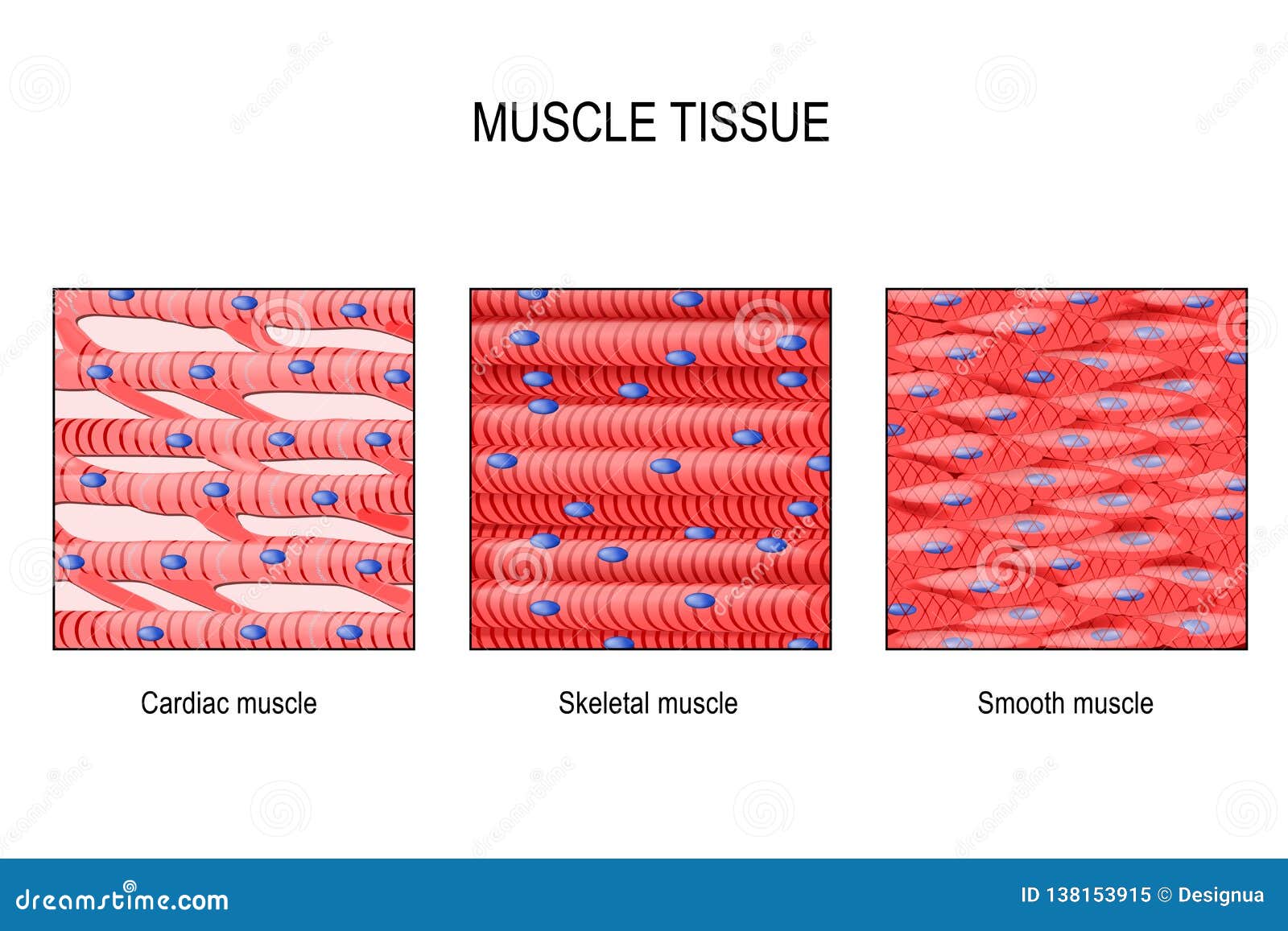
Muscle Tissue Skeletal Smooth And Cardiac Stock Vector Illustration In the muscular system, muscle tissue is categorized into three distinct types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific role. skeletal muscle moves bones and other structures. cardiac muscle contracts the heart to pump blood. the smooth muscle tissue that forms organs. Muscle tissue is subdivided into three broad categories: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. the three types of muscle can be distinguished by both their locations and their microscopic features. skeletal muscle is found attached to bones. it consists of long multinucleate fibers. Muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body. there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. most of the body’s skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart and pumps blood. One of the primary differences between smooth muscle and skeletal cardiac muscle cells is the fact that the contractile proteins (actin myosin) are not organized into sarcomeres; therefore they lack striations as seen in other muscle tissue types. instead, actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments are scattered across the sarcoplasm of the cell.

Comments are closed.