Secondary Consumer Example

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Learn what a secondary consumer is and see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers. find out how they function in the food chain and why they are important for the ecosystem. Learn what secondary consumers are, how they fit into the trophic pyramid, and what types of organisms they include. see examples of carnivores and omnivores that feed on primary consumers in different ecosystems.
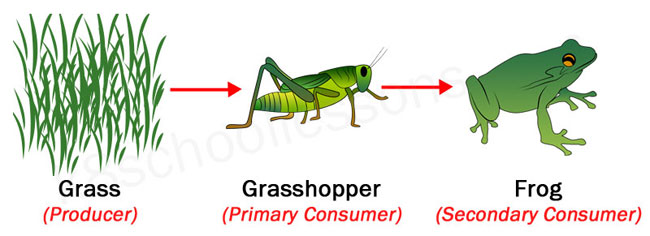
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Learn what secondary consumers are, how they feed on primary consumers, and why they are important for ecosystems. see examples of aquatic and terrestrial secondary consumers, and how they can switch between trophic levels. We can see examples of these levels in the diagram below. the green algae are primary producers that get eaten by mollusks (the primary consumers). the mollusks then become lunch for the slimy sculpin fish, a secondary consumer, which is itself eaten by a larger fish, the chinook salmon (tertiary consumer). Examples of secondary consumers fall into one of two categories: carnivores or omnivores. carnivores are animals that eat only the meat of other animals. carnivores come in all shapes and sizes. For instance, a wolf preying on rabbits or a frog eating insects are examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. omnivorous diet: some secondary consumers are omnivores, so their diet includes both animal and plant based foods. an example is a bear that eats fish (a primary consumer) and berries (a primary producer).

Comments are closed.