Tertiary Consumer Definition Science

Ppt The Food Chain Powerpoint Presentation Id 706666 A tertiary consumer is an animal that eats primary and secondary consumers, usually a carnivore or an omnivore. learn about the ecological role of tertiary consumers, their examples in terrestrial and marine ecosystems, and how humans fit into this category. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. it eats both primary and secondary consumers as its main source of food. learn about some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and their ecological roles.
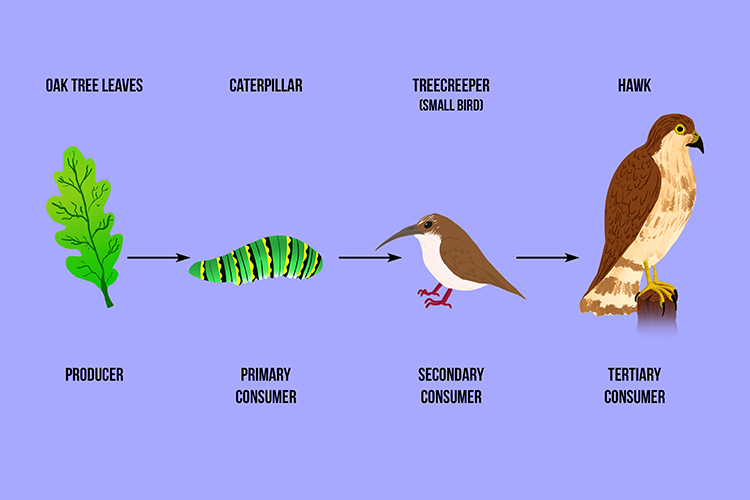
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain The tertiary consumers could both be exclusively carnivorous, or even omnivorous, and feed on both primary consumers and secondary consumers. definition of tertiary consumer. tertiary consumers are animals that consume other animals to obtain nutrition from them. most importantly, they are at the highest level of the food chain. function of. Consumers are organisms that consume (eat) other organisms to sustain themselves. organisms that are consumers include heterotrophs like some animals, fungi, and bacteria. a tertiary consumer is an organism that obtains the energy it needs from consuming other consumers at different levels, from eating primary consumers or secondary consumers. Tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the third trophic level in a food chain, primarily feeding on secondary consumers. they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the population of other species. Consumer (food chain) a consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually.
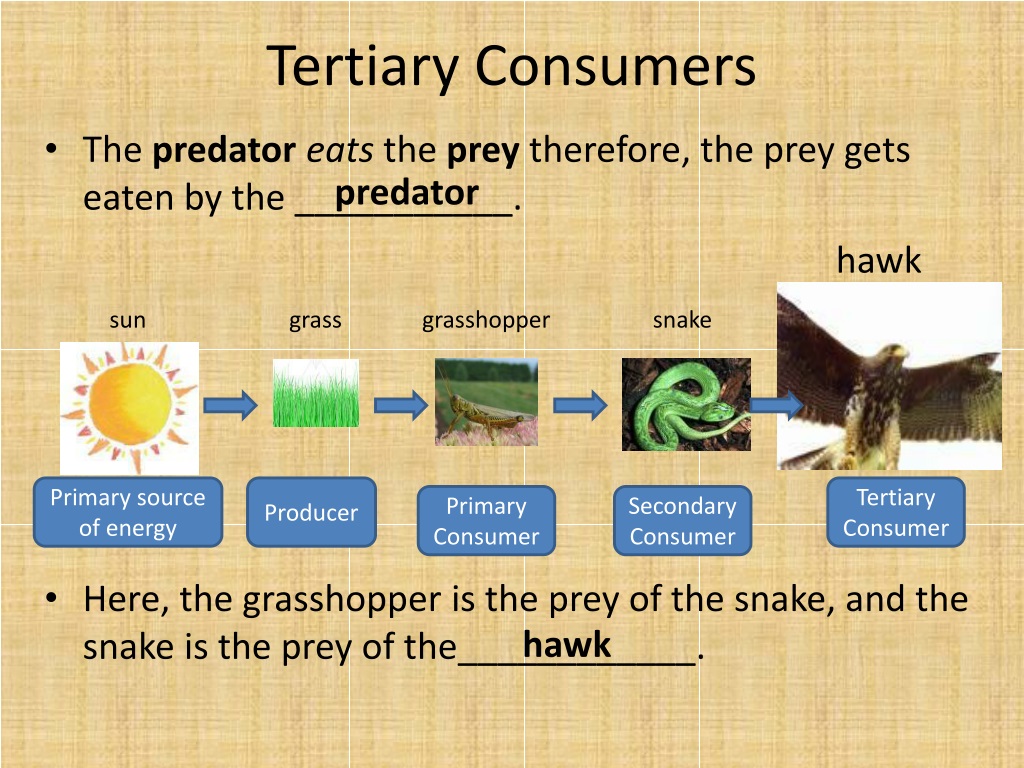
Ppt Food Chains Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 9522090 Tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the third trophic level in a food chain, primarily feeding on secondary consumers. they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the population of other species. Consumer (food chain) a consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually. Tertiary consumer examples. some examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, sea lions, eagles, hawks, lions, tigers, crocodiles, pythons, and polar bears. these animals rule their range, eating both secondary and primary consumers and easily defending their territories from other species. many tertiary consumers also don’t have to compete. Tertiary consumers play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the population of secondary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers include large predators like lions, eagles, and sharks. they are less abundant than primary and secondary consumers due to energy loss at each trophic level. tertiary consumers can.
