Macroeconomics Supply Demand

Macroeconomics Explained Macroeconomics Demand And Supply Circular The law of supply and demand is a fundamental concept of economics and a theory popularized by adam smith in 1776. the principles of supply and demand are effective in predicting market behavior. Step 3. it is important to remember that in step 2, the only thing to change was the supply or demand. therefore, coming into step 3, the price is still equal to the initial equilibrium price. since either supply or demand changed, the market is in a state of disequilibrium. thus, there is either a surplus or shortage.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/g367-5c79c858c9e77c0001d19d1d.jpg)
Illustrated Guide To The Supply And Demand Equilibrium The law of supply and demand reflects two central economic principles that describe the relationship between price, supply, and demand. the law of demand posits that demand declines when prices. Supply and demand is a fundamental concept in economics that describes how prices and quantities of goods and services are determined in a market economy. the law of supply and demand states that the price of a good or service will vary based on the availability of the product (supply) and the level of consumer interest in purchasing the. Alvin e. roth. supply and demand, in economics, relationship between the quantity of a commodity that producers wish to sell at various prices and the quantity that consumers wish to buy. it is the main model of price determination used in economic theory. the price of a commodity is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in a market. Introduction to the aggregate supply–aggregate demand model; 24.1 macroeconomic perspectives on demand and supply; 24.2 building a model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply; 24.3 shifts in aggregate supply; 24.4 shifts in aggregate demand; 24.5 how the ad as model incorporates growth, unemployment, and inflation.

Supply And Demand Plot Alvin e. roth. supply and demand, in economics, relationship between the quantity of a commodity that producers wish to sell at various prices and the quantity that consumers wish to buy. it is the main model of price determination used in economic theory. the price of a commodity is determined by the interaction of supply and demand in a market. Introduction to the aggregate supply–aggregate demand model; 24.1 macroeconomic perspectives on demand and supply; 24.2 building a model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply; 24.3 shifts in aggregate supply; 24.4 shifts in aggregate demand; 24.5 how the ad as model incorporates growth, unemployment, and inflation. These constraints on what an economy can supply at the macroeconomic level do not disappear just because of an increase in demand. combining supply and demand in macroeconomics. two insights emerge from this overview of say’s law with its emphasis on macroeconomic supply and keynes’ law with its emphasis on macroeconomic demand. Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.
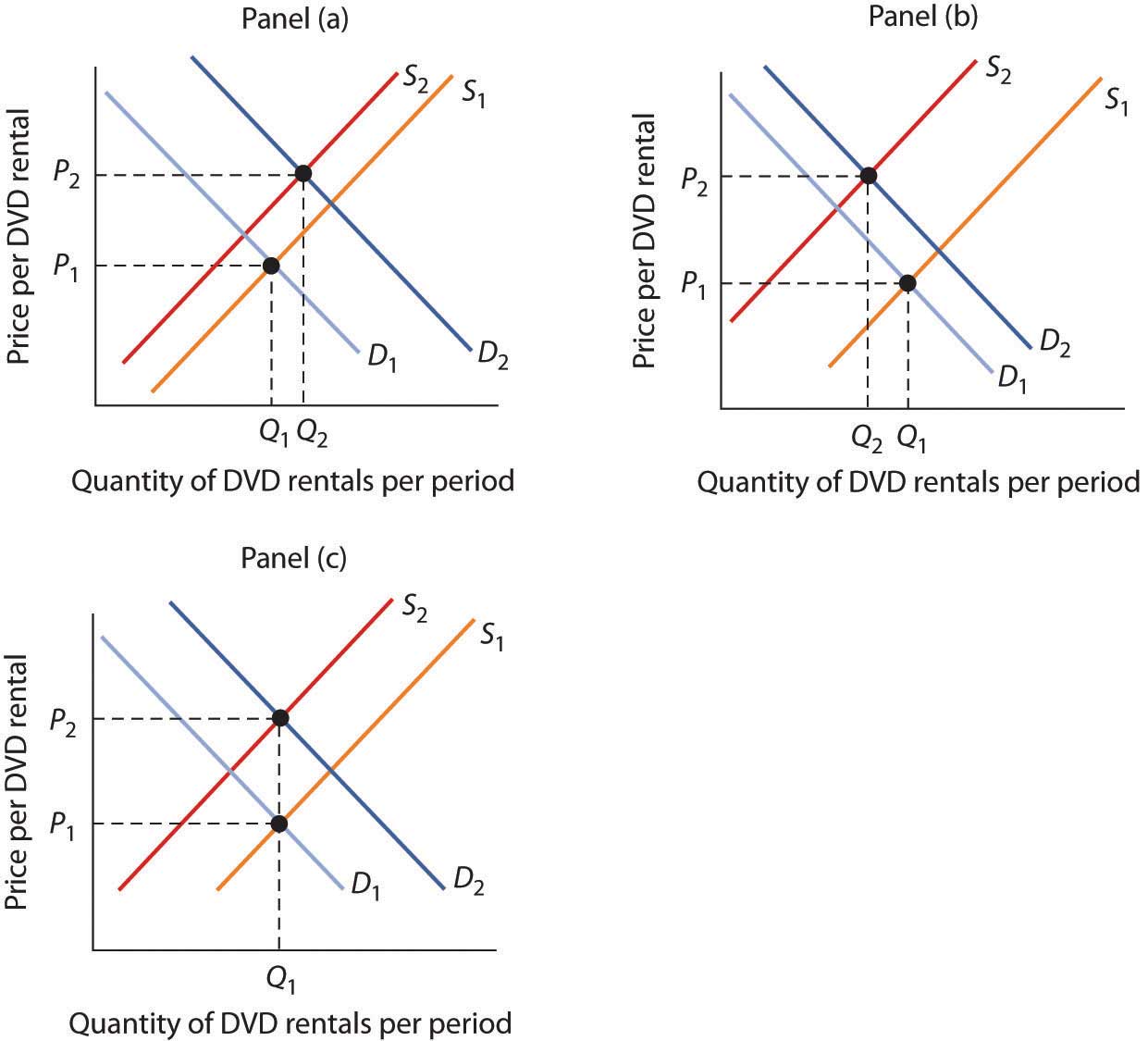
3 3 Demand Supply And Equilibrium вђ Principles Of Macroeconomics These constraints on what an economy can supply at the macroeconomic level do not disappear just because of an increase in demand. combining supply and demand in macroeconomics. two insights emerge from this overview of say’s law with its emphasis on macroeconomic supply and keynes’ law with its emphasis on macroeconomic demand. Figure 3.4 demand and supply for gasoline the demand curve (d) and the supply curve (s) intersect at the equilibrium point e, with a price of $1.40 and a quantity of 600. the equilibrium price is the only price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.

Justin S Ap Macroeconomics Blog Supply And Demand Graph Examples

Comments are closed.