Producer Surplus Vs Consumer Surplus
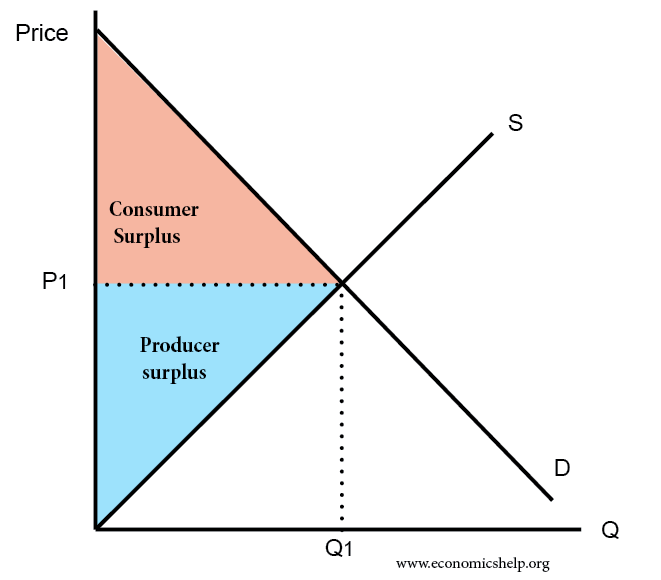
Consumer Surplus And Producer Surplus Economics Help Consumer surplus and producer surplus. Learn the definitions, diagrams and examples of consumer surplus and producer surplus, the differences between what consumers and producers pay and what they would be willing to pay or sell. see how elasticity, monopolies, price discrimination and free trade affect these concepts.

Consumer And Producer Surplus Edexcel Economics Revision Learn how to calculate and illustrate consumer surplus, producer surplus, and social surplus using demand and supply curves. see how efficiency and allocative efficiency are related to surplus concepts. Learn what consumer and producer surplus are and how they are affected by changes in demand and supply. find out how price elasticity of demand and supply influences the incidence of surpluses. Lesson overview: consumer and producer surplus (article). The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers.
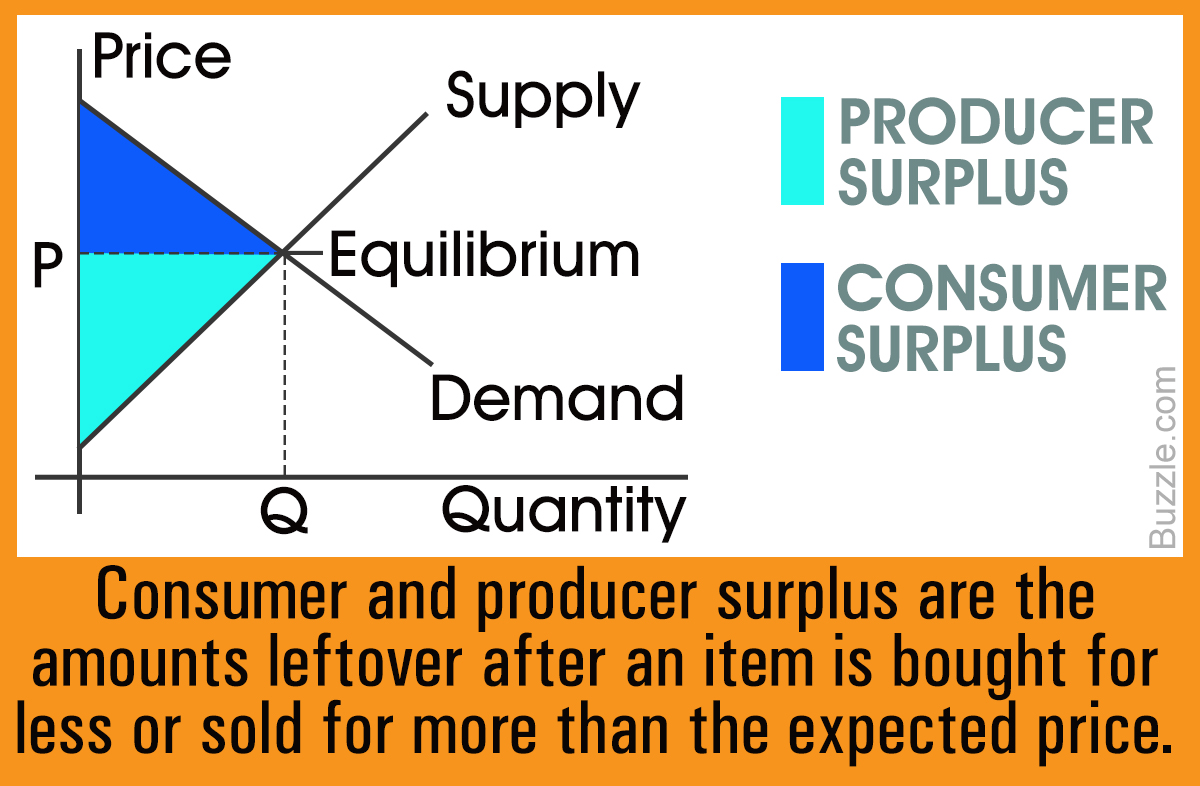
Consumer And Producer Surplus Market Efficiency 1 Consumer Surplus Lesson overview: consumer and producer surplus (article). The amount that a seller is paid for a good minus the seller’s actual cost is called producer surplus. in figure 1, producer surplus is the area labeled g—that is, the area between the