Health Consequences Of High Sugar Consumption Nutritional Psychology
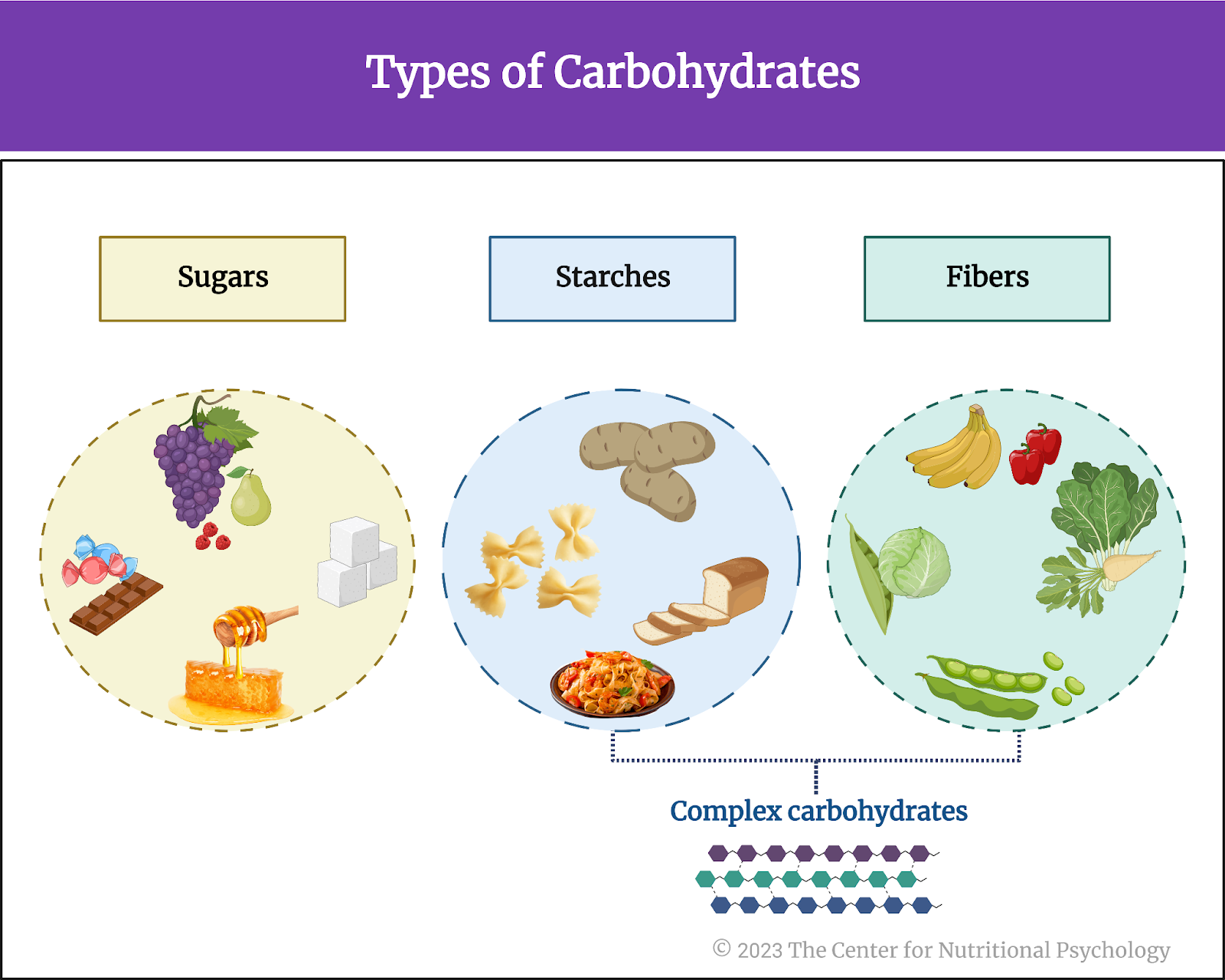
Health Consequences Of High Sugar Consumption Nutritional Psychology Numerous studies have linked a high intake of sugars with an increased risk of various adverse health outcomes. these include obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, dental caries, and abnormal fat accumulation in tissues where fat is not normally stored, such as the liver, muscles, pancreas, heart, and others. Abstract. excessive sugar intake represents an increased risk of developing non communicable diseases (e.g., obesity, cardiometabolic diseases, and dental diseases). still, it is unclear whether people are aware of these adverse health outcomes. the current study systematically examined the extent to which people associate health conditions.
