Solved 2 Consider The Following Nuclear Decay A B C In Chegg

Solved 2 Consider The Following Nuclear Decay A B C In Chegg Question: consider the following nuclear decay: a b c in which the nuclei a and b decay with decay constants λa and λb, respectively. nucleus c is stable. (a) show that in terms of the fraction of nuclei a that hasn't decayed, the number of nuclei of b is given by: nb=n0λb−λaλa(f−fλb λa) where f is the fraction of a that hasn't decay. There are 2 steps to solve this one. 2. consider the following nuclear decay: 222rn 218po a. (a) if the kinetic energy of the alpha particle emitted is 6.61 mev and the mass of 218 po is 218.008973 amu, calculate the mass of 222rn. assume m (a) = 4.001506 amu and 1 amu = 931.5 mev c2. (2 marks) (b) show that for an alpha decay, the kinetic.

Solved Consider The Following Nuclear Decay Equations Chegg The general reaction is as follows: a zxparent → a − 4 z − 2x ′ daughter 4 2αalphaparticle. the daughter nuclide contains two fewer protons and two fewer neutrons than the parent. thus α particle emission produces a daughter nucleus with a mass number a − 4 and a nuclear charge z − 2 compared to the parent nucleus. N = n0 2n. if the decay constant (λ) is large, the half life is small, and vice versa. to determine the relationship between these quantities, note that when t = t1 2, then n = n0 2. thus, equation 10.4.4 can be rewritten as. n0 2 = n0e − λt1 2. dividing both sides by n0 and taking the natural logarithm yields. There are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (α) beta (β) and gamma (γ). the α decay equation is a zxn →a − 4 z − 2yn − 2 4 2he2. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy e related to the mass destroyed Δm by e = (Δm)c2. there are three forms of beta decay. Problem 3.1.10. technetium 99 is prepared from 98 mo. molybdenum 98 combines with a neutron to give molybdenum 99, an unstable isotope that emits a β particle to yield an excited form of technetium 99, represented as 99 tc *. this excited nucleus relaxes to the ground state, represented as 99 tc, by emitting a γ ray.

Solved Complete The Following Equations For Nuclear Decay Chegg There are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (α) beta (β) and gamma (γ). the α decay equation is a zxn →a − 4 z − 2yn − 2 4 2he2. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy e related to the mass destroyed Δm by e = (Δm)c2. there are three forms of beta decay. Problem 3.1.10. technetium 99 is prepared from 98 mo. molybdenum 98 combines with a neutron to give molybdenum 99, an unstable isotope that emits a β particle to yield an excited form of technetium 99, represented as 99 tc *. this excited nucleus relaxes to the ground state, represented as 99 tc, by emitting a γ ray. Radioactive dating. radioactive dating is a technique that uses naturally occurring radioactivity to determine the age of a material, such as a rock or an ancient artifact. . the basic approach is to estimate the original number of nuclei in a material and the present number of nuclei in the material (after decay), and then use the known value of the decay constant λ λ and equation 10.10 to. On the right hand side, sum of superscripts = 142 a 3 (1) = 145 a. a = 236 – 145 = 91. the symbol for a nucleus is a zx. the element with z = 36 is krypton. thus, the unknown nucleus is 91 36kr. the balanced nuclear equation is. 235 92 u 1 0 n →142 56 ba 91 36 kr 31 0n. answer link. the sums of the superscripts and of the.
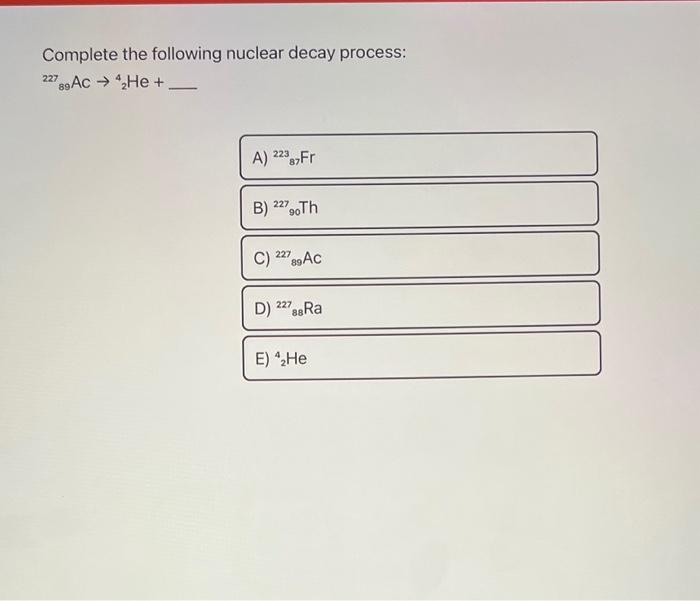
Solved Complete The Following Nuclear Decay Process Chegg Radioactive dating. radioactive dating is a technique that uses naturally occurring radioactivity to determine the age of a material, such as a rock or an ancient artifact. . the basic approach is to estimate the original number of nuclei in a material and the present number of nuclei in the material (after decay), and then use the known value of the decay constant λ λ and equation 10.10 to. On the right hand side, sum of superscripts = 142 a 3 (1) = 145 a. a = 236 – 145 = 91. the symbol for a nucleus is a zx. the element with z = 36 is krypton. thus, the unknown nucleus is 91 36kr. the balanced nuclear equation is. 235 92 u 1 0 n →142 56 ba 91 36 kr 31 0n. answer link. the sums of the superscripts and of the.

Solved Consider The Following Nuclear Decay Chegg

Comments are closed.