Mechanical Engineering An Overview Of A Cooling Tower Indicating Flow
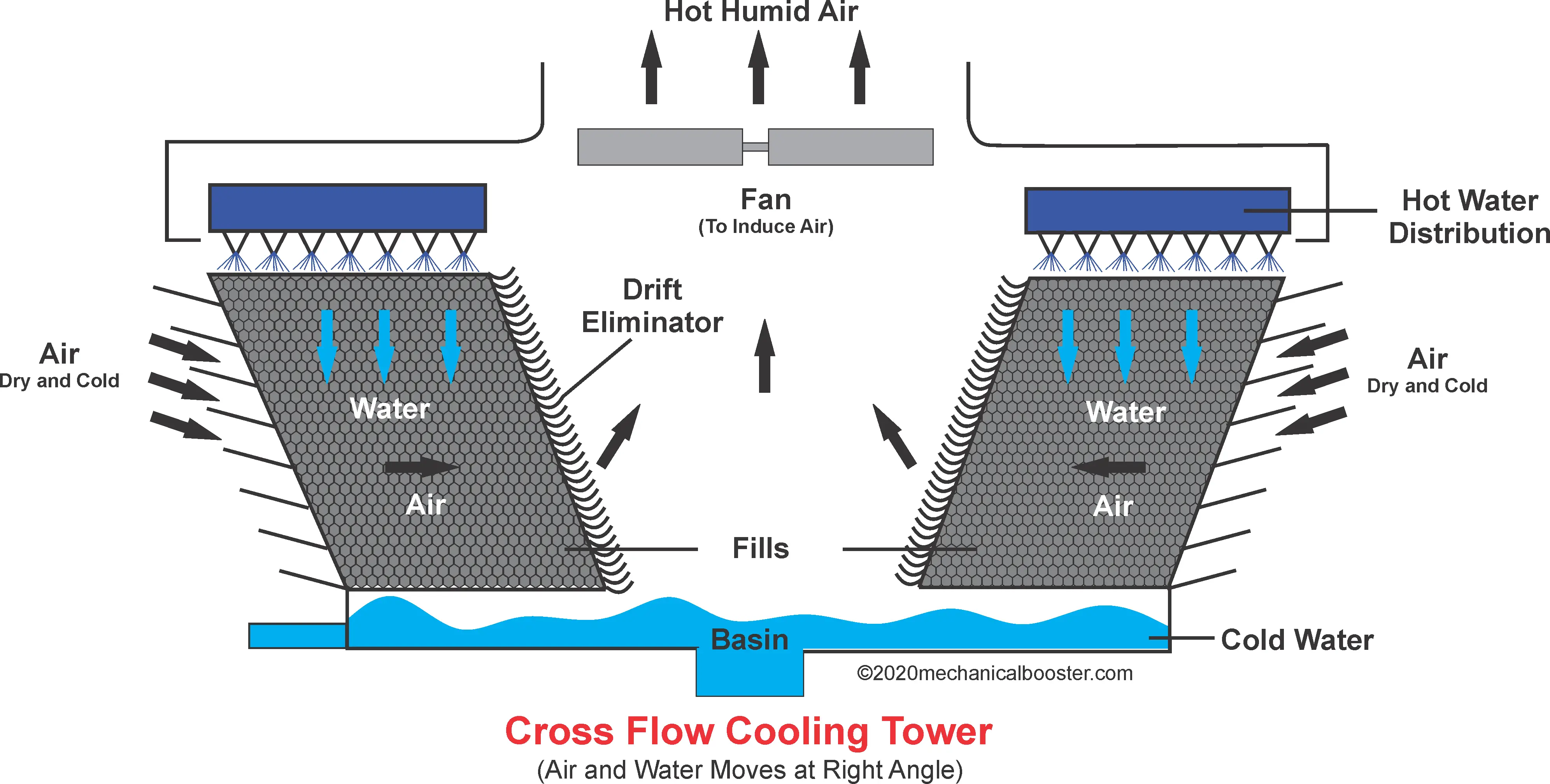
What Is A Cooling Tower And How It Works Mechanical Booster The open circuit type with mechanical draft is the most commonly used cooling tower in hgshp systems. fig. 12.2 shows cross flow and counter flow cooling towers of the open circuit type with mechanical draft. in the cross flow cooling tower, fig. 12.2 (a), air flow is directed perpendicular to the water flow. Mechanical draft cross flow cooling towers are generally used in a large scale water cooled condenser based air conditioning plants for removing heat from warm water which comes out from the condensing unit. during this process considerable amount of water in the form of drift (droplets) and evaporation is carried away along with the circulated air. in this paper, the performance evaluation of.
