Solved Complete The Following Equations For Nuclear Decay Chegg

Solved Complete The Following Equations For Nuclear Decay Chegg 2. complete the following equations for nuclear decay, and state whether each process is alpha decay, beta decay, or gamma decay. (a) 5 8 b → (b) 84 210 po → 82 206 pb (c) 84 207 po ∗ → 84 207 po. 1. complete the following equations for nuclear decay, and state whether each process is alpha decay, beta decay, or gamma decay. 2. complete the following equation for fission. 3. complete the following equation for fission. 252 98 cf > 4 (1 0) n. here’s the best way to solve it.
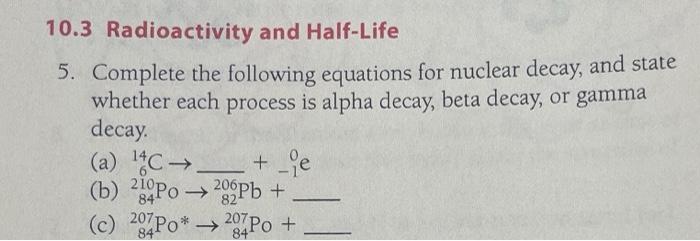
Solved Complete The Following Equations For Nuclear Decay Chegg Nuclear reaction energy, such as released in α decay, can be found using the equation e = (Δm)c2. we must first find Δm, the difference in mass between the parent nucleus and the products of the decay. this is easily done using masses given in appendix a. solution. the decay equation was given earlier for 239pu; it is. (a) the decay equation is 222 ra → a x 14 c. identify the nuclide a x. (b) find the energy emitted in the decay. the mass of 222 ra is 222.015353 u. (a) write the complete α decay equation for 226 ra. (b) find the energy released in the decay. (a) write the complete α decay equation for 249 cf. (b) find the energy released in the decay. The nuclear reaction can be written as: 12 25 mg 2 4 he 1 1 h z a x. where a is the mass number and z is the atomic number of the new nuclide, x. because the sum of the mass numbers of the reactants must equal the sum of the mass numbers of the products: 25 4 = a 1, or a = 28. similarly, the charges must balance, so:. The general reaction is as follows: a zxparent → a − 4 z − 2x ′ daughter 4 2αalphaparticle. the daughter nuclide contains two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent. thus α particle emission produces a daughter nucleus with a mass number a − 4 and a nuclear charge z − 2 compared to the parent nucleus.

Solved Complete The Following Nuclear Equation For The Decay Cheggо The nuclear reaction can be written as: 12 25 mg 2 4 he 1 1 h z a x. where a is the mass number and z is the atomic number of the new nuclide, x. because the sum of the mass numbers of the reactants must equal the sum of the mass numbers of the products: 25 4 = a 1, or a = 28. similarly, the charges must balance, so:. The general reaction is as follows: a zxparent → a − 4 z − 2x ′ daughter 4 2αalphaparticle. the daughter nuclide contains two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent. thus α particle emission produces a daughter nucleus with a mass number a − 4 and a nuclear charge z − 2 compared to the parent nucleus. 10.3 radioactivity and half life 5. complete the following equations for nuclear decay, and state whether each process is alpha decay, beta decay, or gamma decay. (a) 6 14 c → − 1 o e (b) 84 210 po → 82 206 pb (c) 84 207 po ∗ → 84 207 po. Problem 3.1.10. technetium 99 is prepared from 98 mo. molybdenum 98 combines with a neutron to give molybdenum 99, an unstable isotope that emits a β particle to yield an excited form of technetium 99, represented as 99 tc *. this excited nucleus relaxes to the ground state, represented as 99 tc, by emitting a γ ray.

Solved 5 Complete The Following Nuclear Decay Equations A Che 10.3 radioactivity and half life 5. complete the following equations for nuclear decay, and state whether each process is alpha decay, beta decay, or gamma decay. (a) 6 14 c → − 1 o e (b) 84 210 po → 82 206 pb (c) 84 207 po ∗ → 84 207 po. Problem 3.1.10. technetium 99 is prepared from 98 mo. molybdenum 98 combines with a neutron to give molybdenum 99, an unstable isotope that emits a β particle to yield an excited form of technetium 99, represented as 99 tc *. this excited nucleus relaxes to the ground state, represented as 99 tc, by emitting a γ ray.
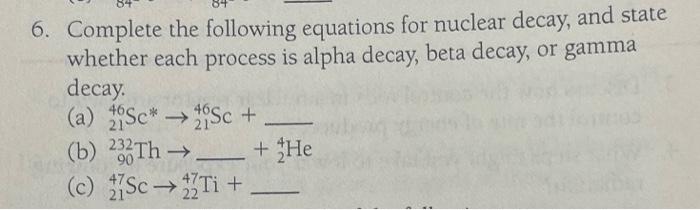
Solved Complete The Following Equations For Nuclear Decay Chegg

Comments are closed.