Normal Bladder Ultrasound
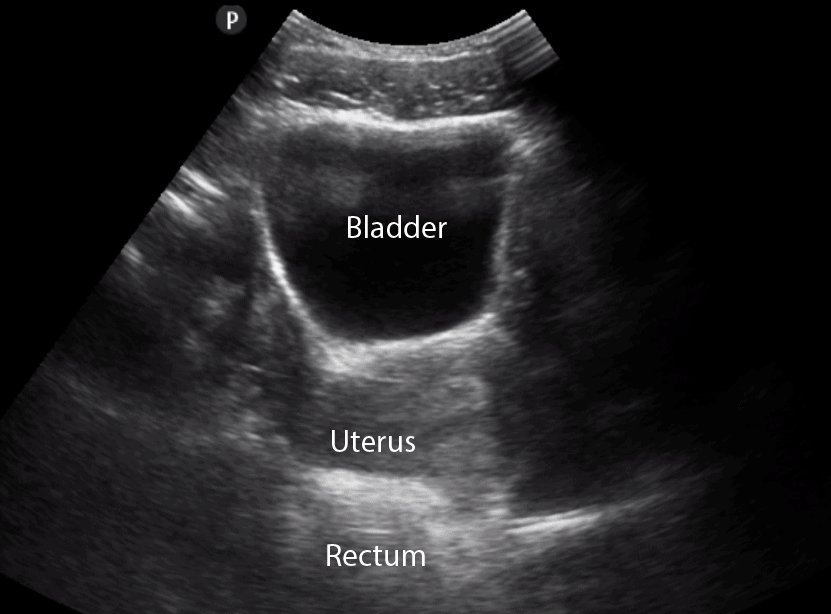
Normal Bladder Ultrasound Examine the bladder sagitally in the midline. now angle laterally & sweep the probe both left and right to check the lateral margins. rotate 90 degrees into the axial (transverse) plane. sweep through from the superior dome to the bladder base. ensure the ultrasound beam is projected as close to perpendicular to the bladder wall as possible. Learn how to use point of care ultrasound (pocus) to evaluate the bladder at the bedside. this guide covers bladder anatomy, volume calculation, and common pathology such as urinary retention, stones, and masses.
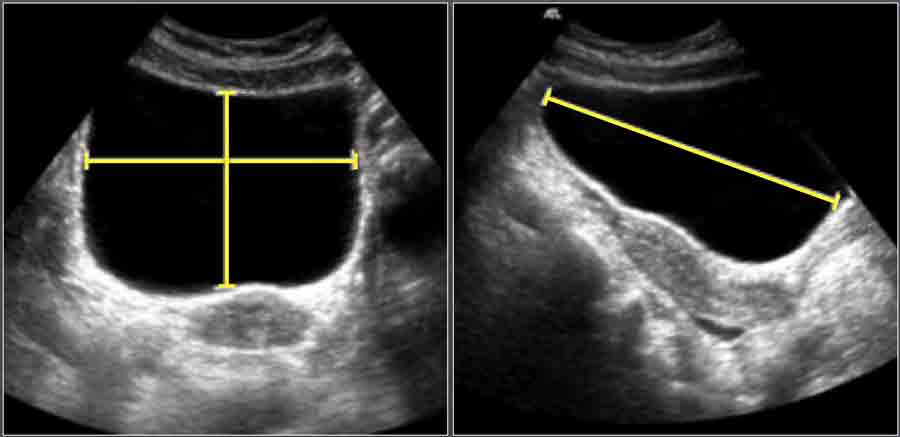
The Radiology Assistant Normal Values In Pediatric Ultrasound A bladder ultrasound is a painless and noninvasive tool that can help you get answers for your bladder problems. if you experience things like urine leaking or incontinence, a doctor may want to. Urinary bladder wall thickening is a common finding and its significance depends on whether the bladder is adequately distended. in both adults and children, the wall may be considered thickened on ultrasound if it measures 6: * normal adult bladder volume is 300 400 ml 7. Bladder ultrasound is an imaging technique widely recognized for its efficacy in examining the bladder and surrounding areas. this non invasive, safe, and relatively quick procedure has become an important tool in diagnosing and managing many urological conditions. it uses high frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the bladder. Urologists use ultrasounds to see how the bladder is draining during urination. ultrasounds can also detect other causes of overactive bladder. overactive bladder (oab) is not a disease but a.