market price and the segment of the supply curve below the equilibrium. to summarize, producers created and sold 28 tablets to consumers. In this example, producer surplus equals ½ x 60 x 50 = 1,500. similar to consumer surplus, the area of the triangle is the sum of all producer surpluses gained from each transaction in the market. for the 10th unit sold, somebody was willing to charge about $9 but could make a sale for $50, thereby gaining a producer surplus of $41. Learn how to calculate and compare consumer surplus and economic surplus, the benefits that consumers and producers get from a market transaction. see examples, charts, and the market equilibrium point where both surpluses are maximized.
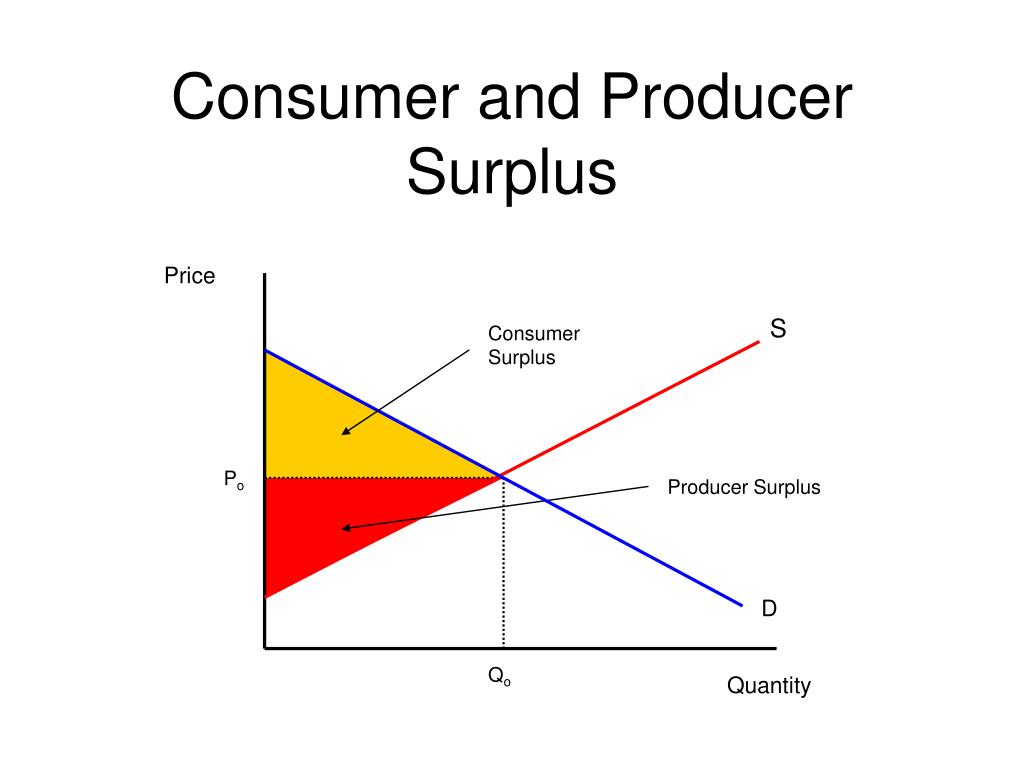
Consumer Producer Surplus Graph In this example, producer surplus equals ½ x 60 x 50 = 1,500. similar to consumer surplus, the area of the triangle is the sum of all producer surpluses gained from each transaction in the market. for the 10th unit sold, somebody was willing to charge about $9 but could make a sale for $50, thereby gaining a producer surplus of $41. Learn how to calculate and compare consumer surplus and economic surplus, the benefits that consumers and producers get from a market transaction. see examples, charts, and the market equilibrium point where both surpluses are maximized.

Comments are closed.