Physics 142 Lesson 3 3d Nuclear Decay And Conservation Laws

Physics 142 Lesson 3 3d Nuclear Decay And Conservation Laws Youtube A lecture corresponding to chapter 31.4 of "college physics" by urone, hinrichs, dirks, and sharma. available via openstax: ( openstax.org details co. There are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (α) beta (β) and gamma (γ). the α decay equation is a zxn →a − 4 z − 2yn − 2 4 2he2. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy e related to the mass destroyed Δm by e = (Δm)c2. there are three forms of beta decay.
How To Use Conservation Of Charge To Determine Unknown Coefficients In As discussed in atomic physics, the general relationship is e = (∆ m) c2. here, e is the nuclear reaction energy (the reaction can be nuclear decay or any other reaction), and Δ m is the difference in mass between initial and final products. when the final products have less total mass, Δ m is positive, and the reaction releases energy (is. Define and discuss nuclear decay. state the conservation laws. explain parent and daughter nucleus. calculate the energy emitted during nuclear decay. nuclear decay has provided an amazing window into the realm of the very small. nuclear decay gave the first indication of the connection between mass and energy, and it revealed the existence of. Section summary. when a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (), beta (), and gamma (). the decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy related to the mass destroyed by. When a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ). the α decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy e related to the mass destroyed ∆ m by e = (∆ m) c2.

Physics 142 Lesson 3 5d Particles Patterns And Conservation Laws Section summary. when a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (), beta (), and gamma (). the decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy related to the mass destroyed by. When a parent nucleus decays, it produces a daughter nucleus following rules and conservation laws. there are three major types of nuclear decay, called alpha (α), beta (β), and gamma (γ). the α decay equation is. nuclear decay releases an amount of energy e related to the mass destroyed ∆ m by e = (∆ m) c2. Nuclear decay gave the first indication of the connection between mass and energy, and it revealed the existence of two of the four basic forces in nature. in this section, we explore the major modes of nuclear decay; and, like those who first explored them, we will discover evidence of previously unknown particles and conservation laws. Rate of decay is characterized by half life, the time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay; conservation laws in nuclear reactions. conservation of mass energy: total mass energy of closed system remains constant during nuclear reactions mass can be converted into energy and vice versa (e = m c 2 e=mc^2 e = m c 2).
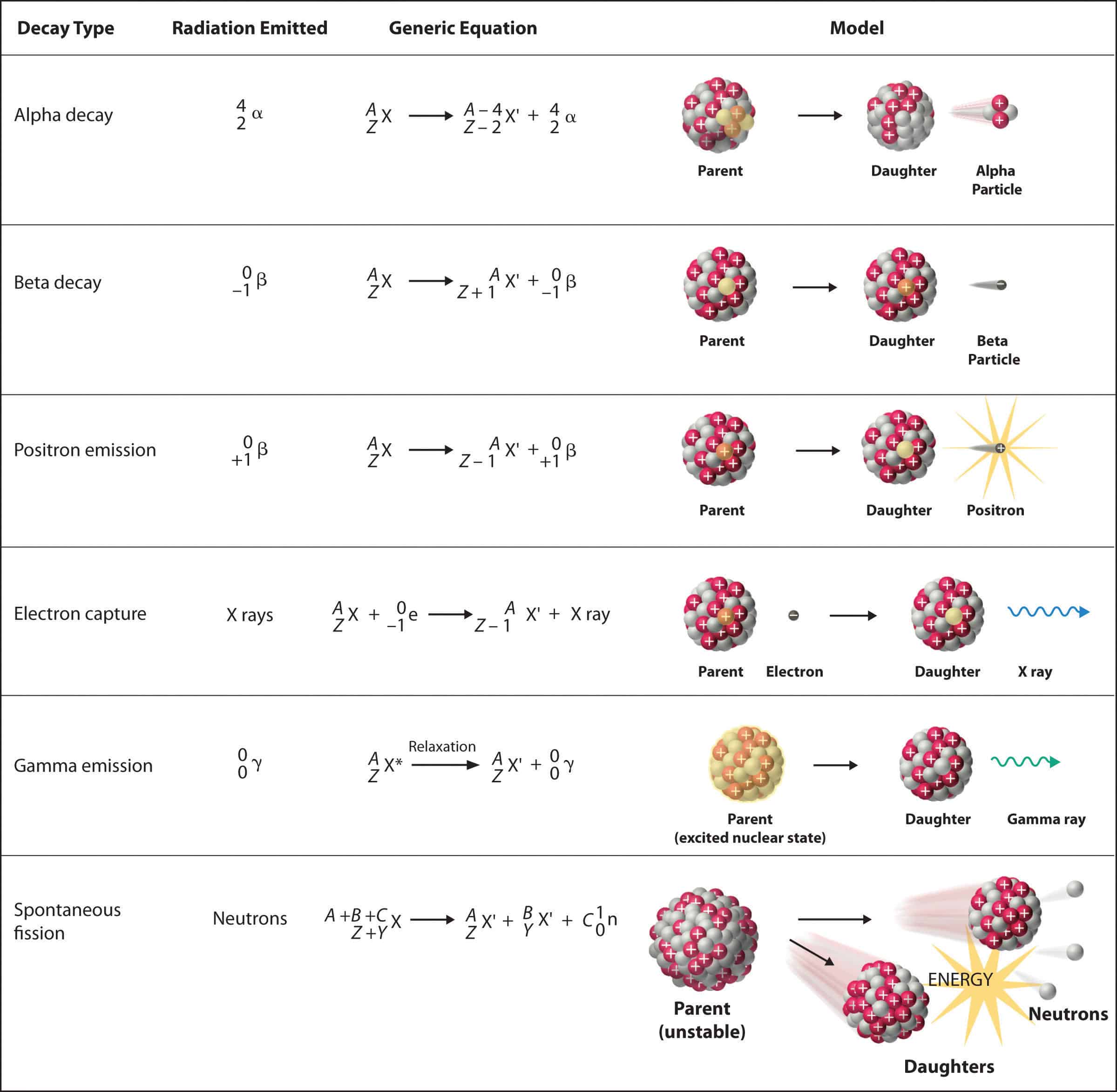
Lead Decay Equation At Olga Rand Blog Nuclear decay gave the first indication of the connection between mass and energy, and it revealed the existence of two of the four basic forces in nature. in this section, we explore the major modes of nuclear decay; and, like those who first explored them, we will discover evidence of previously unknown particles and conservation laws. Rate of decay is characterized by half life, the time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay; conservation laws in nuclear reactions. conservation of mass energy: total mass energy of closed system remains constant during nuclear reactions mass can be converted into energy and vice versa (e = m c 2 e=mc^2 e = m c 2).

Nuclear Decay Equations Gcse Physics Revision

Comments are closed.