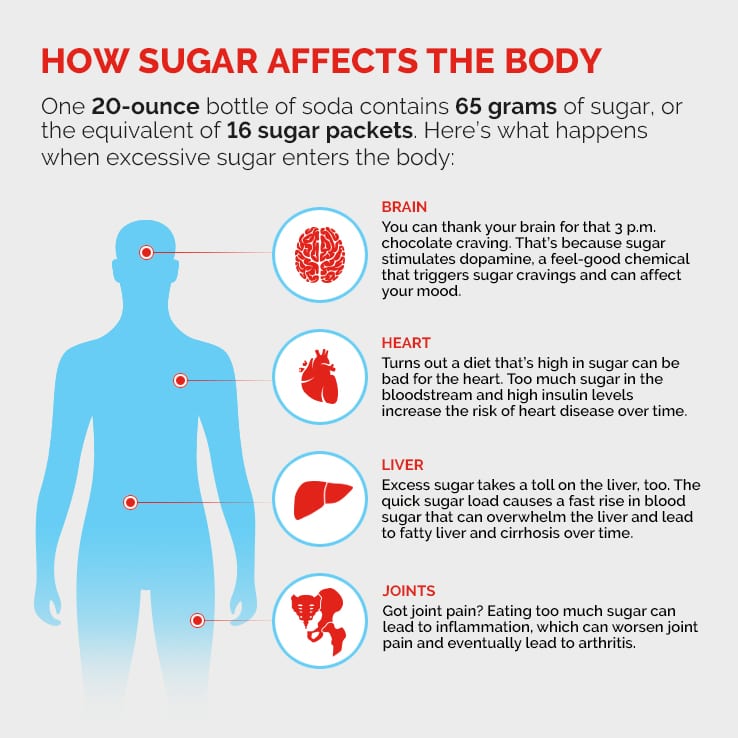
Excess Sugar Consumption Is It Ruining Your Health It is hypothesised that impacts of chronic high sugar consumption on mood are a subsequent effect of the neurological impacts of sugar consumption. western diets have been associated with systemic inflammation, neuroinflammation, and reduced bdnf in the hippocampus, impairing synaptic plasticity, executive function, and mental health [214,218. Introduction. sugar consumption is increasingly discussed as an intervention target to reduce prevalence of obesity, diabetes and other non communicable diseases 1, 2.in britain, adults consume approximately double, and in the u.s. triple, the recommended level of added sugar for additional health benefits (5% of energy intake), with sweet foods and drinks contributing three quarters of the. 2. common neuronal pathways for sucrose consumption, addiction, emotions and obesity. addiction is characterized by a difficulty to control habitual behaviour even in the face of negative consequences (lindgren et al., 2018). early addiction research focused on drugs of abuse such as alcohol, morphine and nicotine. Sugars. sweetening agents. sugar is highly palatable and rewarding, both in its taste and nutritive input. excessive sugar consumption, however, may trigger neuroadaptations in the reward system that decouple eating behavior from caloric needs and leads to compulsive overeating. excessive sugar intake is in turn associated wi ….

Health Consequences Of High Sugar Consumption Nutritional Psychology 2. common neuronal pathways for sucrose consumption, addiction, emotions and obesity. addiction is characterized by a difficulty to control habitual behaviour even in the face of negative consequences (lindgren et al., 2018). early addiction research focused on drugs of abuse such as alcohol, morphine and nicotine. Sugars. sweetening agents. sugar is highly palatable and rewarding, both in its taste and nutritive input. excessive sugar consumption, however, may trigger neuroadaptations in the reward system that decouple eating behavior from caloric needs and leads to compulsive overeating. excessive sugar intake is in turn associated wi …. Schematic depiction of how nutrition influences cognition and emotion. overeating, obesity, acute high fat diet consumption, poor early life diet or early life adversity can produce an. Junk food consumption—which includes highly processed meals, fast food, unhealthy snacks, and beverages with added sugar—has been connected to negative effects on mental health. the purpose of this study by ejtahed et al. (2024) is to use current literature to methodically assess the relationship between adult mental health issues and junk.

Comments are closed.