How The Crankshaft Works All The Details How A Car Works

How The Crankshaft Works All The Details How A Car Works Crankshaft. the combustion of fuel shoots the piston straight down the cylinder, it’s the job of the crankshaft to convert this linear motion into rotation basically by swinging around and pushing the piston back up the cylinder. the terminology of a crankshaft is quite specialist, so we’ll start with naming a few parts. A crankshaft must be able to accommodate the force generated by the engine without being permanently deformed. it must also be flexible. the animation gives.

How The Crankshaft Works All The Details How A Car Works Welcome to crankshaft 101. once you're done watching this video you will know all the basics you need to know about crankshafts and more! we will cover the m. It works according to the upward and downward movement of the piston. without a crank, a reciprocating engine can’t deliver the piston’s reciprocating motion to the drive shaft. in simple words, a reciprocating engine can’t move a vehicle without a crankshaft. it works on the crank mechanism. the crankshaft is located inside the engine block. The crankshaft is a critical component of an internal combustion engine, responsible for converting linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion to power the vehicle. its functions include supporting the connecting rods, balancing the rotating mass, and transmitting power to the transmission or other accessories. The crankshaft can be driven by single or multiple pistons. the number of crankpins in the crankshaft depends on the number of pistons used in the engine. i.e. the crankshaft used for single cylinder motorcycle engines has a single crankpin. while the crankshaft used in a 4 cylinder car engine has 4 crankpins.

Inside Of A Crankshaft The crankshaft is a critical component of an internal combustion engine, responsible for converting linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion to power the vehicle. its functions include supporting the connecting rods, balancing the rotating mass, and transmitting power to the transmission or other accessories. The crankshaft can be driven by single or multiple pistons. the number of crankpins in the crankshaft depends on the number of pistons used in the engine. i.e. the crankshaft used for single cylinder motorcycle engines has a single crankpin. while the crankshaft used in a 4 cylinder car engine has 4 crankpins. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, [1] that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. [2] the crankpins are also called rod bearing journals, and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. they are made from steel or cast iron. To withstand the heavy loads involved, crankshafts have a hardened surface and a tough core. therefore, crankshafts are often made of forged steel. the continuous grain course enables a high torsion resistance to be achieved. the bearing positions on the crankshaft are surface hardened, making them more resistant to wear.

Crankshaft Parts Function Types Diagram More Pdf The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, [1] that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. [2] the crankpins are also called rod bearing journals, and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. they are made from steel or cast iron. To withstand the heavy loads involved, crankshafts have a hardened surface and a tough core. therefore, crankshafts are often made of forged steel. the continuous grain course enables a high torsion resistance to be achieved. the bearing positions on the crankshaft are surface hardened, making them more resistant to wear.
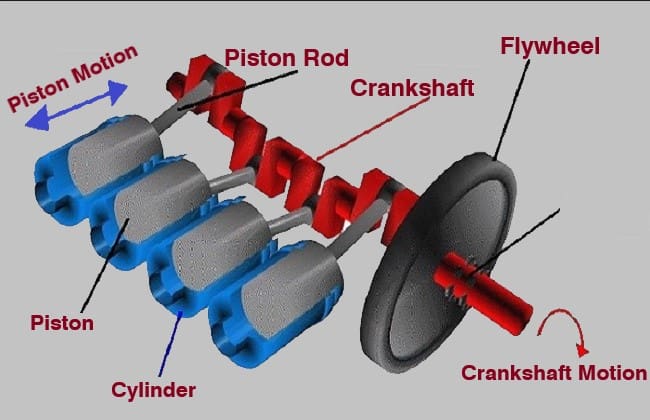
What Is A Crankshaft How Does A Crankshaft Work

Comments are closed.