Probability Distribution Formulas
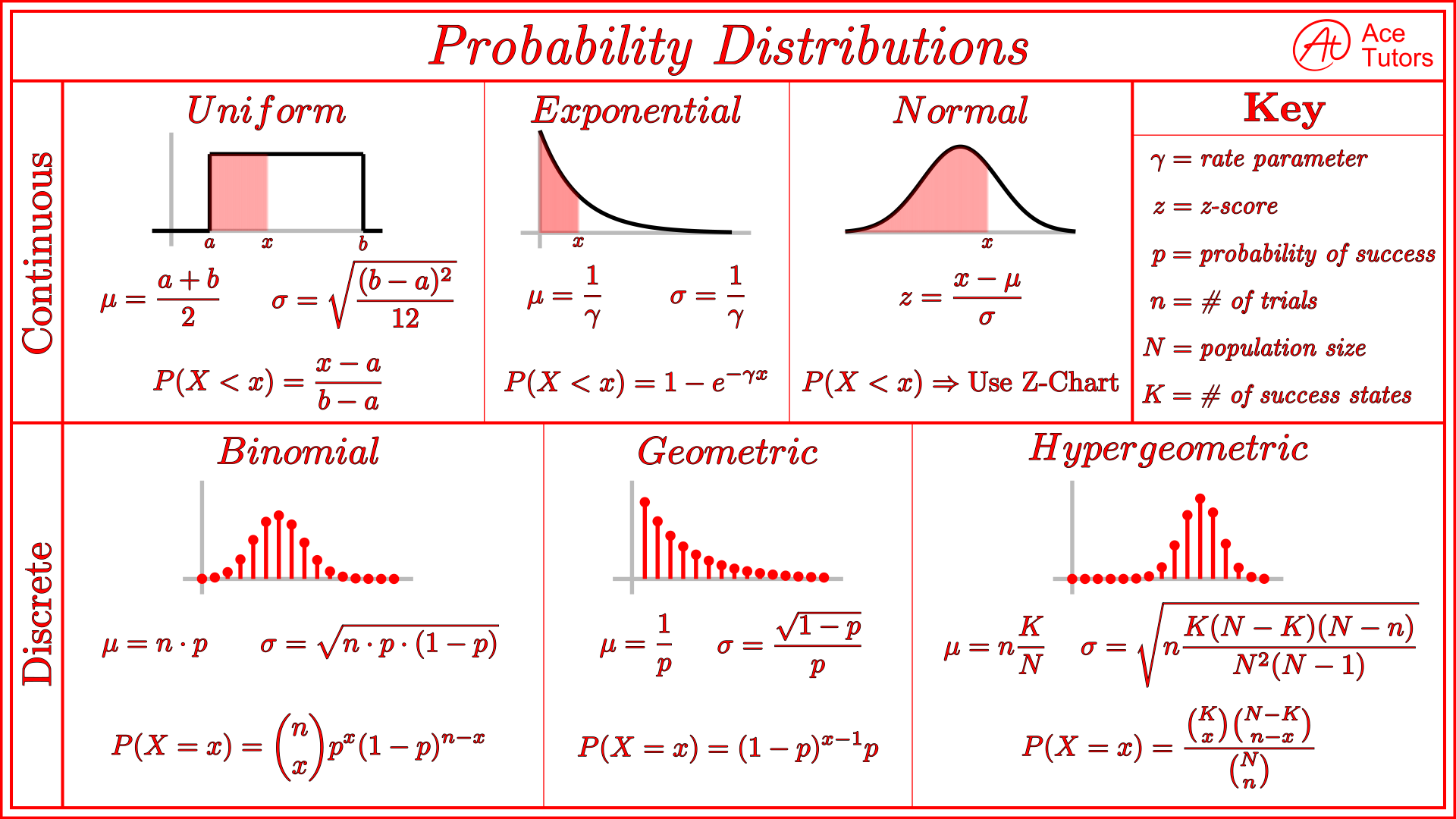
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet Calculus Ace Tutors Blog Probability distribution | formula, types, & examples. published on june 9, 2022 by shaun turney. revised on june 21, 2023. a probability distribution is a mathematical function that describes the probability of different possible values of a variable. probability distributions are often depicted using graphs or probability tables. If x is a random variable that follows a normal distribution then it is denoted as x ∼ n (μ,σ2) x ∼ n (μ, σ 2). the probability distribution formulas are given below: probability distribution function: f (x) = p = (z ≤ x−μ σ) = Φ(x−μ σ) p = (z ≤ x − μ σ) = Φ (x − μ σ) probability density function: f (x) = 1 σ√.
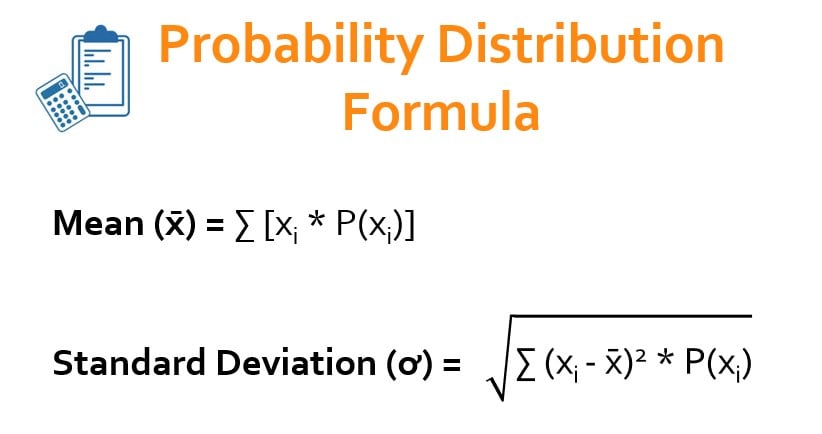
Probability Distribution Formula Examples With Excel Template A probability distribution function indicates the likelihood of an event or outcome. statisticians use the following notation to describe probabilities: p (x) = the likelihood that random variable takes a specific value of x. the sum of all probabilities for all possible values must equal 1. furthermore, the probability for a particular value. V. t. e. in probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is the mathematical function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible outcomes for an experiment. [1][2] it is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the probabilities of events (subsets of the sample space). [3]. Probability distribution formula mainly refers to two types of probability distribution which are normal probability distribution (or gaussian distribution) and binomial probability distribution. to recall, a table that assigns a probability to each of the possible outcomes of a random experiment is a probability distribution table. You can calculate the probability in a normal distribution using the z score formula: p (x < x) = Φ(x – μ ) σ, where Φ is the cumulative distribution function, x is the value, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.to calculate the probability in a normal distribution given the mean (μ) and variance (σ2), you can use the z.

Comments are closed.