L S Of Testes And C S Of Testes Male Reproductive System By Jjs Sir
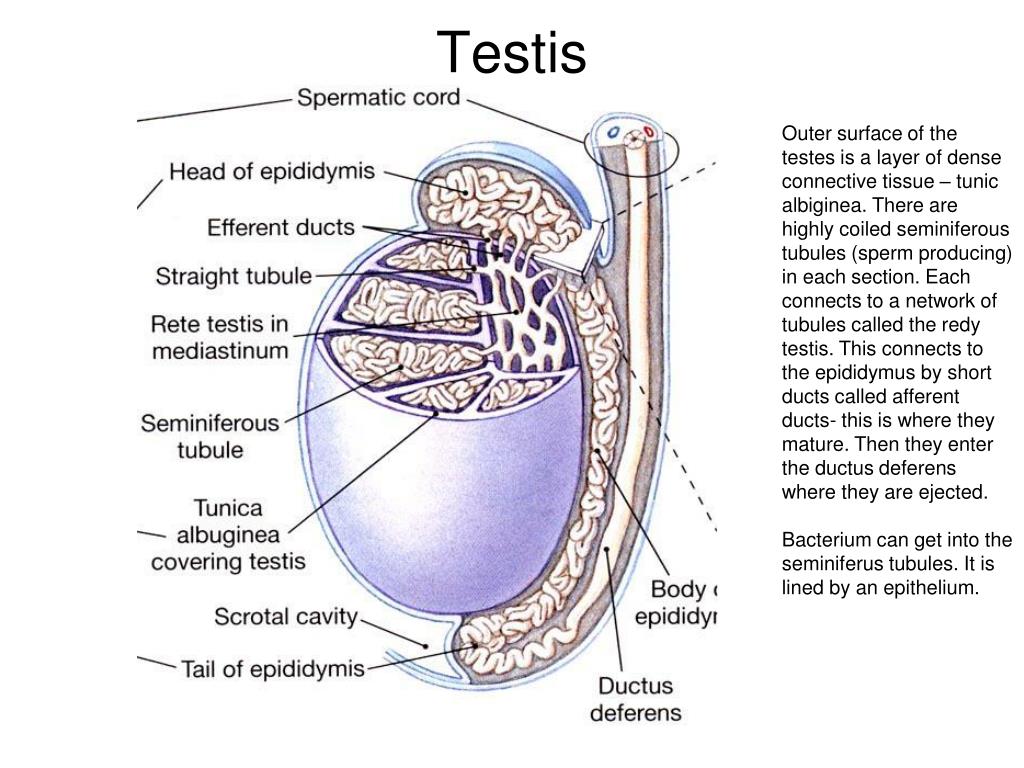
Ppt Histology Of The Reproductive Systems Powerpoint Presentation Date: 31 08 2020session 1the main highlight of this class is that the pace is class pace, so it gives a feeling that you are in your class room if you like m. The male reproductive system consists of the internal and external reproductive organs. the former consist of the testes, epididymis, spermatic cord, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct and accessory glands, while the latter comprise the penis and the scrotum. the functions of this entire system are numerous, including hormone induced sexual.
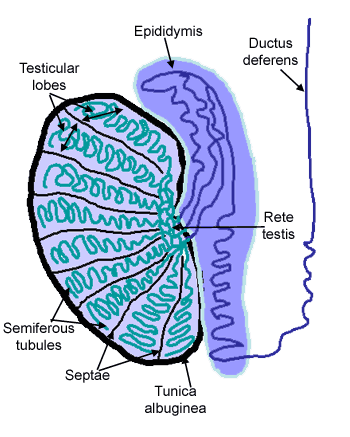
Male Reproductive The Histology Guide Figure 23.2.1: male reproductive system. (a) lateral view of the uncircumcised (foreskin is still present) penis and the scrotum. (b) lateral view of a circumcised (foreskin removed) penis with the glans penis and corona exposed. (c) sagittal view of the male pelvis with reproductive and urinary organs labeled. The male reproductive system summary of key points testes. in each testis approximately each of 250 lobules contains one or more very long, convoluted seminiferous tubules in a sparse, vascular stroma containing testosterone producing interstitial cells (of leydig). The male reproductive system consists of the internal structures: the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate, and the external structures: the scrotum and penis. these structures are well vascularized with many glands and ducts to promote the formation, storage, and ejaculation of sperm for fertilization, and to produce important androgens for male development.[1] the major male androgen. The structures of the male reproductive system include the testes, the epididymides, the penis, and the ducts and glands that produce and carry semen. sperm exit the scrotum through the ductus deferens, which is bundled in the spermatic cord. the seminal vesicles and prostate gland add fluids to the sperm to create semen.

Comments are closed.