Opioid Agonists Introduction Medicine Keys For Mrcps

Opioid Agonists Introduction Medicine Keys For Mrcps Opioid agonists, introduction; opioid agonists, uses leave a reply. your email address will not be published. required fields are marked * comment * name. email. website. Opioid drugs include full agonists, partial agonists, and antagonists–measures of intrinsic activity or efficacy. morphine is a full agonist at the μ (mu) opioid receptor, the major analgesic opioid receptor (table 31–1). opioids may also differ in receptor binding affinity.

Opioid Agonists Uses Medicine Keys For Mrcps The utilization of opioids in clinical pharmacology started after the extraction of morphine from the opium poppy papaver somniferum in 1806 with its use further intensified after the discovery of hypodermic needles in 1853.[1] opioids divide into two types, those being endogenous and exogenous. some endogenous opioids that bind to the receptors are enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins. 1. context. opioids are mu receptor agonists and have been an important part of pain treatment for thousands of years. in order to use these drugs appropriately and successfully in patients, whether to control pain, to treat opiate induced side effects, or opiate withdrawal syndrome, a solid understanding of the pharmacology of such drugs is crucial (). Learning outcomes. by the end of this section, you should be able to: 14.3.1 identify the characteristics of opioid agonist and antagonist drugs used to treat pain.; 14.3.2 explain the indications, actions, adverse reactions, and contraindications of opioid agonist and antagonist drugs used to treat pain. Since immune cells express opioid receptors, opioids may be involved in the regulation of inflammatory processes, with mor ligands playing the most significant immunomodulatory role. cabot et al. [ 184 ] showed that inflammation may increase the expression of pomc mrna in immune cells, what results in elevated β endorphin production and.
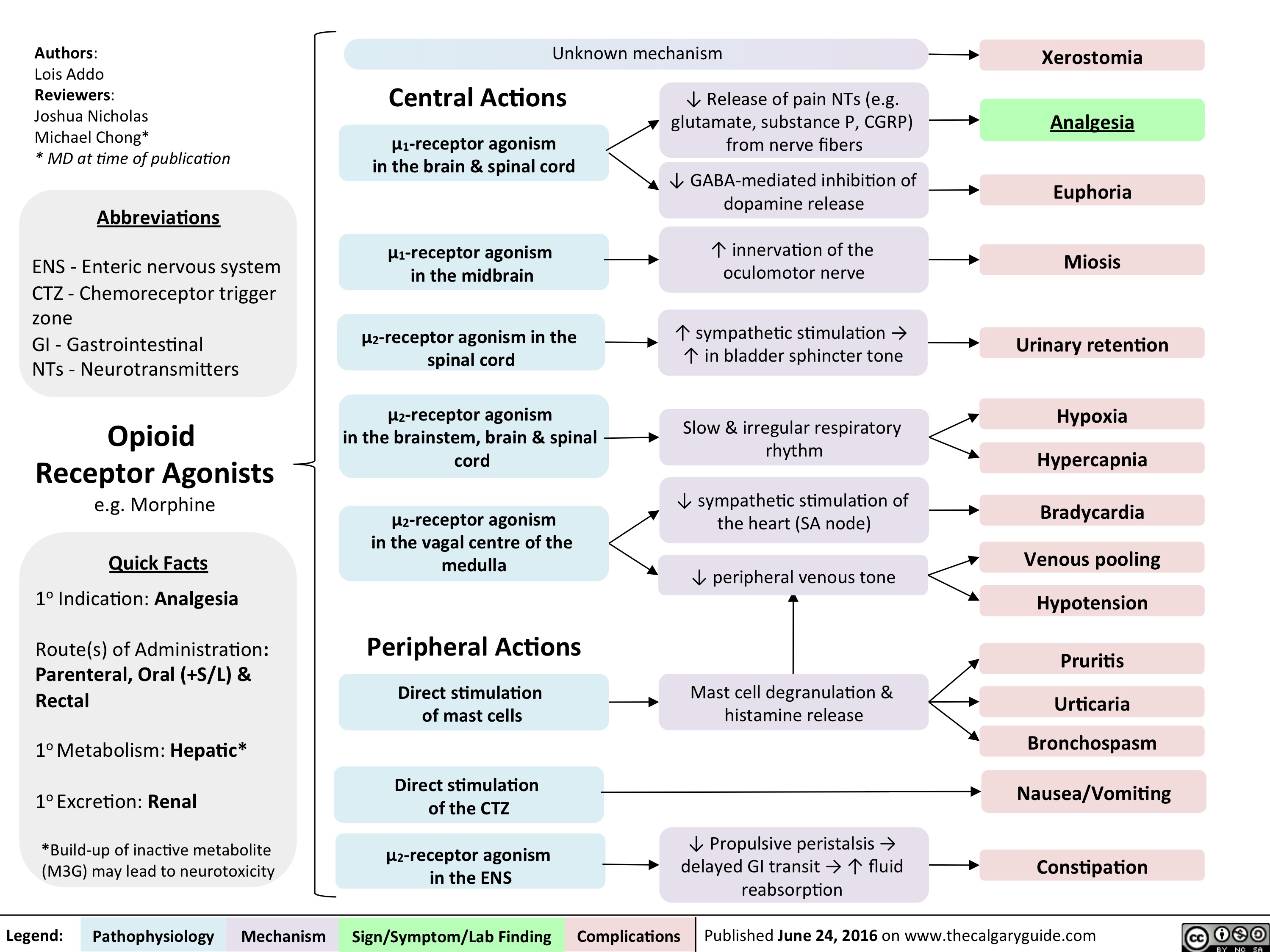
Opioid Receptor Agonists Calgary Guide Learning outcomes. by the end of this section, you should be able to: 14.3.1 identify the characteristics of opioid agonist and antagonist drugs used to treat pain.; 14.3.2 explain the indications, actions, adverse reactions, and contraindications of opioid agonist and antagonist drugs used to treat pain. Since immune cells express opioid receptors, opioids may be involved in the regulation of inflammatory processes, with mor ligands playing the most significant immunomodulatory role. cabot et al. [ 184 ] showed that inflammation may increase the expression of pomc mrna in immune cells, what results in elevated β endorphin production and. General. the existence of receptors for opiate drugs was first proposed in 1954 by beckett and casy [1] based on their studies of structure activity relationships for antinociceptive activity in a series of synthetic opiates. these receptors are called 'opioid' since we now know their endogenous ligands are peptides with effects resembling. Takeaway. opioid agonists are substances that activate opioid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems. they have several uses, from pain management to treating opioid use disorder.

Comments are closed.