Informal Proof Of The Pythagorean Theorem Examples Solutions Videos
Informal Proof Of The Pythagorean Theorem Examples Solutions Videos Examples, videos, and solutions to help grade 8 students learn the pythagorean theorem and an informal proof of the theorem. new york state common core math module 2, grade 8, lesson 15 worksheets for grade 8 lesson 15 student outcomes • students will know the pythagorean theorem and be shown an informal proof of the theorem. C = 5. answer: the length of the hypotenuse is 5 inches. example 2: find the length of one side of a right triangle if the length of the hypotenuse is 10 inches and the length of the other side is 9 inches. solution: step 1: write down the formula. c2 = a2 b2. step 2: plug in the values. 10 2 = 9 2 b2.
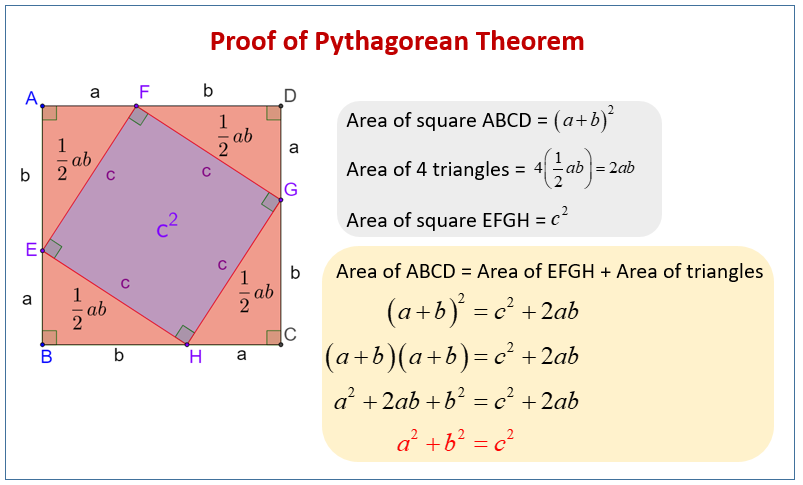
How To Use An Informal Proof Of The Pythagorean Theorem Geometry 1. determine the length of side c in each of the triangles below. 2. determine the length of side b in each of the triangles below. 3. determine the length of qs. (hint: use the pythagorean theorem twice.) the following video shows the pythagorean theorem proof using similar triangles: show step by step solutions. Step 1: from the figure, determine the length of each of the legs of the right triangles. use these values to compute the area of the large square. let a and b be the lengths of the legs of the. Total area of the outside square = within a square proof: area of four triangles. 2 area2 = 2 − 2 of= 2 inside square 2 2thus, we have shown the pythagore. are within a square.example 1 (2 minutes)example 1now that we know what the pythagorean theorem is, let’s practice using it to. find the length of a hypotenuse of a right triangle.determin. What is the pythagorean theorem? you can learn all about the pythagorean theorem, but here is a quick summary: the pythagorean theorem says that, in a right triangle, the square of a (which is a×a, and is written a 2) plus the square of b (b 2) is equal to the square of c (c 2): a 2 b 2 = c 2. proof of the pythagorean theorem using algebra.

Comments are closed.