Solved Which Of The Following Reactions And Decays Are Chegg

Solved For Each Of The Following Decays Or Reactions Chegg Part a. for the decay reaction. k → μ ν μ. view the full answer step 2. unlock. step 3. unlock. step 4. unlock. Which of the following reactions and decays are possible? for those forbidden, explain what laws are violated. (a) π p n η0 this reaction violates (b) π p n π0 this reaction violates (c) π p p e this reaction violates (d) p e ve this decay violates (e) μ e vµ this decay violates (f) p n e ve this decay violates.

Solved The Following Reactions Or Decays Involve One Or More Chegg Question: the following reactions or decays involve one or more neutrinos. in each case, supply the missing neutrino (νe, νμ, or ντ) or antineutrino. (use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as necessary: nu bare, nu barμ, or nu barτ. use a plus sign to assemble a collection of two or more neutrinos, for example. Example 12.5.3 12.5. 3: the integrated rate law for a second order reaction. the reaction of butadiene gas (c 4 h 6) with itself produces c 8 h 12 gas as follows: 2c4h6(g) c8h12(g) 2 c 4 h 6 (g) c 8 h 12 (g) the reaction is second order with a rate constant equal to 5.76 × 10 −2 l mol min under certain conditions. Nuclear reaction energy, such as released in α decay, can be found using the equation e = (Δm)c2. we must first find Δm, the difference in mass between the parent nucleus and the products of the decay. this is easily done using masses given in appendix a. solution. the decay equation was given earlier for 239pu; it is. Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable isotope (the parent isotope or parent nuclide) undergoes a reaction, producing at least one daughter nuclide. the daughter(s) may be either stable or unstable isotopes. some types of decay involve transmutation, where the parent isotope decays and yields a daughter isotope of a different element.

Solved Given The Following Write The Decay Reaction For Chegg Nuclear reaction energy, such as released in α decay, can be found using the equation e = (Δm)c2. we must first find Δm, the difference in mass between the parent nucleus and the products of the decay. this is easily done using masses given in appendix a. solution. the decay equation was given earlier for 239pu; it is. Radioactive decay occurs when an unstable isotope (the parent isotope or parent nuclide) undergoes a reaction, producing at least one daughter nuclide. the daughter(s) may be either stable or unstable isotopes. some types of decay involve transmutation, where the parent isotope decays and yields a daughter isotope of a different element. We're going to have reactions here or we have to indicate the type of neutrino needed to balance the reaction. so in this first case where we see this mule on, not only do we have to conserve left on number, but we have to conserve the specific type of lepton number. The half life of a first order reaction is a constant that is related to the rate constant for the reaction: t 1 2 = 0.693 k. radioactive decay reactions are first order reactions. the rate of decay, or activity, of a sample of a radioactive substance is the decrease in the number of radioactive nuclei per unit time.
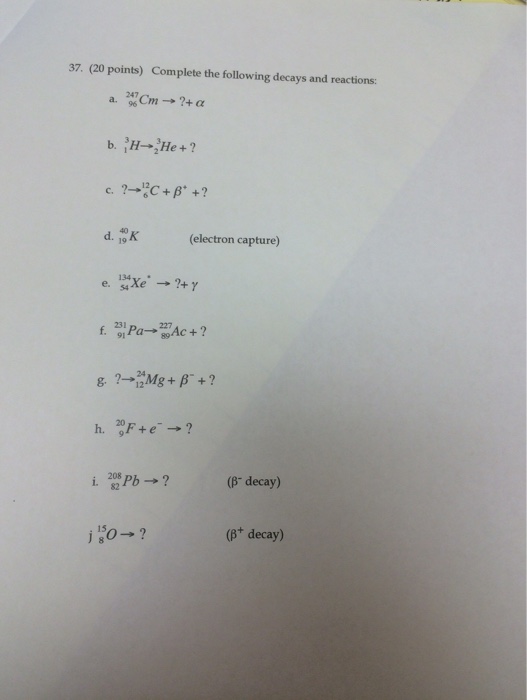
Solved Complete The Following Decays And Reactions 247 96cm Chegg We're going to have reactions here or we have to indicate the type of neutrino needed to balance the reaction. so in this first case where we see this mule on, not only do we have to conserve left on number, but we have to conserve the specific type of lepton number. The half life of a first order reaction is a constant that is related to the rate constant for the reaction: t 1 2 = 0.693 k. radioactive decay reactions are first order reactions. the rate of decay, or activity, of a sample of a radioactive substance is the decrease in the number of radioactive nuclei per unit time.

Comments are closed.