Reproductive System Testes
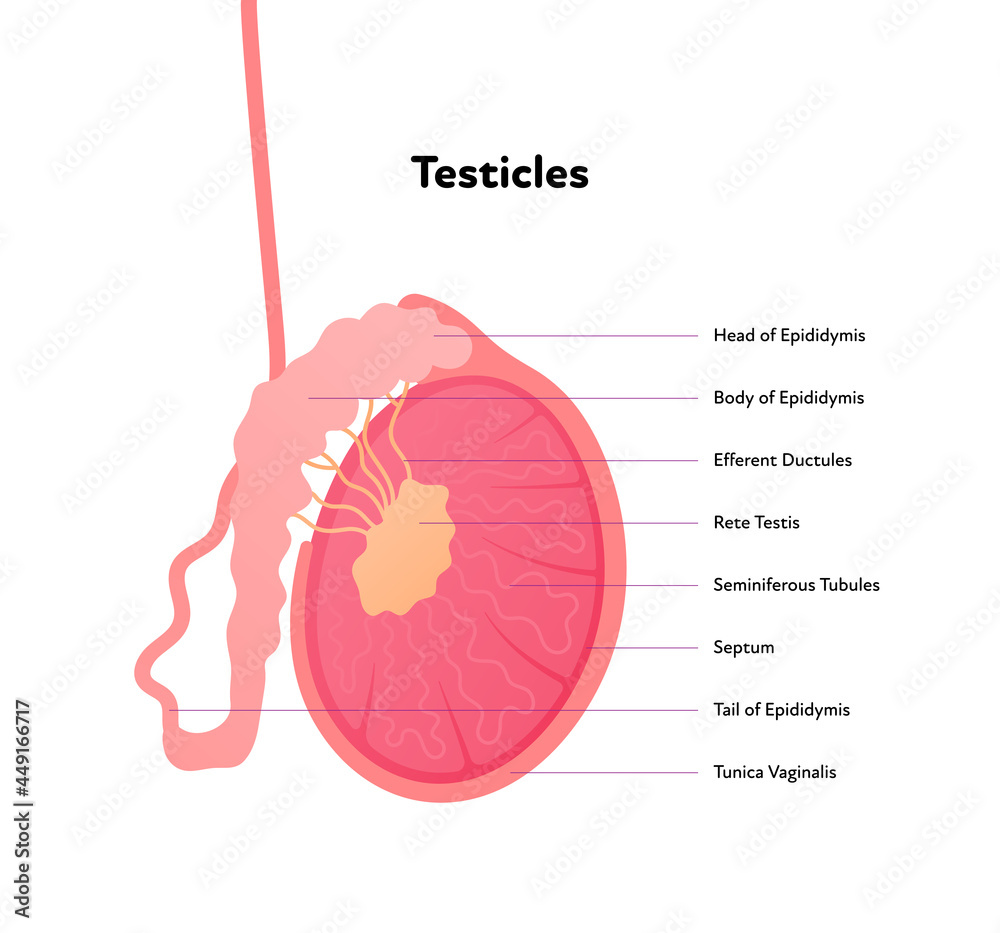
Stockvector Human Reproductive System Anatomy Inforgaphic Chart Vector The testes, or testicles, are two egg shaped sex organs that play an important role in the male reproductive system. they are where sperm cells are produced and are also responsible for the production of the sex hormone testosterone . A testicle (pronounced “teh stuh kl”) is part of the anatomy of men and people assigned male at birth (amab). generally, you’ll have two testicles. these body parts make sperm and hormones. other names for your testicles are male gonads or testes (pronounced “teh steez”). one testicle is called a testis. there are other more casual.
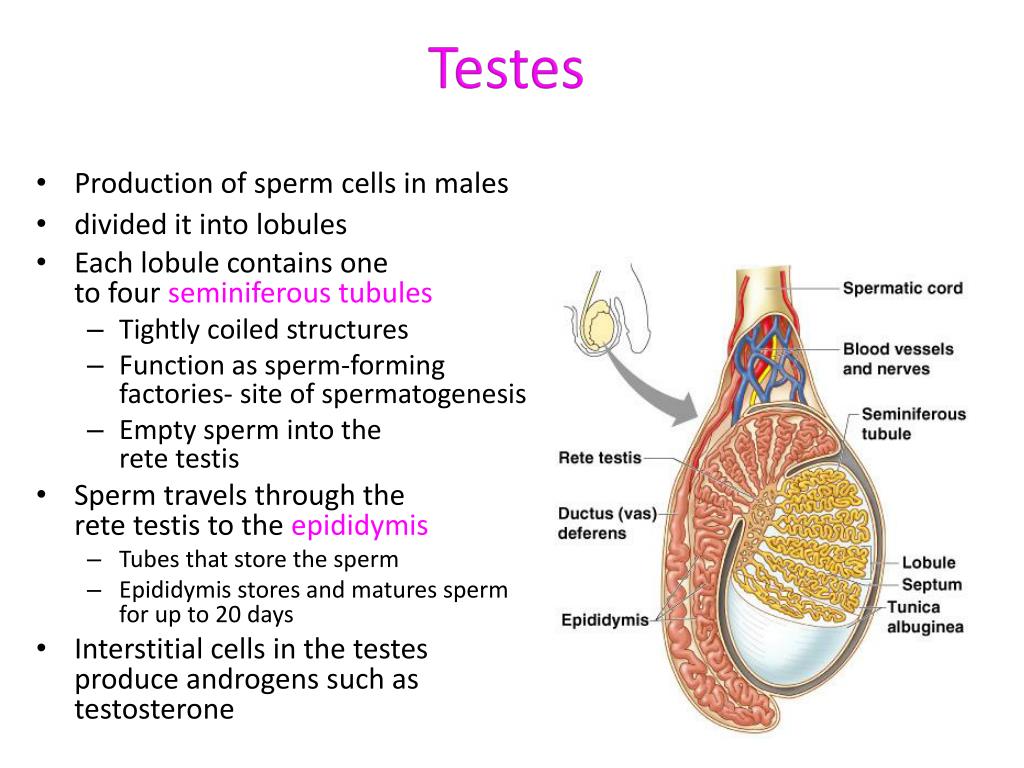
Ppt Reproductive Strategies Male Reproductive System Powerpoint The testes are two oval shaped organs in the male reproductive system. we’ll go over the different structures within each testis and how they function. you’ll also learn about the kinds of. The male reproductive system includes a group of organs that make up the reproductive system and urinary system in men and people assigned male at birth (amab). the male reproductive system contains internal and external parts. internal parts are inside your body, and external parts are outside your body. together, these organs help you urinate. Human reproductive system testes, hormones, anatomy: the two testes, or testicles, which usually complete their descent into the scrotum from their point of origin on the back wall of the abdomen in the seventh month after conception, are suspended in the scrotum by the spermatic cords. each testis is 4 to 5 cm (about 1.5 to 2 inches) long and is enclosed in a fibrous sac, the tunica. The testes and epididymis are paired structures, located within the scrotum. the testes are the site of sperm production and hormone synthesis, while the epididymis has a role in the storage of sperm. in this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the testes and epididymis – their structure, vasculature, innervation and clinical correlations.

