Testicular Torsion Management At Susanne Campbell Blog

Testicular Torsion Management At Susanne Campbell Blog Encoded search term (testicular torsion) and testicular torsion. testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. this is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicle and preserving future fertility. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency, with an annual incidence of 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years. 6 historically, the.

Testicular Torsion Management At Susanne Campbell Blog Testicular torsion (tt), usually a spontaneous twisting of the testis around the spermatic cord causing subsequent ischemia, affects 1 4000 men younger than 25 years of age [1,2]. it is a urological emergency. Testicular torsion is the rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord, which can obstruct its blood supply and lead to necrosis. most often, testicular torsion affects young adolescents. the most common cause is the congenital failure of the testicles to strongly attach to the scrotum. symptoms can include sudden severe pain of the. The role, effectiveness, and statistical significance of diagnostic and management strategies to determine which strategies should be utilized in the emergency setting for the rapid diagnosis and management of testicular torsion are also reviewed. a search strategy was formulated to identify publications relating to testicular torsion. Testicular torsion occurs primarily in pubertal boys and young men. testicular torsion, the spontaneous twisting of the spermatic cord leading to compromise of testicular blood flow, occurs in 1 4000 males younger than 25 years and rarely in newborns. 1 risk factors include underlying bell clapper deformity, undescended testicle, trauma and.

Testicular Torsion Management At Susanne Campbell Blog The role, effectiveness, and statistical significance of diagnostic and management strategies to determine which strategies should be utilized in the emergency setting for the rapid diagnosis and management of testicular torsion are also reviewed. a search strategy was formulated to identify publications relating to testicular torsion. Testicular torsion occurs primarily in pubertal boys and young men. testicular torsion, the spontaneous twisting of the spermatic cord leading to compromise of testicular blood flow, occurs in 1 4000 males younger than 25 years and rarely in newborns. 1 risk factors include underlying bell clapper deformity, undescended testicle, trauma and. Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency. a high index of suspicion is important to ensure timely diagnosis and management. increased public awareness is important in reducing embarrassment and increasing the number of patients presenting within 6 hours of symptoms developing. a history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion. The main symptom of testicular torsion is sudden, severe pain in one of your testicles. it can occur at any time — when you’re awake, sleeping, standing, sitting or active. other testicular torsion symptoms include: painful swelling on one side of your scrotum. a visible lump on a testicle. one testicle is higher in your scrotum than the other.
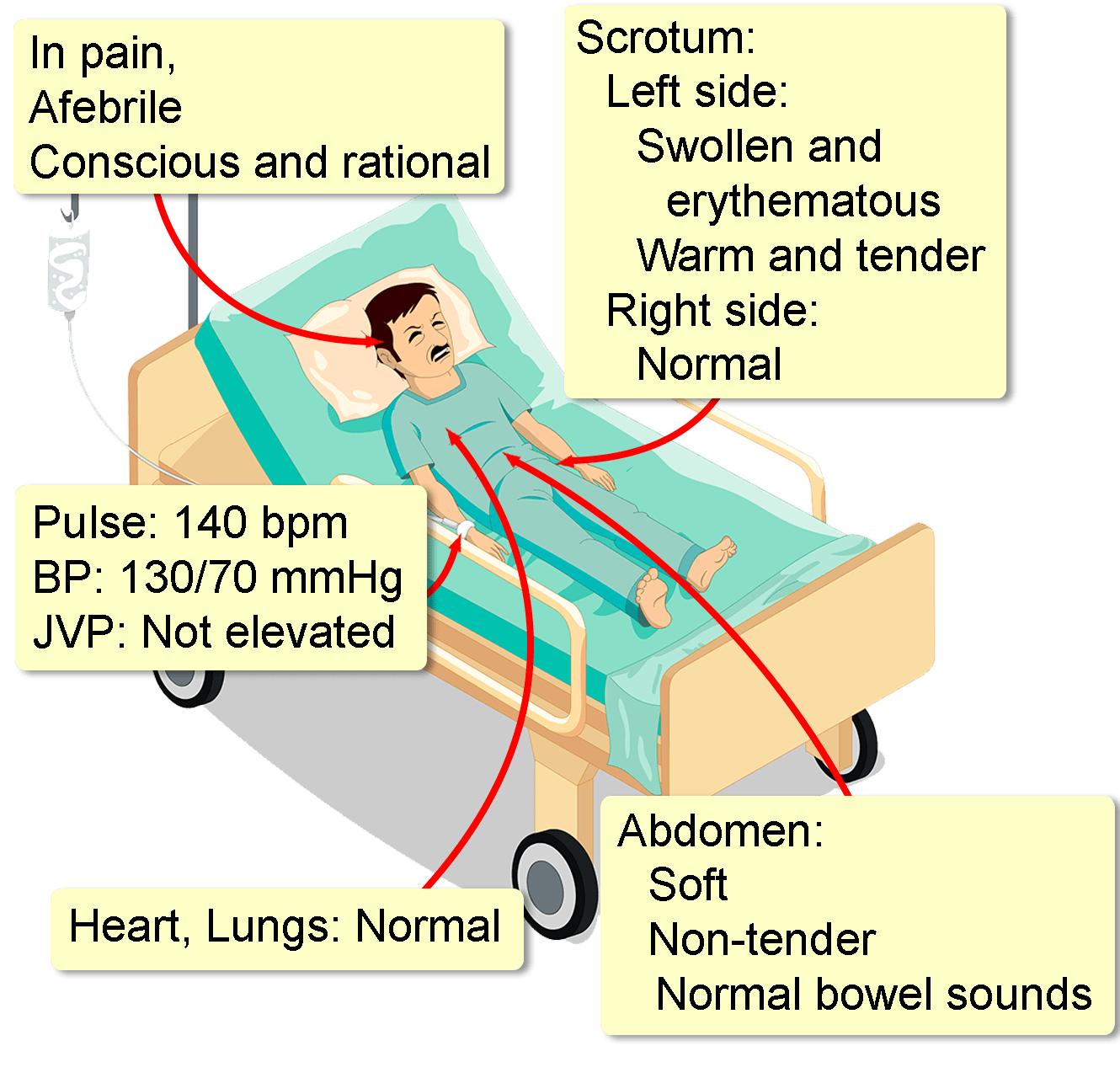
Testicular Torsion Management At Susanne Campbell Blog Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency. a high index of suspicion is important to ensure timely diagnosis and management. increased public awareness is important in reducing embarrassment and increasing the number of patients presenting within 6 hours of symptoms developing. a history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion. The main symptom of testicular torsion is sudden, severe pain in one of your testicles. it can occur at any time — when you’re awake, sleeping, standing, sitting or active. other testicular torsion symptoms include: painful swelling on one side of your scrotum. a visible lump on a testicle. one testicle is higher in your scrotum than the other.

Testicular Torsion Management At Susanne Campbell Blog

Comments are closed.