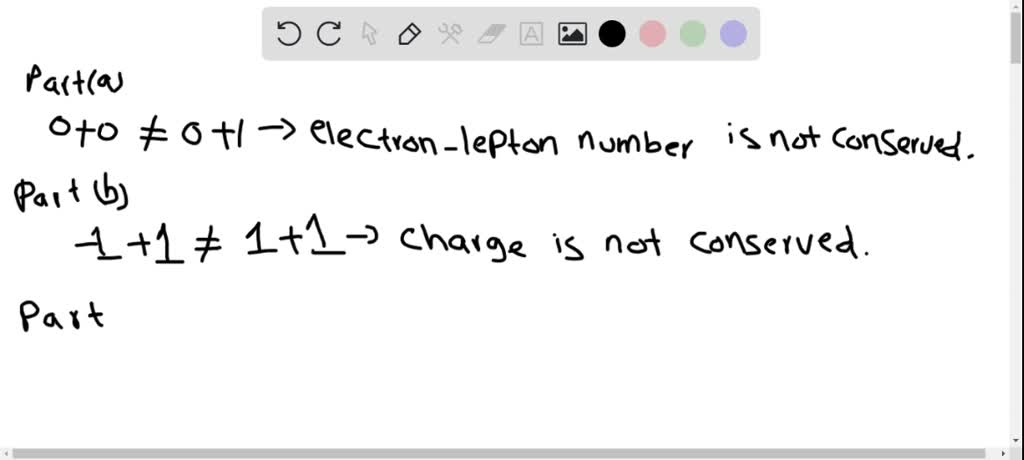
Solved The Following Decays Are Forbidden Determine A Conservation

Solved For Each Of The Following Forbidden Decays Determine What Solutions for chapter 30 problem 35ap: each of the following decays is forbidden. for each process determine a conservation law that is violated.(a) μ− → e− γ(b) n → p e− νe(c) a0 → p π0(d) p → e π0(e) Ξ0 → n π0 … get solutions get solutions get solutions done loading looking for the textbook?. Question: consider the following forbidden decays. a. Λ0→p π0 b. p→e π0 c. Ξ0→n π0 d. n→p e− ve e. μ−→e− γ for each of these decays, select all of the following conservation laws which are violated. 1. electron lepton number 2. muon lepton number 3. baryon number 4. charge 5. strangeness. there are 3 steps to solve this one.
Solved The Following Decays Are Forbidden Determine A Conservation Use baryon number, lepton number, and strangeness conservation to determine if particle reactions or decays occur. conservation laws are critical to an understanding of particle physics. strong evidence exists that energy, momentum, and angular momentum are all conserved in all particle interactions. the annihilation of an electron and positron. Step 1. the charge on left side of equation is − 1 and the total charge on right side of equation is also − 1 2. each of the following decays is forbidden. for each, identify the conservation law (s) that is (are) not obeyed. (a) μ− →e− γ (b) Λ0 →p π0 (c) p→π π0 (d) Ξ0 →n π0. Nuclear reaction energy, such as released in α decay, can be found using the equation e = (Δm)c2. we must first find Δm, the difference in mass between the parent nucleus and the products of the decay. this is easily done using masses given in appendix a. solution. the decay equation was given earlier for 239pu; it is. Allowed and forbidden particle decays. discrete particles tend to be unstable and to decay into two or more particles of lesser mass unless they are forbidden to do so by some principle or conservation law. this tendency is sometimes referred to as the totalitarian principle. it is instructive to look at some allowed and forbidden decays and to.
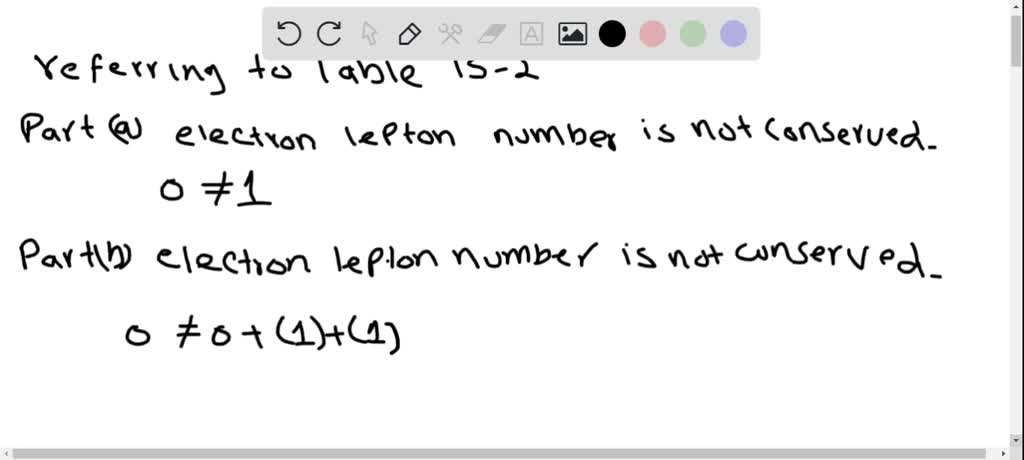
Solved The Following Decays Are Forbidden Determine A Conservation Law Nuclear reaction energy, such as released in α decay, can be found using the equation e = (Δm)c2. we must first find Δm, the difference in mass between the parent nucleus and the products of the decay. this is easily done using masses given in appendix a. solution. the decay equation was given earlier for 239pu; it is. Allowed and forbidden particle decays. discrete particles tend to be unstable and to decay into two or more particles of lesser mass unless they are forbidden to do so by some principle or conservation law. this tendency is sometimes referred to as the totalitarian principle. it is instructive to look at some allowed and forbidden decays and to. So the 40 for conservation laws are listed on the right and this is what we will check them. akins to see which one day actually violate starting from the easiest richest in charge for the by barrel number dead lepton number and 20 strangeness value so free first. Problem 11 easy difficulty. the following decays are forbidden. determine a conservation law that each violates. (a) $\mu^{ } \rightarrow \mathrm{e}^{ } \gamma$.

Comments are closed.