Mri For Perianal Fistula Radiology Key
Mri For Perianal Fistula Radiology Key Mri for perianal fistula. fig. 15.1. normal anatomy of the pelvic floor and anal sphincters. the levator ani (lev ani) muscles blend with the puborectalis (pr) which in turn merges with the circular external sphincter (ext). the internal sphincter is continuous with the muscularis propria of the rectum, running the length of the anal canal and. Perianal fistulas are a major cause of morbidity. fistulas are defined as an abnormal communication between 2 epithelium lined surfaces. in the case of a perianal fistula, the connection is between the mucosal layer of the anal canal and the perianal skin. perianal fistulas predominantly affect young adults, especially men in their fourth decade.
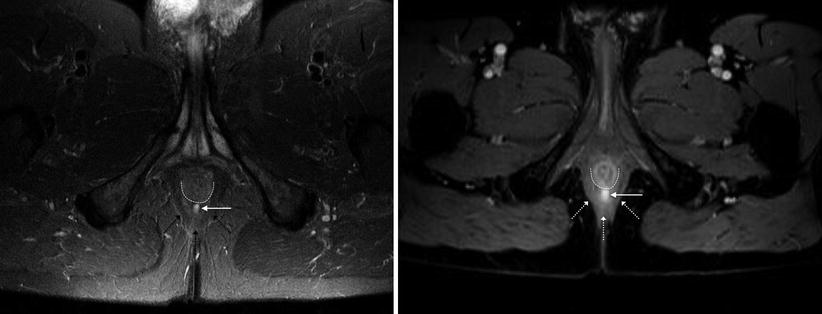
Mri For Perianal Fistula Radiology Key Since secondary tracts can be missed by clinical examination, preoperative mri has emerged to better define the fistula anatomy, select the surgical approach, and thereby avoid recurrence [10–13]. all perianal fistulas are divided into five subtypes . suprasphincteric and extrasphincteric fistulas are placed in the same category as grade v. Perianal fistula. a perianal fistula is an abnormal connection between the epithilialised surface of the anal canal and the skin. the causes of perianal fistulas: primary. obstruction of anal gland which leads to stasis and infection with absces and fistula formation (most common cause). secondary. Pelvic magnetic resonance (mr) imaging is currently the standard for imaging perianal crohn disease. perianal fistulas are a leading cause of patient morbidity because closure often requires multimodality treatments over a prolonged period of time. this review summarizes clinically relevant anal sphincter anatomy, imaging methods, classification systems, and treatment objectives. in addition. A practical guide is proposed to facilitate understanding of imaging findings of fistulizing perianal disease. the online presentation reviews the imaging modalities used in assessment of perianal fistulas, with an emphasis on mri. the pertinent imaging findings of each type of fistula and the most used classification systems are discussed.
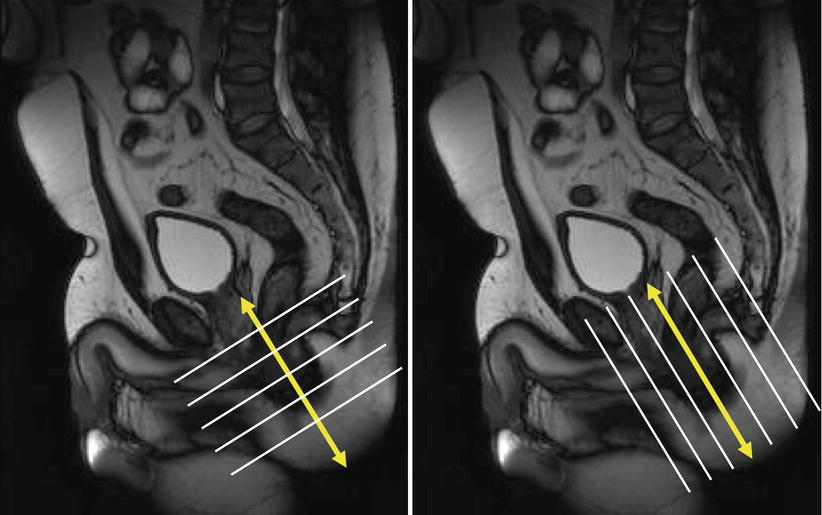
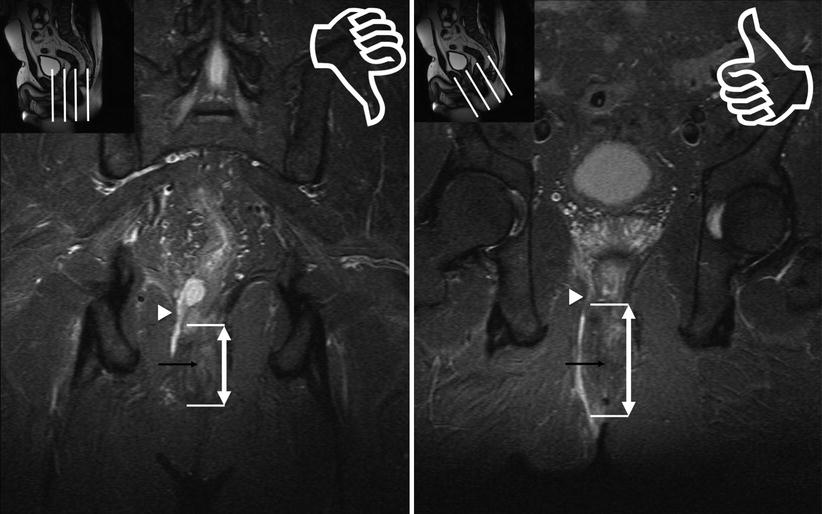
Mri For Perianal Fistula Radiology Key Pelvic magnetic resonance (mr) imaging is currently the standard for imaging perianal crohn disease. perianal fistulas are a leading cause of patient morbidity because closure often requires multimodality treatments over a prolonged period of time. this review summarizes clinically relevant anal sphincter anatomy, imaging methods, classification systems, and treatment objectives. in addition. A practical guide is proposed to facilitate understanding of imaging findings of fistulizing perianal disease. the online presentation reviews the imaging modalities used in assessment of perianal fistulas, with an emphasis on mri. the pertinent imaging findings of each type of fistula and the most used classification systems are discussed. Perianal fistulization is an inflammatory condition that affects the region around the anal canal, causing significant morbidity and often requiring repeated surgical treatments due to its high tendency to recur. to adopt the best surgical strategy and avoid recurrences, it is necessary to obtain precise radiologic information about the location of the fistulous track and the affected pelvic. The pelvic mri protocol for perianal fistula evaluation consists of t1 weighted and high spatial resolution t2 weighted imaging sequences without fat saturation for delineation of the muscle groups, fat planes, and the fistula tract. t2 weighted imaging with fat suppression (and stir) is used to assess edema and fluid containing tracts and.

Comments are closed.