Normal Bladder Ultrasound Bladder ultrasound is an imaging technique widely recognized for its efficacy in examining the bladder and surrounding areas. this non invasive, safe, and relatively quick procedure has become an important tool in diagnosing and managing many urological conditions. it uses high frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the bladder. Urologists use ultrasounds to see how the bladder is draining during urination. ultrasounds can also detect other causes of overactive bladder. overactive bladder (oab) is not a disease but a. The urethra arises from the neck of the bladder and is surrounded by the internal urethral sphincter. the urethra is separated from the symphysis pubis by retropubic fatty space of retzius 6. as the bladder fills with urine it becomes ovoid and extends superiorly into the abdominal cavity 6. contraction is facilitated by the detrusor muscle. A bladder ultrasound requires a full bladder. with that in mind, here are some steps to take in preparation for your bladder ultrasound: empty your bladder one to two hours before the ultrasound. drink one liter or 32 ounces of water 30 minutes before your ultrasound appointment. don’t empty your bladder again until the appointment ends.
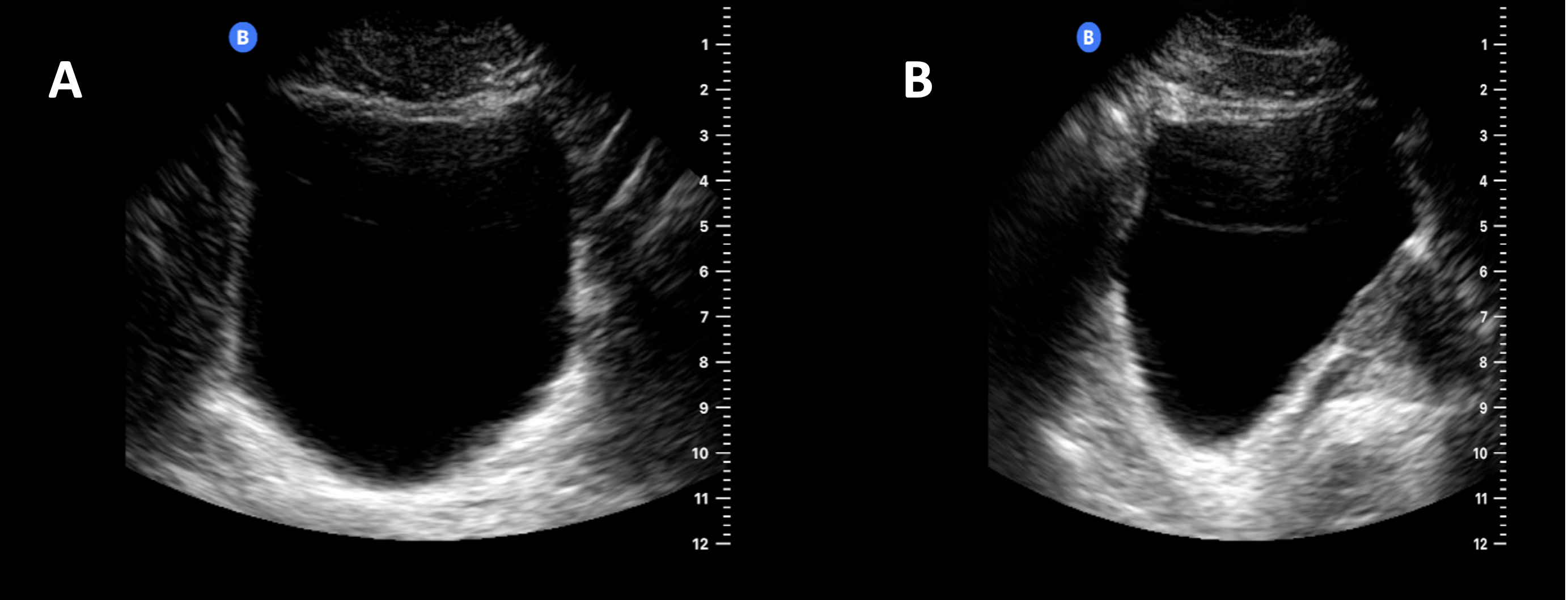
Normal Bladder Ultrasound The urethra arises from the neck of the bladder and is surrounded by the internal urethral sphincter. the urethra is separated from the symphysis pubis by retropubic fatty space of retzius 6. as the bladder fills with urine it becomes ovoid and extends superiorly into the abdominal cavity 6. contraction is facilitated by the detrusor muscle. A bladder ultrasound requires a full bladder. with that in mind, here are some steps to take in preparation for your bladder ultrasound: empty your bladder one to two hours before the ultrasound. drink one liter or 32 ounces of water 30 minutes before your ultrasound appointment. don’t empty your bladder again until the appointment ends.

Comments are closed.