Mechanical Cooling Tower Diagram

Cooling Towers Explained How Does A Cooling Tower Work Cooling tower | piping layout and diagrams. The water is flashed to air as it passes throughout the cooling tower. the air has been pulled using a motor driven electrical "cooling tower fan". when the air and water come into the contact, a little amount of water dissipates, producing a cooling operation. and again the cold water is pumped back to the machine that incorporates heat or the.
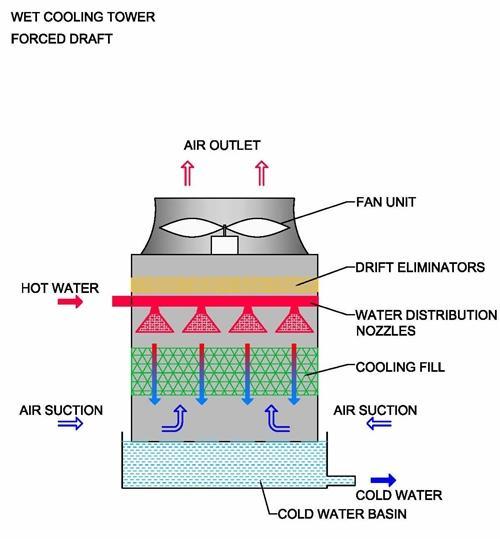
Cooling Tower Diagram A Go To Guide To Learn About Their Function Customization: mechanical draft cooling towers can be customized based on specific project requirements, taking into account factors such as cooling needs, space constraints, and environmental considerations. in summary, mechanical draft cooling towers offer a technologically advanced and adaptable solution for managing heat in industrial. Cooling tower air flowing past fill packaging. combining the spray of water, the thin film of water on the fill packaging and the flow of cool air you get a great amount of heat transfer. flow of air and condenser water. just to recap. warm condenser water enters the tower and is sprayed over the fill packaging. Because of using the fans, the air flow can be maintained according to the requirements. the mechanical draft cooling towers can be classified in two types. forced draft. this type of cooling tower used fans or blowers to blow the air into the cooling tower and the fans are located at the bottom and side of the tower. The cooling tower is a critical component of a power plant’s cooling system. the cooling tower’s basic working principle is atmospheric air to cool the hot water. despite this, it is widely employed in various engineering fields and other refrigeration facilities. the cooling tower in a thermal power plant rises at least 9 feet above the.

Cooling Tower Working Principle And Types Of Cooling Tower Because of using the fans, the air flow can be maintained according to the requirements. the mechanical draft cooling towers can be classified in two types. forced draft. this type of cooling tower used fans or blowers to blow the air into the cooling tower and the fans are located at the bottom and side of the tower. The cooling tower is a critical component of a power plant’s cooling system. the cooling tower’s basic working principle is atmospheric air to cool the hot water. despite this, it is widely employed in various engineering fields and other refrigeration facilities. the cooling tower in a thermal power plant rises at least 9 feet above the. The open circuit type with mechanical draft is the most commonly used cooling tower in hgshp systems. fig. 12.2 shows cross flow and counter flow cooling towers of the open circuit type with mechanical draft. in the cross flow cooling tower, fig. 12.2 (a), air flow is directed perpendicular to the water flow. The cold air drawn in through the bottom hits the exchange surface, cooling down the hot water which then drops into the basin at the bottom of the cooling tower. this water is then funnelled back into the industrial system industrial process from where it came and the whole cycle begins again. it is estimated that around 2% of the water which.

Cooling Towers Explained How Does A Cooling Tower Work The open circuit type with mechanical draft is the most commonly used cooling tower in hgshp systems. fig. 12.2 shows cross flow and counter flow cooling towers of the open circuit type with mechanical draft. in the cross flow cooling tower, fig. 12.2 (a), air flow is directed perpendicular to the water flow. The cold air drawn in through the bottom hits the exchange surface, cooling down the hot water which then drops into the basin at the bottom of the cooling tower. this water is then funnelled back into the industrial system industrial process from where it came and the whole cycle begins again. it is estimated that around 2% of the water which.

Comments are closed.