Histology Of Male Reproductive System
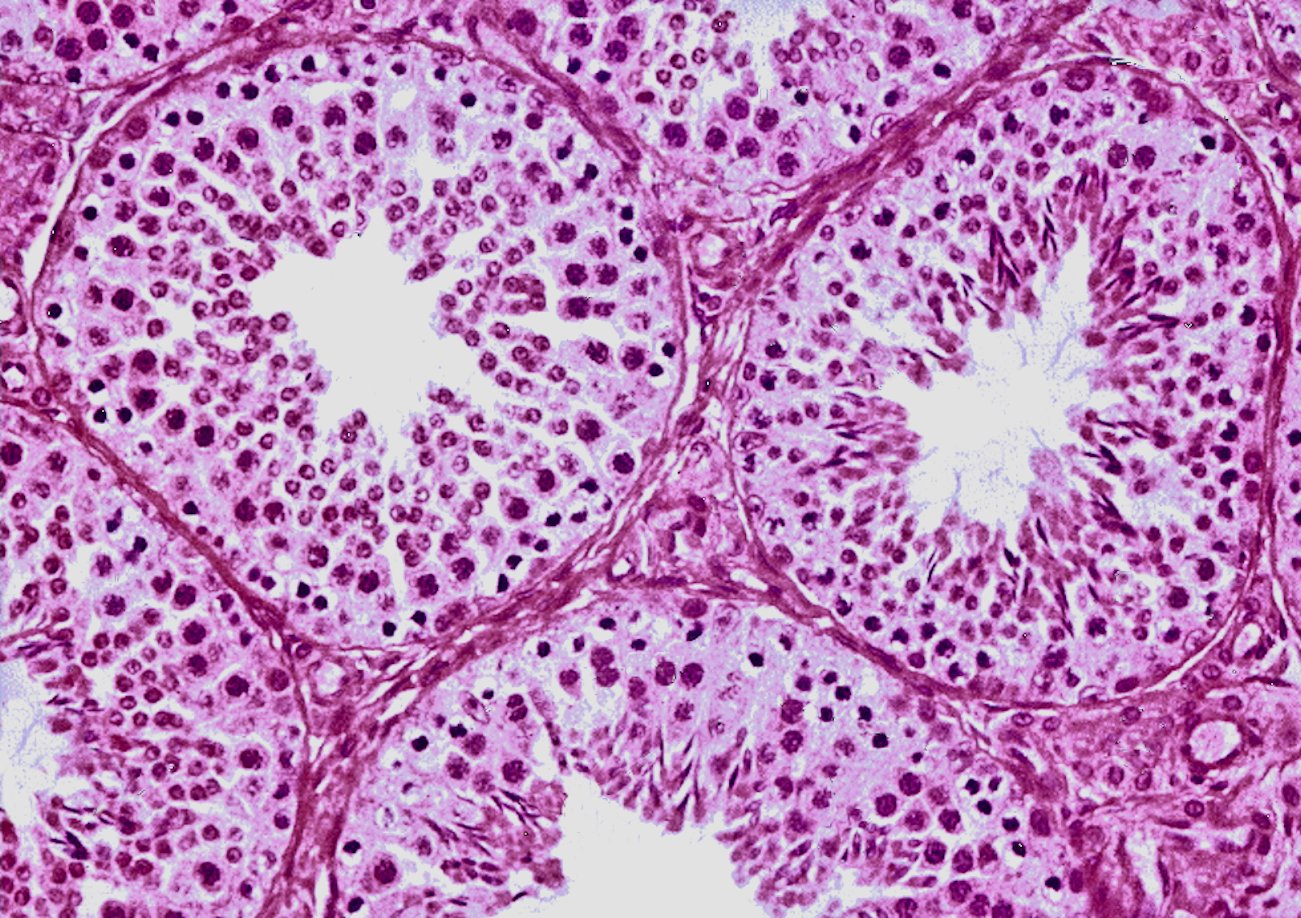
Male Reproductive Dr Kasem Histology Homepage The male reproductive system consists of the internal and external reproductive organs. the former consist of the testes, epididymis, spermatic cord, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct and accessory glands, while the latter comprise the penis and the scrotum. the functions of this entire system are numerous, including hormone induced sexual. Learn about the histology of the male reproductive system, including the testis, epididymis, spermatic cord, seminal vesicle, prostate gland and penis. see slides, electron micrographs and review questions.
