Introduction To Point Of Care Urinary Bladder Ultrasound Point Of
Introduction To Point Of Care Urinary Bladder Ultrasound Point Of The bladder has two ureteric orifices that bring the urine produced in the kidneys to the bladder via the ureters. the third opening is the urethral orifice from which the urine exits the bladder via the urethra during micturition. some common indications for urinary bladder point of care ultrasound (pocus) examination are: bladder volume. The most common indication for point of care ultrasound (poc us) of the urinary tract in the emergency department (ed) is flank pain, responsible for approximately 2 million ed visits in the united states annually. about 20% of patients presenting with flank pain have nephrolithiasis.[1] while computed tomography (ct) imaging is the gold standard for diagnosing urinary tract stones, poc us is.

Introduction To Point Of Care Urinary Bladder Ultrasound Point Of Core tip: point of care renal ultrasonography has emerged as a valuable bedside diagnostic tool for non radiology physicians. it reduces fragmentation of care and quickly provides answers to simple clinical questions thereby enhancing patient care and satisfaction. in addition, using bedside ultrasound as the first line investigation may. I. introduction and indications. point of care (poc) renal ultrasound (us) is a rapid, bedside test for the evaluation of the patient with suspected renal colic or urinary retention. because ureteral stones can be difficult to visualize by us, 1 the secondary finding of hydronephrosis is used to diagnose nephrolithiasis when the clinical. Dysfunctional bladder (urinary retention) evaluating for hydronephrosis with renal ultrasound is one of the most common point of care ultrasound (pocus) applications. thankfully pocus is easy to perform interpret while being very sensitive and specific for diagnosing hydronephrosis. The urinary bladder should be adequately distended but not overdistended. if urinary outflow obstruction is suspected, perform a bladder volume assessment pre and immediate post void. ideally, normal post void urine volume is zero. since, urine is being produced constantly by the kidneys in a well hydrated patient with normal kidney function so.
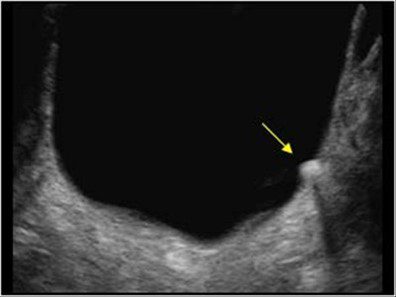
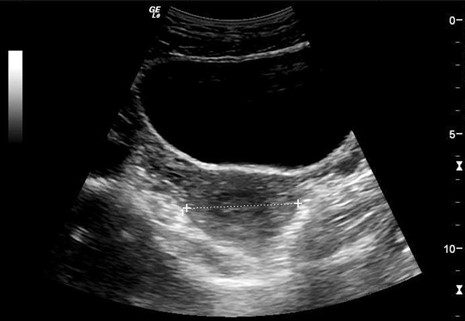
Introduction To Point Of Care Urinary Bladder Ultrasound Point Of Dysfunctional bladder (urinary retention) evaluating for hydronephrosis with renal ultrasound is one of the most common point of care ultrasound (pocus) applications. thankfully pocus is easy to perform interpret while being very sensitive and specific for diagnosing hydronephrosis. The urinary bladder should be adequately distended but not overdistended. if urinary outflow obstruction is suspected, perform a bladder volume assessment pre and immediate post void. ideally, normal post void urine volume is zero. since, urine is being produced constantly by the kidneys in a well hydrated patient with normal kidney function so. Introduction. the potential benefits of point of care ultrasound (pocus) are being increasingly recognised. 1 advances in technology mean reliable ultrasound machines can be taken to the bedside which, in the right hands, has the potential to reduce the time to diagnosis and increase diagnostic accuracy versus clinical assessment alone. 2 despite this, there remains relatively little evidence. Ultrasound evaluation of the urinary system consists of evaluation of the kidneys, bladder, and the ureters near the ureteropelvic (upj) and ureterovesical (uvj) junctions, typically using a 2 – 5 mhz transducer in b mode with the patient in a supine or decubitus position [1, 2]. while a phased array transducer fits well between ribs, the.

Introduction To Point Of Care Urinary Bladder Ultrasound Point Of Introduction. the potential benefits of point of care ultrasound (pocus) are being increasingly recognised. 1 advances in technology mean reliable ultrasound machines can be taken to the bedside which, in the right hands, has the potential to reduce the time to diagnosis and increase diagnostic accuracy versus clinical assessment alone. 2 despite this, there remains relatively little evidence. Ultrasound evaluation of the urinary system consists of evaluation of the kidneys, bladder, and the ureters near the ureteropelvic (upj) and ureterovesical (uvj) junctions, typically using a 2 – 5 mhz transducer in b mode with the patient in a supine or decubitus position [1, 2]. while a phased array transducer fits well between ribs, the.
Introduction To Point Of Care Urinary Bladder Ultrasound Point Of

Comments are closed.