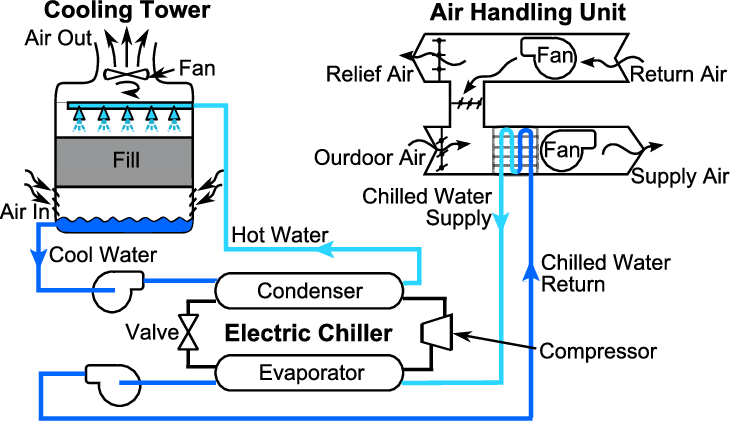
Open Loop Cooling Tower Schematic Customization: mechanical draft cooling towers can be customized based on specific project requirements, taking into account factors such as cooling needs, space constraints, and environmental considerations. in summary, mechanical draft cooling towers offer a technologically advanced and adaptable solution for managing heat in industrial. An ann model used for a forced draft cooling tower with the experimental data as: the ratio of mass flow rate of water to that of mass flow rate of air, the inlet water temperature, and the outlet water temperature, and the inlet air wet bulb temperature are chosen as input variables, while the output obtained is the coefficient of performance and come across that a trained model will give. An optimal design algorithm for mechanical draft counter flow wet cooling towers based on the rigorous poppe method and mixed integer nonlinear programming is presented. the poppe method takes into consideration the effects of the water loss by evaporation and the nonunity of the lewis factor. six case studies demonstrate that there can be large differences between the optimal designs based on. A number of investigations have been considered to reveal differences between the used cooling towers and finally a fluent simulation has been carried out to examine major contours and flow field.

Cooling Towers Explained How Does A Cooling Tower Work An optimal design algorithm for mechanical draft counter flow wet cooling towers based on the rigorous poppe method and mixed integer nonlinear programming is presented. the poppe method takes into consideration the effects of the water loss by evaporation and the nonunity of the lewis factor. six case studies demonstrate that there can be large differences between the optimal designs based on. A number of investigations have been considered to reveal differences between the used cooling towers and finally a fluent simulation has been carried out to examine major contours and flow field. A cooling tower is a heat rejection structure that releases waste heat into the atmosphere by lowering the temperature of a water stream. all heat producing industries use cooling towers for cooling the water for re circulation in the powerplant. the rectangular and circular cooling towers are the two widely used types employed in many industries. Several authors developed heat and mass transfer correlations in terms of the water to air mass flow ratio, like bedekar et al. [12] for a counter flow packed bed mechanical cooling tower with a film type packing, milosavljevic and heikkila [13] for two pilot scale cooling towers with seven types of counter flow film type packings, gharagheizi et al. [14] for two film type packings, lemouari.

Comments are closed.