Secondary Consumer In Food Chain
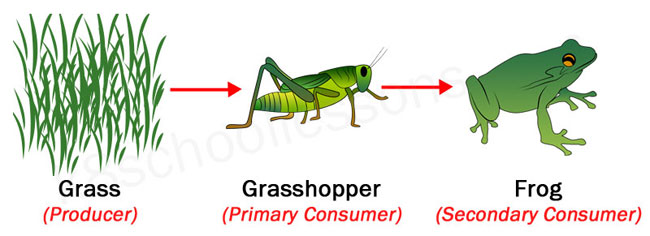
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Learn what a secondary consumer is, how it functions in the food chain, and what types of secondary consumers exist. see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers, and how they relate to primary and tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain. they are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. while primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat. Higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. figure \(\pageindex{2}\): these are the trophic levels of a food. Secondary consumer definition, examples & food chain. Food chain national geographic society food chain.
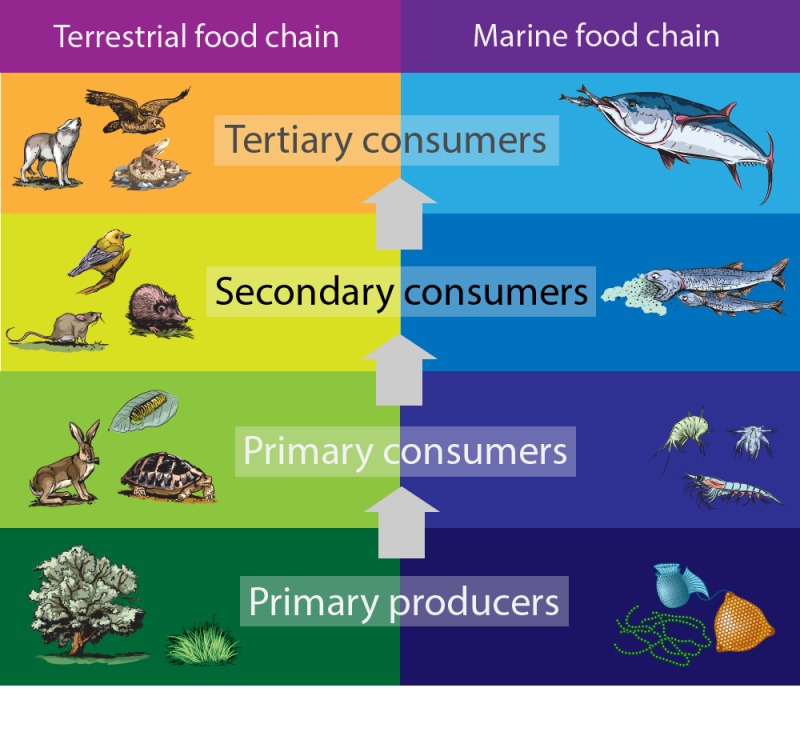
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Secondary consumer definition, examples & food chain. Food chain national geographic society food chain. In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. there is a single path through the chain. each organism in a food chain occupies what is called a trophic level. ###pii ipv4###: food chains and food webs.

The Food Chain For Kids Hubpages In ecology, a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass: primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. there is a single path through the chain. each organism in a food chain occupies what is called a trophic level. ###pii ipv4###: food chains and food webs.

Comments are closed.