Tropical Rainforest Primary Consumers
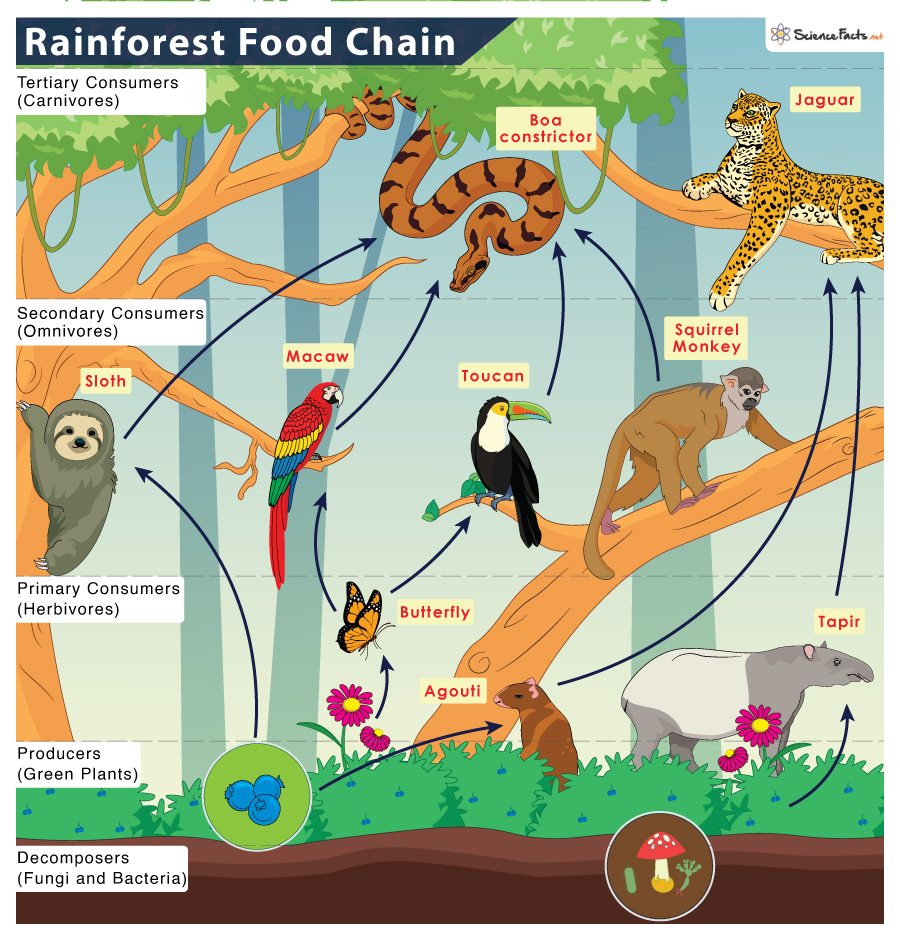
Tropical Rainforest Food Chain Examples And Diagram Learn how energy flows through the rainforest ecosystem with examples of producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. find out how competition and interdependence affect the food chain and the survival of organisms. Learn about the different levels of consumers in the rainforest food chain, from producers to apex predators. find out how monkeys, ocelots, birds of prey and more compete for resources and survive in the jungle.
Food Web For A Tropical Rainforest Tropical rainforest food web | overview & consumers. Examples of primary consumers that live in the tropical rainforest are the proboscis monkey, fruit bat, hummingbird, gorilla, sloth, and lemur. one primary consumer of the tropical rainforest is. Primary consumers feed directly on the primary producers. they are the herbivores of the rainforest and include: insects: such as butterflies and beetles, feeding on leaves and nectar. small mammals: like the agouti, feeding on fruits and seeds. secondary consumers – predators. secondary consumers are the carnivores that prey on primary. Rainforest herbivores, the primary consumers, are the vital link between the plant world and the rainforest food web’s higher levels. these creatures have evolved remarkable ways to thrive on the rainforest’s plant based bounty, developing specialized diets, clever camouflage , and unique survival strategies in a world full of hungry predators.

Rainforest Food Web Primary Consumer Squirrel Monkey Herbivores Primary consumers feed directly on the primary producers. they are the herbivores of the rainforest and include: insects: such as butterflies and beetles, feeding on leaves and nectar. small mammals: like the agouti, feeding on fruits and seeds. secondary consumers – predators. secondary consumers are the carnivores that prey on primary. Rainforest herbivores, the primary consumers, are the vital link between the plant world and the rainforest food web’s higher levels. these creatures have evolved remarkable ways to thrive on the rainforest’s plant based bounty, developing specialized diets, clever camouflage , and unique survival strategies in a world full of hungry predators. In a world of abundant greenery, primary consumers ensure that the sun’s energy does not remain locked within plants but instead flows into many life forms. this transfer is critical for supporting the diverse wildlife found within these tropical realms. primary consumers: act as the vital link between sun soaked plants and higher trophic levels. The primary consumers in the tropical rainforest are leaf cutter ants, tapirs, deers, spiny rats, fruit bats, tamarins, sloths, and others. secondary consumers include birds and snakes, while.

Amazon Rainforest Animals Tropical Rainforest Food Web In a world of abundant greenery, primary consumers ensure that the sun’s energy does not remain locked within plants but instead flows into many life forms. this transfer is critical for supporting the diverse wildlife found within these tropical realms. primary consumers: act as the vital link between sun soaked plants and higher trophic levels. The primary consumers in the tropical rainforest are leaf cutter ants, tapirs, deers, spiny rats, fruit bats, tamarins, sloths, and others. secondary consumers include birds and snakes, while.

Comments are closed.