Male Reproductive System Histology Male reproductive system. 075 . seminal vesicle, h&e, 20x . virtual slide. imagescope. secondlook histology complete and basic tissues. mobile apps for free. Introduction. the main functions of the male reproductive system, are to produce spermatozoa, androgens (sex hormones principally testosterone) and to facilitate fertilisation, by introducing spermatozoa into the femal genital tract (copulation). the male reproductive system includes the testis, genital ducts, accessory sex glands and penis. Learn about the structure and function of the male reproductive system, including the testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis. see diagrams and images of the histology of spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis and sertoli cells. The epididymis is a single, coiled duct (~250 µm in diameter and ~4 meters in length) in which sperm undergo maturation (motility and capacitance). sperm are stored in the tail of the epididymis. pseudostratified columnar epithelium. has a smooth luminal surface (unlike the "wavy" or "saw toothed" appearance of the efferent ductules.

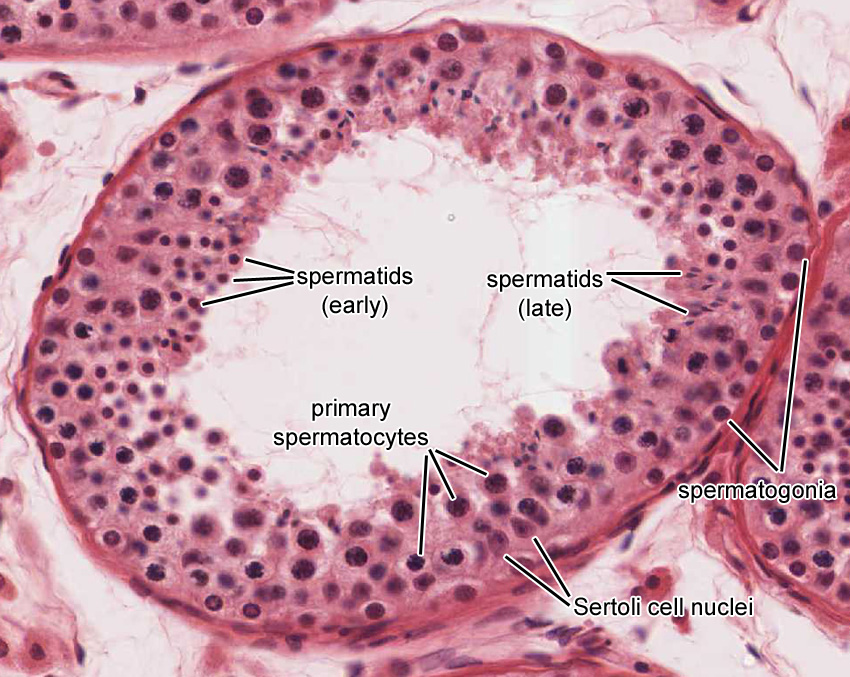
Male Reproductive System Picture With Label Learn about the structure and function of the male reproductive system, including the testes, epididymis, ductus deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate and penis. see diagrams and images of the histology of spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis and sertoli cells. The epididymis is a single, coiled duct (~250 µm in diameter and ~4 meters in length) in which sperm undergo maturation (motility and capacitance). sperm are stored in the tail of the epididymis. pseudostratified columnar epithelium. has a smooth luminal surface (unlike the "wavy" or "saw toothed" appearance of the efferent ductules. The male reproductive system summary of key points testes in each testis approximately each of 250 lobules contains one or more very long, convoluted seminiferous tubules in a sparse, vascular stroma containing testosterone producing interstitial cells (of leydig). After studying all of the resources available, your knowledge of the “male reproductive system” should include the following: recognise and name the structures of the male reproductive system. understand the gross structure of the testis. identify all of the cells of the seminiferous epithelium.

Comments are closed.