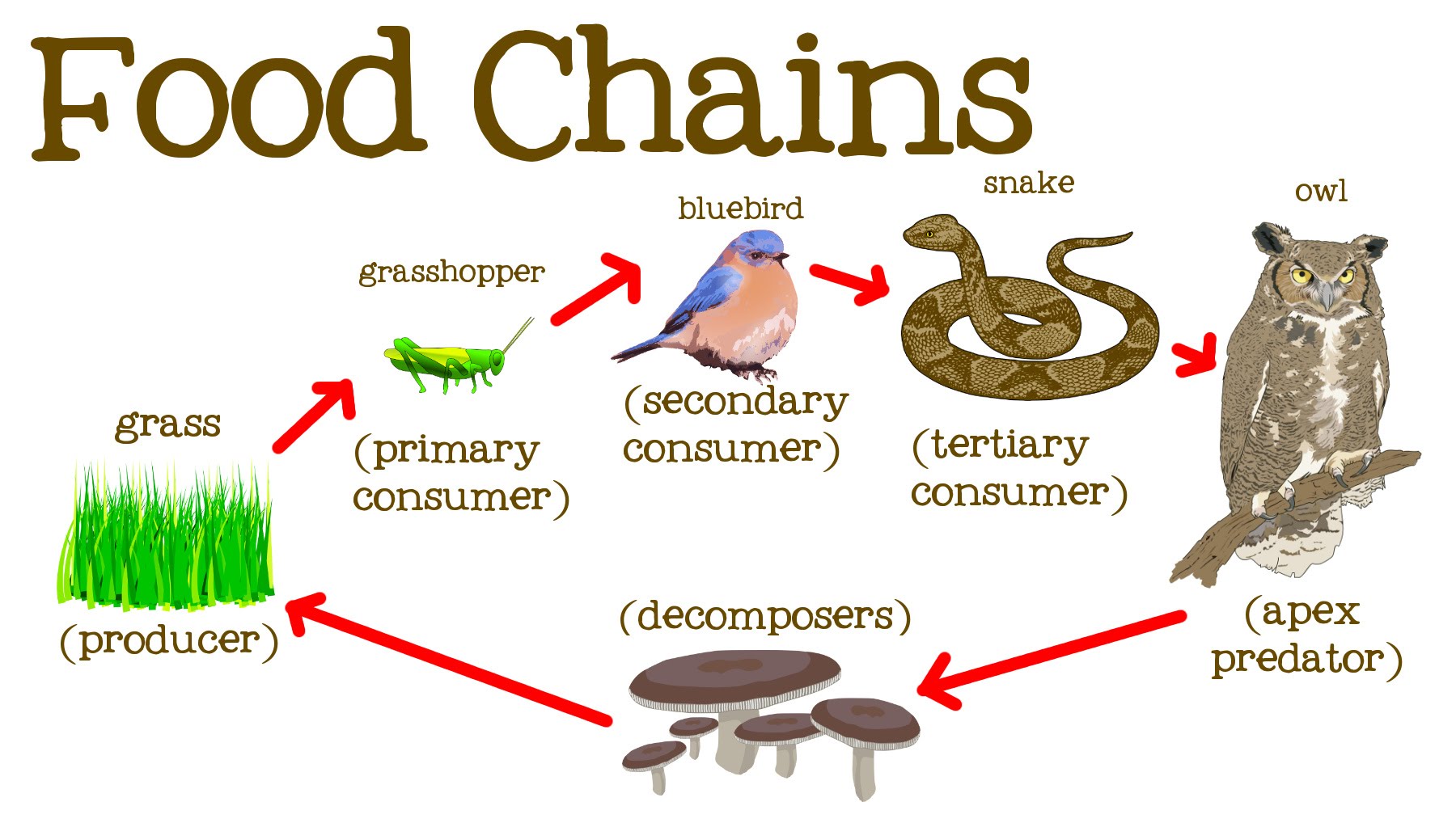
What Is A Tertiary Consumer In An Ecosystem Tertiary consumer examples. some examples of tertiary consumers include sharks, sea lions, eagles, hawks, lions, tigers, crocodiles, pythons, and polar bears. these animals rule their range, eating both secondary and primary consumers and easily defending their territories from other species. many tertiary consumers also don’t have to compete. Tertiary consumers play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by controlling the population of secondary consumers. examples of tertiary consumers include large predators like lions, eagles, and sharks. they are less abundant than primary and secondary consumers due to energy loss at each trophic level. tertiary consumers can.

Comments are closed.