L S Of Testes And C S Of Testes Male Reproductive System By Jjs Sir Human reproductive system testes, hormones, anatomy: the two testes, or testicles, which usually complete their descent into the scrotum from their point of origin on the back wall of the abdomen in the seventh month after conception, are suspended in the scrotum by the spermatic cords. each testis is 4 to 5 cm (about 1.5 to 2 inches) long and is enclosed in a fibrous sac, the tunica. The testes and epididymis are paired structures, located within the scrotum. the testes are the site of sperm production and hormone synthesis, while the epididymis has a role in the storage of sperm. in this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the testes and epididymis – their structure, vasculature, innervation and clinical correlations. The continued presence of testosterone is necessary to keep the male reproductive system working properly, and leydig cells produce approximately 6 to 7 mg of testosterone per day. testicular steroidogenesis (the manufacture of androgens, including testosterone) results in testosterone concentrations that are 100 times higher in the testes than. The following is an overview of the male reproductive anatomy: scrotum. the bag of skin that holds and helps to protect the testicles. the testicles make sperm and, to do this, the temperature of the testicles needs to be cooler than the inside of the body. this is why the scrotum is located outside of the body. click image to enlarge.
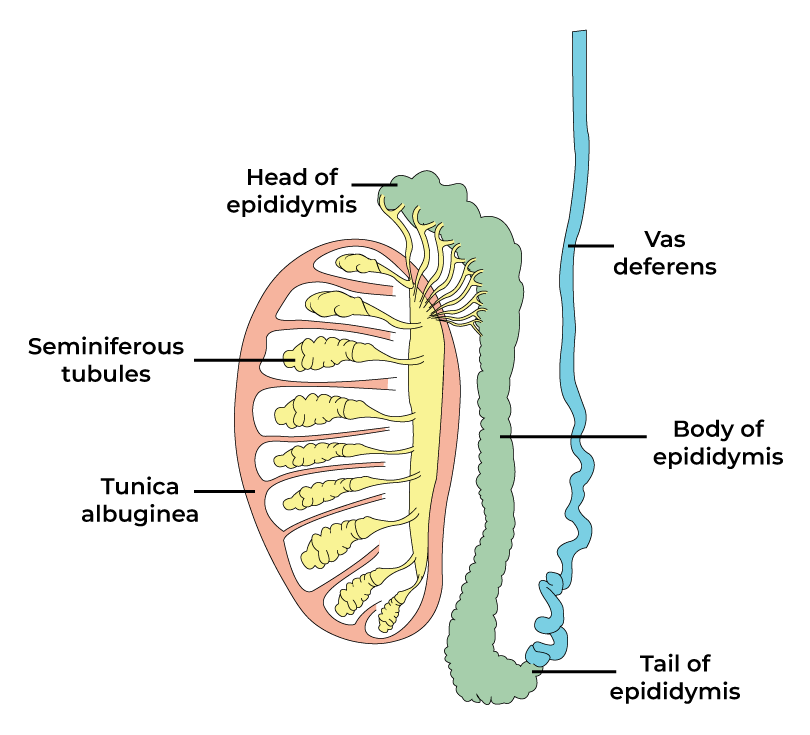
Testes Anatomy And Functions Geeksforgeeks The continued presence of testosterone is necessary to keep the male reproductive system working properly, and leydig cells produce approximately 6 to 7 mg of testosterone per day. testicular steroidogenesis (the manufacture of androgens, including testosterone) results in testosterone concentrations that are 100 times higher in the testes than. The following is an overview of the male reproductive anatomy: scrotum. the bag of skin that holds and helps to protect the testicles. the testicles make sperm and, to do this, the temperature of the testicles needs to be cooler than the inside of the body. this is why the scrotum is located outside of the body. click image to enlarge.

Comments are closed.