Savings Vs Debt Portfolio Consumer Math Answers

Consumer Math Unit 1 Savings Vs Debt Portfolio Doc Card Name Apr View consumer math unit 1 savings vs debt portfolio.doc from math unit 1 at connections academy online. card name (apr %) mark2 (6.5%) bee4 (10.1%) existing balance $475.00 $1,311.48 credit ai chat with pdf. View savings vs debts portfolio.doc from aa 1card name (apr %) mark2 (6.5%) bee4 (10.1%) existing balance $475.00 $1,311.48 credit limit $3,000.00 $2,500.00 you have $400.00 each month to pay off ai chat with pdf.

Chapter 3 Consumer Maths Saving And Investments Part 3 Risk Consumer math unit 1 savings vs debt portfolio.doc view consumer math unit 1 savings vs debt portfolio.doc from math unit 1 at connections 1544961 762016 104846 am 1988337915.docx. Emergency savings. cash set aside to cover the cost of unexpected events. liquidity. is how quickly and easily you can access your assets and convert them into cash. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like interest rate, compound interest, the rule of 72 and more. Consumer math b. unit 1 debt vs savings. 1.1 1.4 secured and unsecured debt. 1.6 1.9 how credit affects budget. 1.9 savings vs debt portfolio. 1.10 1.13 new used cars and renting or buying a home. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like an example of an unsecured debt is a (n) ., unsecured debt interest rates are usually when compared to secured debt., you have a student loan for $12,674.00. what number is the rate multiplier in the i = prt formula if you have an average credit rating? and more.
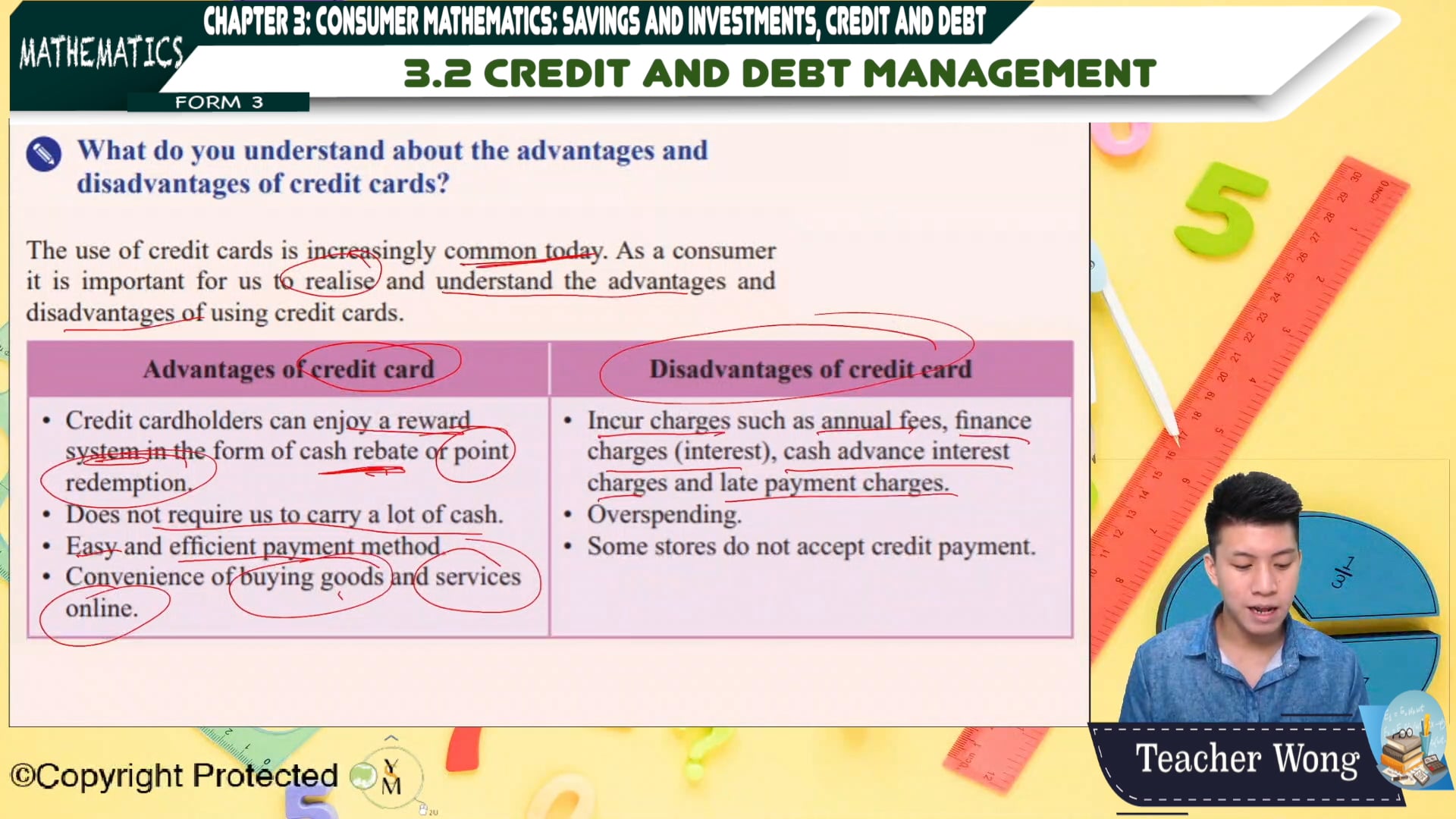
Topic 03 Consumer Mathematics вђ Savings And Investments Credit And Consumer math b. unit 1 debt vs savings. 1.1 1.4 secured and unsecured debt. 1.6 1.9 how credit affects budget. 1.9 savings vs debt portfolio. 1.10 1.13 new used cars and renting or buying a home. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like an example of an unsecured debt is a (n) ., unsecured debt interest rates are usually when compared to secured debt., you have a student loan for $12,674.00. what number is the rate multiplier in the i = prt formula if you have an average credit rating? and more. A. pay the minimum amount required each bill. u1 l5 future wealth. you should have revolving credit lines. d. 2 to 6. the maximum outstanding balance you should have on a credit card with a $4,000.00 limit is . c. $2,000.00. at the start of january, you have a credit card with a balance of $498, a credit limit of $900, and an interest. Note that your answer may come out slightly differently if you had evaluated the logs to decimals and rounded during your calculations, but your answer should be close. for example if you rounded log(2) to 0.301 and log(1.005) to 0.00217, then your final answer would have been about 11.577 years.

Investing Consumer Math Unit Notes Activities Quiz Presentation A. pay the minimum amount required each bill. u1 l5 future wealth. you should have revolving credit lines. d. 2 to 6. the maximum outstanding balance you should have on a credit card with a $4,000.00 limit is . c. $2,000.00. at the start of january, you have a credit card with a balance of $498, a credit limit of $900, and an interest. Note that your answer may come out slightly differently if you had evaluated the logs to decimals and rounded during your calculations, but your answer should be close. for example if you rounded log(2) to 0.301 and log(1.005) to 0.00217, then your final answer would have been about 11.577 years.

Comments are closed.