Pressurized Cooling System Diagram

Pressurized Water Cooling System Youtube 1. the heart of any cooling system is the radiator. it plays an integral part of the system by removing heat from the coolant as it passes through the core. air moving through the radiator cools. The primary system tran sfers the heat from the fuel to the steam generator, where the secondary system begins. the steam formed in the steam generator is transferred by the secondary system to the main turbine generator, where it is converted into electricity. after passing through the low pressure turbine, the steam is routed to the main.

Water Cooling System In Engine Types Of Water Cooling System A system with an adjustable pressure valve will permit the pressure to increase to a preset level and to avoid boiling the water. a water pressure gauge (and warning light) can give the driver an idea where his car cooling system stands. the temperature should increases at the same rate as the cooling system pressure. 1] removes extra heat: it is the main function of the engine cooling system to carry away the excess heat generated by the engine. 2] helps to attain optimum temperature faster: the optimum temperature means the temperature at which the engine gives better performance. thus, after starting the engine, it is necessary that the engine should. The modes can be summarized as: mode 1 – normal power: the reactor is critical, produces more than 5% of nominal power, and the coolant is at the operating temperature of 300°c and 155 bar. mode 2 – start up: the reactor is critical, its power is beneath 5% of nominal but its coolant is at normal operating temperature. The cap is actually a pressure release valve, and on cars it is usually set to 15 psi. the boiling point of water increases when the water is placed under pressure. when the fluid in the cooling system heats up, it expands, causing the pressure to build up. the cap is the only place where this pressure can escape, so the setting of the spring.
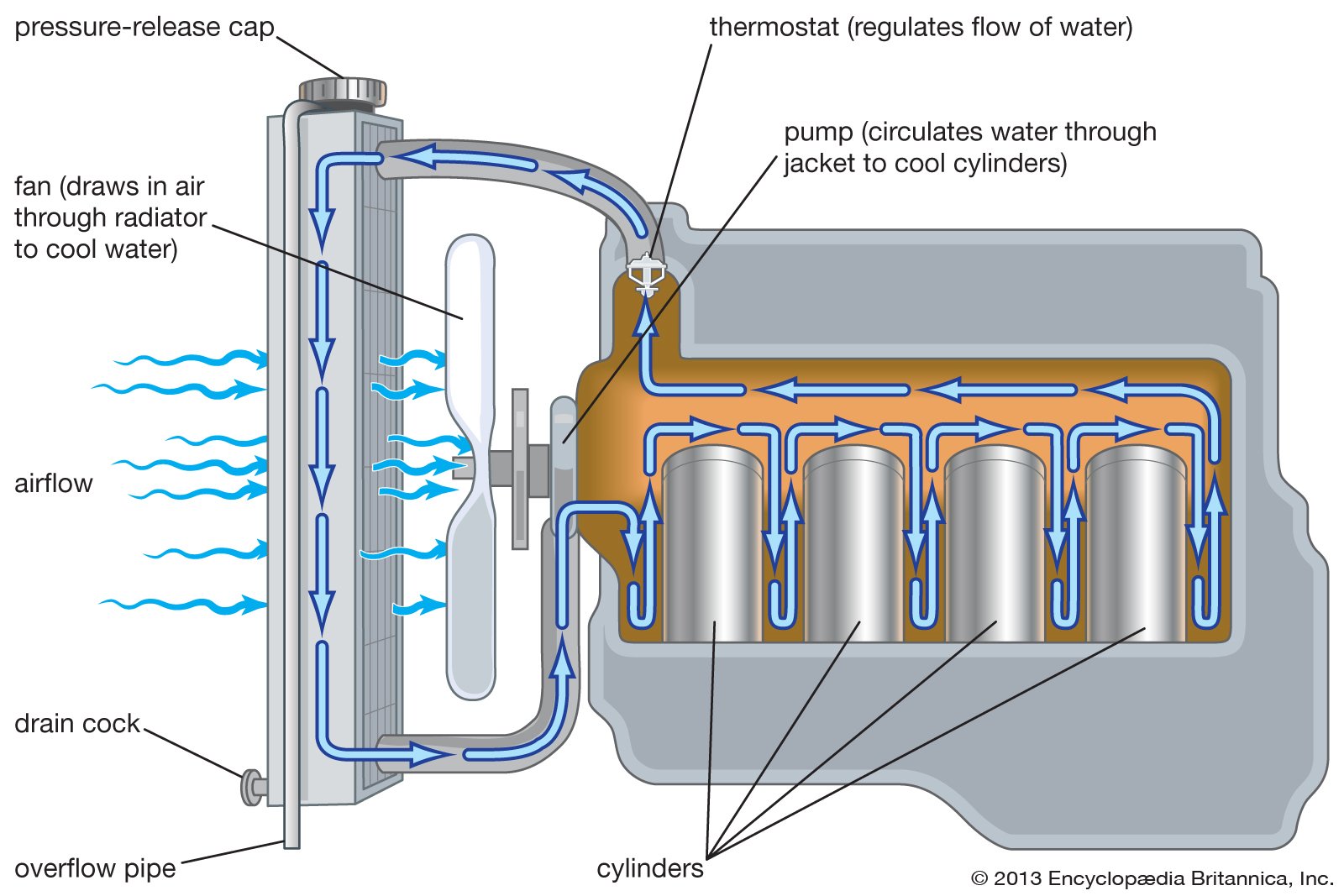
How Engine Cooling System Works Animation At William Farris Blog The modes can be summarized as: mode 1 – normal power: the reactor is critical, produces more than 5% of nominal power, and the coolant is at the operating temperature of 300°c and 155 bar. mode 2 – start up: the reactor is critical, its power is beneath 5% of nominal but its coolant is at normal operating temperature. The cap is actually a pressure release valve, and on cars it is usually set to 15 psi. the boiling point of water increases when the water is placed under pressure. when the fluid in the cooling system heats up, it expands, causing the pressure to build up. the cap is the only place where this pressure can escape, so the setting of the spring. A water cooling system is a complex heat exchanger comprising special coolant fluid, pipes, some clever regulating valves and a car radiator and an expansion tank. propelled by the water pump, coolant flows from the radiator to the engine, where it travels around the main engine block, in which the pistons go up and down, and the cylinder head. The extra pressure is limited by the radiator cap, which has a pressure valve in it. excessive pressure opens the valve, and coolant flows out through an overflow pipe. in a cooling system of this type there is a continual slight loss of coolant if the engine runs very hot. the system needs topping up from time to time.

Schematic Diagram Of Pressurized Internal Cooling Grinding Wheel A water cooling system is a complex heat exchanger comprising special coolant fluid, pipes, some clever regulating valves and a car radiator and an expansion tank. propelled by the water pump, coolant flows from the radiator to the engine, where it travels around the main engine block, in which the pistons go up and down, and the cylinder head. The extra pressure is limited by the radiator cap, which has a pressure valve in it. excessive pressure opens the valve, and coolant flows out through an overflow pipe. in a cooling system of this type there is a continual slight loss of coolant if the engine runs very hot. the system needs topping up from time to time.

Comments are closed.