Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Definition Properties Examples
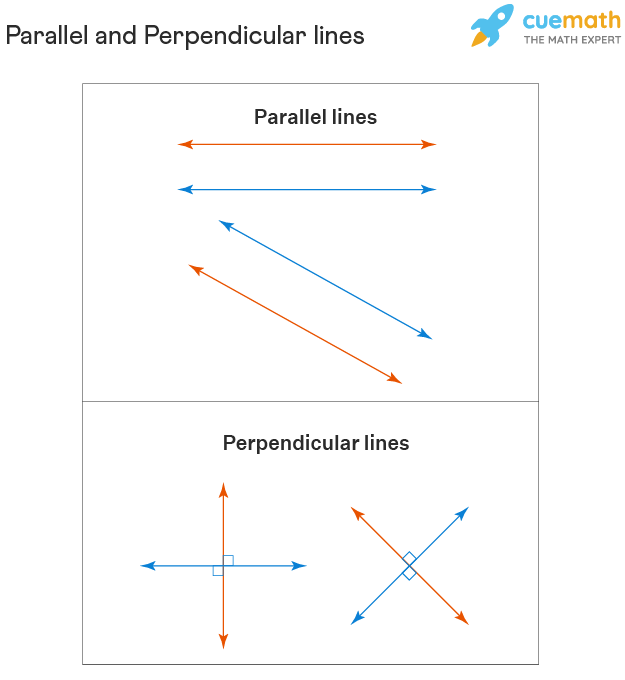
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Definition Properties Examples Parallel lines are the lines that never intersect each other. thus, two parallel lines always maintain a constant distance between them. perpendicular lines are the two lines that intersect each other at a right angle. we come across examples of parallel lines and perpendicular lines in daily life. observe the white lines or stripes in a marked. For example, the opposite sides of a square and a rectangle have parallel lines in them, and the adjacent lines in the same shapes are perpendicular lines. if we see a few real world examples, we can notice parallel lines in them, like the opposite sides of a notebook or a laptop, represent parallel lines, and the intersecting sides of a.

Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Example: find the equation of the line that is: parallel to y = 2x 1; and passes though the point (5,4) the slope of y = 2x 1 is 2. the parallel line needs to have the same slope of 2. we can solve it by using the "point slope" equation of a line: y − y 1 = 2(x − x 1) and then put in the point (5,4): y − 4 = 2(x − 5) that is an answer!. Solution: step 1: find the slope . first, find the slope of the given line. to do this, solve for to change standard form to slope intercept form, . in this form, you can see that the slope is , and thus . step 2: substitute the slope you found and the given point into the point slope form of an equation for a line. Both parallel and perpendicular lines are coplanar. parallel lines never intersect, while perpendicular lines always intersect at a 90 degree angle. parallel and perpendicular lines are two key concepts in geometry. here are the definitions of parallel and perpendicular, a look at their properties, and how to use slope to identify them. Example 3: given 1 coordinate and the gradient. two lines, d and e are written in the form y = mx c. the gradient of the line d is equal to 0.4 and intersects the y axis at the point (0,5). the line e is parallel to d and goes through the point (10,12).
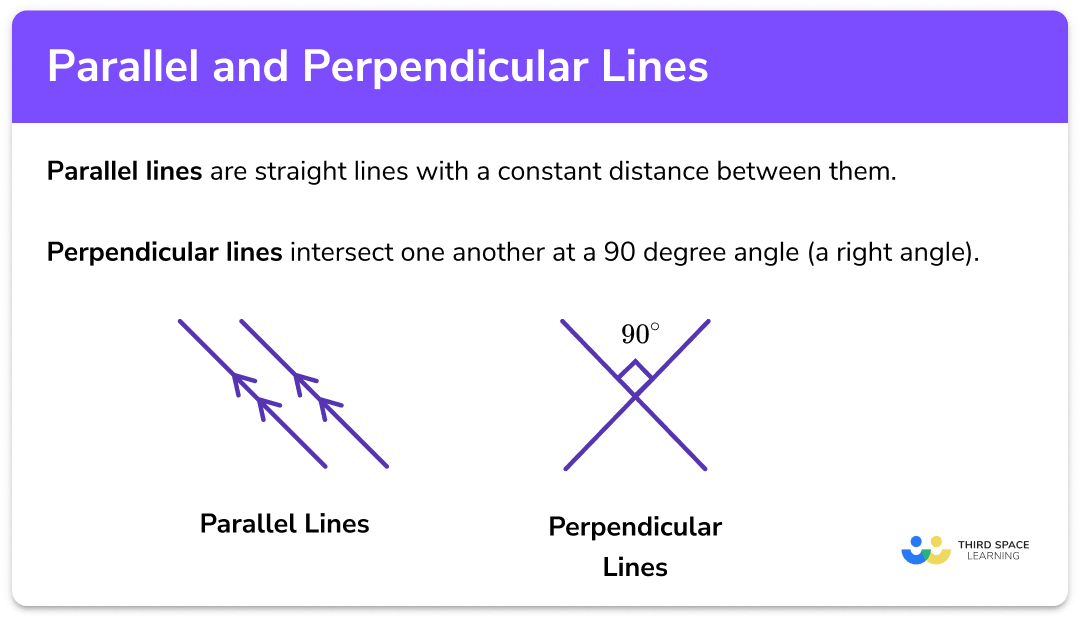
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Both parallel and perpendicular lines are coplanar. parallel lines never intersect, while perpendicular lines always intersect at a 90 degree angle. parallel and perpendicular lines are two key concepts in geometry. here are the definitions of parallel and perpendicular, a look at their properties, and how to use slope to identify them. Example 3: given 1 coordinate and the gradient. two lines, d and e are written in the form y = mx c. the gradient of the line d is equal to 0.4 and intersects the y axis at the point (0,5). the line e is parallel to d and goes through the point (10,12). The letters t and l are examples of perpendicular lines. by definition, parallel lines are two lines on the same plane that never intersect. the letters n and z contain pairs of parallel lines. when determining if two lines are parallel or perpendicular, the slope is the key. Two lines are said to be perpendicular if they intersect at right angles (90o). slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines. in analytic geometry, we often track the angles using the slopes of the involved lines. so it’s only natural that we use slopes (generally denoted by the letter m) when working with parallel and perpendicular lines too.

Comments are closed.