The Lac Operon Explained
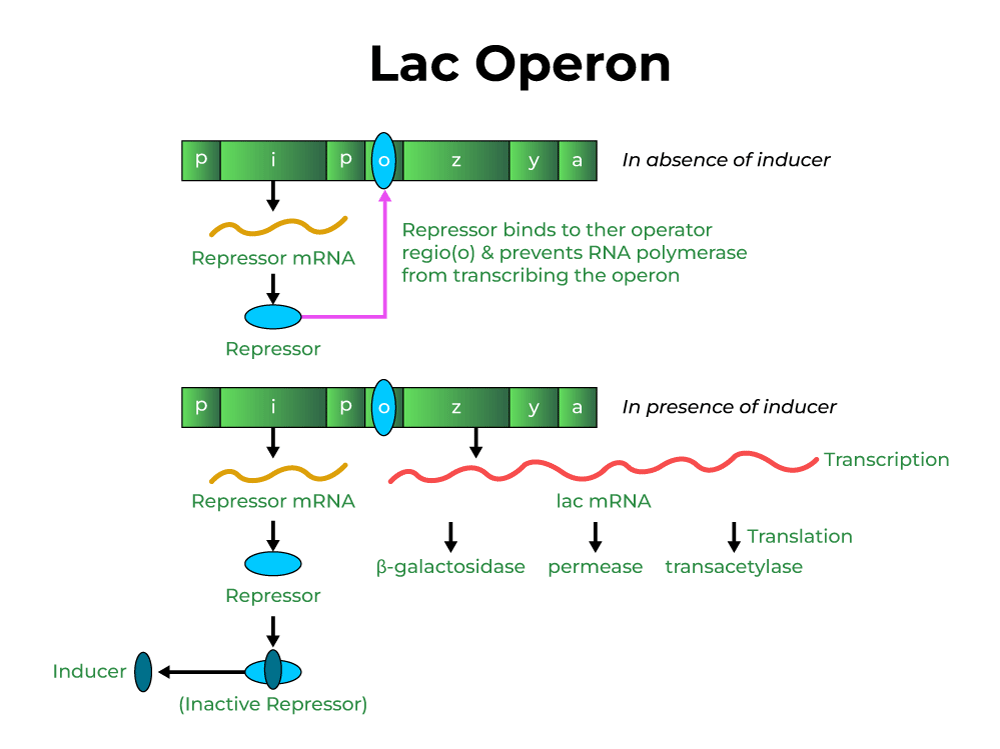
Lac Operon Concept Diagrams Regulation The lac operon is required for the transport and metabolism of lactose. the laci gene is constitutively expressed, meaning that it is continuously transcribed by cells whether lactose is present or not. in the absence of lactose, the laci protein binds to the promoter of the lac operon, preventing rna polymerase (rnap) from binding. The lactose operon (lac operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in e. coli and many other enteric bacteria.although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most enteric bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of β galactosidase. [1].

Lac Operon Concept Diagram Notes Gene Regulation 12.1: the lac operon. The lac operon is a genetic regulatory sequence found in bacteria that codes for the production of enzymes necessary for lactose metabolism. the operon is controlled by a repressor protein, laci, which binds to an operator site on the dna upstream of the genes and prevents their expression. when lactose is present, it binds to laci and. The lactose (lac) operon is a group of genes involved in lactose metabolism. they are found in bacteria, most notably escherichia coli (e. coli), that use lactose as the alternate energy source when glucose is absent. the bacteria express the lac operon genes to use lactose, which encodes key enzymes for lactose uptake and metabolism. The lac operon is a well known example of an inducible gene network that regulates the transport and metabolism of lactose in escherichia coli. it encodes the genes for the internalization of extracellular lactose and then its conversion to glucose. the lactose operon of e. coli is turned on only when lactose is available (and glucose, the.

Comments are closed.