Synchronous Urinary Bladder And Prostate Cancer вђ Radiology

Synchronous Urinary Bladder And Prostate Cancer вђ Radiology Cas A study reported a prevalence rate of 1.7% of multiple primary malignant tumours. synchronous bladder and prostate cancers in an elderly is not uncommon. a study shown 27% unsuspected prostate cancer in cystoprostatectomy specimen of bladder cancer patients. however, lower incidence in one of the study done in asian population, about 4%. Terminology. the aim of prostate mri is to detect clinically significant prostate cancer, as insignificant prostate cancer is common 35. however, this term is without a consensus definition 35,36 (c. 2024) and has been defined as one or more of the following (noting variability within criterion) 31 35: prostate specific antigen (psa) >10 ng ml.
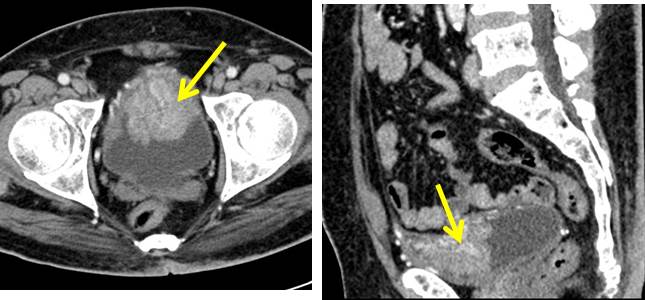
Synchronous Urinary Bladder And Prostate Cancer вђ Radiology Cas This has increased the desire to preserve the continence and erectile function in patient undergoing rcp for bladder cancer; however, the risk of not removing the synchronous pca should be considered. in effect, in our cohort, 33,3% of patients was affected by clinically significant prostate cancer. Citation, doi, disclosures and article data. transitional cell carcinoma (tcc), also called urothelial cell carcinoma (ucc) of the bladder, is the most common primary neoplasm of the urinary bladder, and bladder tcc is the most common tumor of the entire urinary system. this article concerns itself with transitional cell carcinomas of the. It is an accurate tool in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. in pi rads v2.1 clinically significant cancer is defined on pathology as: gleason score ≥ 7 including 3 4 with prominent but not predominant gleason 4 component and or. tumor volume > 0.5cc and or. extraprostatic extension (epe). The management of advanced prostate cancer has changed substantially with the availability of multiple effective novel treatments, which has led to improved disease survival. in the era of personalized cancer treatments, more precise imaging may help physicians deliver better care. more accurate local staging and earlier detection of metastatic disease, accurate identification of.

Synchronous Urinary Bladder And Prostate Cancer вђ Radiology Cas It is an accurate tool in the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer. in pi rads v2.1 clinically significant cancer is defined on pathology as: gleason score ≥ 7 including 3 4 with prominent but not predominant gleason 4 component and or. tumor volume > 0.5cc and or. extraprostatic extension (epe). The management of advanced prostate cancer has changed substantially with the availability of multiple effective novel treatments, which has led to improved disease survival. in the era of personalized cancer treatments, more precise imaging may help physicians deliver better care. more accurate local staging and earlier detection of metastatic disease, accurate identification of. Bladder cancer is a broad term used to describe all types of cancers affecting the urinary bladder: transitional cell carcinoma (urinary bladder): most common primary neoplasm of the bladder. squamous cell carcinoma (urinary bladder): accounts for around 3 8% of all bladder cancers. adenocarcinoma (urinary bladder): accounts for around 1% of. 8.4.3 radiotherapy for metastatic prostate cancer radiation therapy for prostate cancer with oligometastases definition of oligometastases. the theory of oligometastases was first proposed by hellman and weichselbaum as an intermediate state between localized and widespread systemic disease.

Synchronous Urinary Bladder And Prostate Cancer вђ Radiology Cas Bladder cancer is a broad term used to describe all types of cancers affecting the urinary bladder: transitional cell carcinoma (urinary bladder): most common primary neoplasm of the bladder. squamous cell carcinoma (urinary bladder): accounts for around 3 8% of all bladder cancers. adenocarcinoma (urinary bladder): accounts for around 1% of. 8.4.3 radiotherapy for metastatic prostate cancer radiation therapy for prostate cancer with oligometastases definition of oligometastases. the theory of oligometastases was first proposed by hellman and weichselbaum as an intermediate state between localized and widespread systemic disease.

Synchronous Urinary Bladder And Prostate Cancer вђ Radiology Cas

Comments are closed.